Introduction to Amazon
Amazon, which is a United States incorporated company, has its main offices in Seattle, Washington, DC. The corporation is the main retailer business that offers its services in an online environment in the US. It started its business as a bookstore before diversifying its products. Today, Amazon also makes various consumer electronics such as Amazon Kindle, eBook reader, Fire Phone, and Fire TV among others. It is also a major player in the cloud-computing industry. The company offers products in the form of services and experiences. After long use of products, their demand may decline due to the emergence of alternative higher quality products or better service experiences. The tastes and preferences of a product’s target market may also change. This situation results in a sharp decline in the product’s returns (Kim & Wilemon, 2007). To ensure that an organization continues to operate competitively in such situations, it is compelled to develop new products, which meet the emerging environmental changes. This strategy is evident in the case of the Amazon Company, which has diversified its product lines. This paper develops and discusses a market innovation strategy and execution plan for the Amazon business. However, it first offers a brief overview of the company and its core mission and value proposition. It also presents the marketing and the organizational design model using the business framework design.
Brief Overview of the Amazon Company
Amazon is a global pioneer in the online retail market. It has grown from an organization that mainly focuses on the sale of books to a business that offers DVDs, electronics, home furnishings, kitchenware and gadgets, and apparel. The company also sells a wide range of other commodities. For example, according to Reference For Business (2015), via third-party settlements, the Amazon Company also deals with merchandise from renowned vendors such as the Toysrus Company, the Borders Group, and the Virgin Wines among others. After making its first net profit in 2001, Amazon demonstrated that it could achieve its mission by establishing proper mechanisms that could trigger more profits.
The Amazon Company’s mission is centered on customers shopping in an online environment. The organization’s core mission entails being the world’s client-focused business whose business environment can attract more and more new buyers in their attempt to observe and realize any commodity or service they are interested in via an online portal (Reference for Business, 2015). This mission has laid out the way forward for the company since its inception. The company’s CEO and its founder, Bezos, consider the mission the guiding force that explains his many leadership decisions that have prevailed for over 18 years of Amazon’s existence. Indeed, the unwavering commitment to this mission reveals the continuous success of the Amazon Company in the online retail market. Amazon’s value proportion is guaranteeing convenience and offering competitive prices to its global customers (Reference for business, 2015).
The company has designed a marketing and organizational model with processes that enable innovation. This framework can be demonstrated using Business Model Design Canvas. Alexander Osterwalder and his business research counterpart Yves Pigneur. Canvas’ framework describes a shared language that is meant for describing a business plan together with its assessment and visualization. This model has nine main building blocks, which help in focusing on various attributes of any business. In the case of the Amazon business, this model may be demonstrated schematically as shown in figure 1.
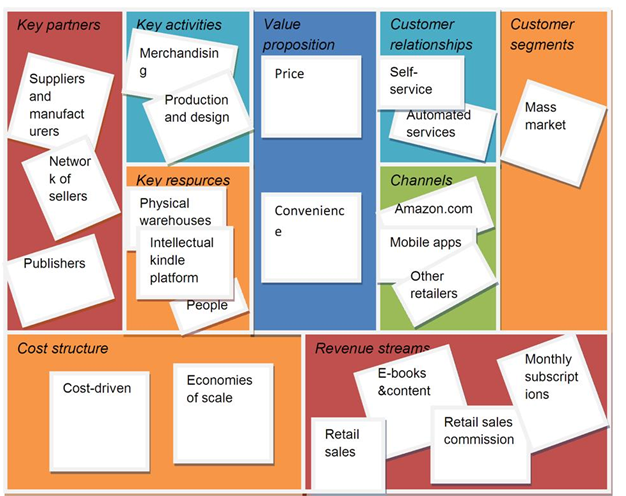
From the above Canvas framework, irrespective of the company’s business line, the organization ensures consistency in all aspects of its way of doing business. Its core value proposition remains to ensure convenience and offers friendly prices to its consumers, regardless of the service or products that customers want to purchase. Upon focusing on prices and convenience, the company possesses the capability of continued expansion into new areas to become a major leading retail online company around the world as stated in its mission. The company uses its high buying power to warrant dominance in the marketplace. The availability of key resources also ensures the development of new products such as Amazon publishing and AutoRip.
The Market Innovation and Execution Plan for AMAZON
Marketing and Organizational Design Models that Drive Innovation
The Diamond Model can help to drive innovation at the Amazon Company. The structure has five main aspects of novelty, namely the plan, procedures, organization, connections, and knowledge. From the context of strategy, Amazon may contemplate three key subjects that include the presence of a premeditated proposal to foster novelty (administrative revolution and knowledge division), placement of the proposal in tandem with the corporate approach, and the existence of reputable strategies for guaranteeing the effective implementation of the business structures (Tidd & Bessant, 2009). The company needs to put in place internal processes for ensuring that revolutionized services and products serve its customers’ needs.
The organization is an important aspect of innovation since it (innovation) flourishes in a setting that upholds a free exchange of thoughts (Von Stamm, 2009). The organization needs to permit employees to communicate their ideas to help them in assessing their innovativeness. To this extent, the company’s organizational structure needs to encourage innovation. Innovation occurs through the facilitation of connections. Innovative concepts originate from both an organization’s inner sponsor, as well as outdoor benefactors (Von Stamm, 2009). Thus, the opportunity for nurturing innovation may be low or high based on the capacity of the Amazon business to establish healthy and long-lasting relationships with suppliers, firms, academic partners, specialists, competitors, and even customers.
Without learning from the environment and the emerging trends, the Amazon business cannot develop evidence-based strategies for transformation in the process of creating innovative merchandise. Education regulates the capability of organizations to instill robust and operational teaching and improvement platforms to guarantee progress in understanding and proficiency of their workforces as an approach for establishing a state-of-the-art atmosphere. By evaluating the Amazon Company’s learning programs, its ability to produce and acquire information through linkages determines the extent of its innovation.
Marketing and Organizational Processes that Enable Innovation
Innovation means the introduction of a new idea or way of doing things using the already existing resources. In the commercial situation, innovation occurs when fresh goods or services are presented and magnificently commercialized (Tidd & Bessant, 2009). In the service segment, experimental investigations reveal that innovation can help organizations to establish superior quality and low-priced services (Dorner, Gassmann & Gebauer, 2011). This implication of innovation is incredibly important for the Amazon business, considering that its value proposition rests on the platforms of offering competitive prices to its customers. Thus, there is a need to instill strong internal processes that foster innovation. This goal requires the development of effective marketing and organizational design models that can drive innovation. For the Amazon Corporation, such models need to be based on the principle of knowledge sharing and continuous organizational transformation where Amazon’s internal processes function as the facilitator for such a model.
Developing internal innovation processes requires the contemplation of the degree of suppleness and strength in the processes that Amazon deploys in establishing fresh supplies and services. This strategy should be based on the perspective of the capacity of the merchandise and services to continue meeting customer needs. The degree of Amazon’s capacity to manage internal processes may reveal and drive its innovation. For example, the development of organizational processes and strategies for evaluating and assessing the learning capabilities of the Amazon’s employees and other stakeholders who form the company’s linkages provides the pillar on which the assessment of the innovation can be conducted. This appraisal should be based on the capacity of the organization to share information on past failures and success stories (Tidd & Bessant, 2009). Therefore, internal processes should foster a free flow of information while at the same time encouraging its sharing.
Success Factors for People and Innovation
Innovation is commonly produced through the mutual action of job groups (Von Stamm, 2009). Thus, measuring the extent of incorporating a multi-skilled labor force in areas of premeditated focus may help in illuminating the degree of organizational dedication to innovation. In the perspective of the Amazon Company, nurturing innovation may reflect the intensity and rate of adopting both open and hidden forms of innovation such as new marketing activities.
In ensuring the success of people and innovation, the Amazon business needs to consider six important factors, which include sovereignty, limitations, confidence, liberty of experimentation, deploying novelty as a plan for executing the top-down vs. bottom-up organizational culture. Autonomy entails giving people control over what they intend to innovate and create. To attain the success of people and innovation, micro-managing innovation is inappropriate (Hansen & Birkinshaw, 2007). Innovation subjects an organization and employees to vulnerabilities. Therefore, a mistrust culture provides hindrances to the success of innovation. Although it is incredibly important to ensure autonomy, constraints are important to drive invention. Kanter (2006) supports this assertion by presenting research that demonstrates how people are more creative if constraints are provided in their workplaces.
Freedom of experimentation refers to permitting people to keep on trying new ideas. Adjustment of the new findings and withdrawing from attempting something else then follow in an iterating manner. This process consumes organizations’ financial resources. Therefore, experimentation requires constraints. The success of people and innovation requires the establishment of an appropriate match between top-down and bottom-up leadership. Indeed, if the top leadership is the only force that can propel innovation, its failure is almost inevitable. Using innovation as a plan to innovation calls upon people to deploy innovative techniques and processes in figuring out possible innovation execution plans.
Recommendations and the Creation of Essential Innovation Success Measures using an Innovation Dashboard
The issue of developing a great business and ensuring its effective operation to guarantee long-term existence in the marketplace requires effective strategies for managing innovation. In business operations, the best strategies are the ones, which can be measured. An innovation dashboard can help to display how well the Amazon Company’s innovation strategies are yielding success for the company. This dashboard can be constructed from various measures that are designed concerning input, processes, and output. Amazon can deploy seven fundamentals in measuring various innovation metrics under three categories.
Under the input category, a company should measure its strategic thinking and portfolio management (Morris, 2008). Under strategic thinking, the company needs to question whether its innovation focuses on the core areas of business success, whether it can change consistently with the markets, its degree of flexibility, and the capability of converting strategies into innovation initiatives. Under portfolio management, the company needs to respond to whether it is developing new brands first enough and/or how its portfolio measures up to competitors’ plans.
The second category of measures should consider investigation, ideation, intuition, directing, innovation, development, and market expansion. The corresponding metrics for these elements should reflect the core value proposition. For example, under market development, the company needs to determine whether it is balancing its efforts of reaching new customers while retaining the existing ones and the degree of its understanding of customers. It also needs to review how it responds to their needs. The company needs to determine how best its sales match its customer needs while at the same time responding to the issue of how innovation translates into gross revenue and sales margin. It also needs to determine the increase in the number of customers, compare the expected results, and the actual results of innovation in terms of sales and cost-saving.
Integration of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and its Sustainability and Evaluation
After facing problems that are related to the manufacture and delivery of merchandise, logistics network managers at the Amazon Company should integrate data about the effects of supply chain and logistics approaches on physical and environmental accomplices in a bid to create a socially corporate organization. This plan is pivotal in helping to resolve various challenges that relate to supply chain management in business environments that are characterized by changing trends because of globalization, intensive competition, and the need for securing the environment where the organizations appear.
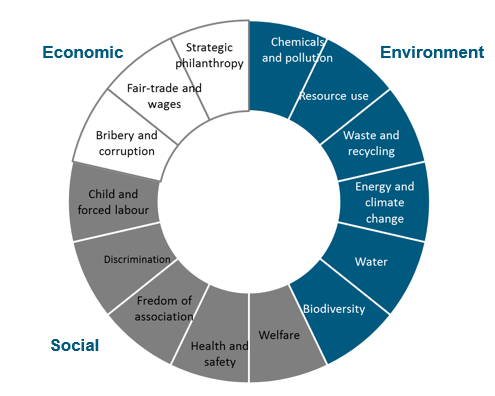
At the Amazon Company, there is a need for dependable, supple, and economical commercial structures that can sustain client differentiation (Bullinger, Kuhner & van Hoof, 2002). In organizations that supply products to the global market such as the Amazon business, logistics system management laborers encounter a myriad of intricate and vigorous supply chain hitches, trends, and expansions, which are incredibly hard to envisage. To resolve this stalemate, the deployment of maintainable supply system tactics is critical through the integration of paradigms of CSR. Amazon can evaluate its CSR and sustainability issues by analyzing its various functions about the elements shown in figure 2.
Market Innovation Execution Strategy and Plan as an Example of how this Plan will be executed in a Particular Market
Amazon’s business model depends on mass consumption. China constitutes one of the important mass markets for any company, akin to its rising economic power, which means an increased purchasing power of its population. Therefore, Amazon’s innovation strategy should focus on developing products and services that target this market. In the execution of the innovation in the Chinese market, the company needs to do modeling, piloting, and an evaluation of the innovation concept using customers or target users via a controlled experiment.
The plan for market innovation strategy in the Chinese market should involve restructuring Amazon’s business structure to promote experiences in the process of developing products and services that meet the local Chinese people’s tastes and preferences. Innovators should begin by completing the testing of various new products and service designs followed by their implementation in the Amazon-China platform. At this platform, the focus shifts to monitoring the new designs, usability, and buyer interest (Baden-Fuller & Morgan, 2010). If the new offering will attract high user attention, the company should release some better versions and permit the experimentation process to progress.
Upon innovation, Amazon should market new offerings, amid the expectations of failure of some of them as other blockbuster innovations. This plan suggests high-risk tolerance, which is a critical component of any innovation process (Baird & Gonzalez-Wertz, 2011). The plan also entails the elimination of different repetitive tasks that relate to new service and product execution to permit employees to take active roles in paying attention to product innovations. This strategy will aid in meeting the Chinese market needs while at the same time addressing its challenges in embracing the company’s products.
Recommendations for the Best Practices from other Companies
Apart from the Diamond Model, Amazon can also borrow the best practices in assessing innovation from Google China. A recommended practice entails assessing innovation through a social corporate model. The business ethics framework considers the capacity of an organization to abide by several novelty rules. Martin (2010) defines these guidelines as involvements that are made by an organization to ensure a positive response to innovation, the influence of modernization on people, and the influence of people on modernization, the interruption of the status quo, the shared concern of innovation, the ability to heighten the modification process, and the elements of the innovated commodities and services. Apart from highlighting the innovativeness of an organization, this framework also provides a strategy for analyzing the efficacy of modernization.
Similar to the Amazon Company, at Google China, innovation attracts change. Thus, the corporate ethics model constitutes one of the important mechanisms for assessing it. The model highlights the necessity for integrating the various environmental dynamics within organizations to yield success in the long term. After experiencing market share challenges, Marissa Mayer joined the Yahoo Company from Google to help in rejuvenating the fortunes of the organization. Amazon can do benchmarking from approaches that Mayer deployed to increase the business’ innovativeness.
Yahoo Company believes that accessing knowledge requires interacting with internal and external stakeholders to identify the possible areas of innovation. This concern highlights the need to establish commodities such that they influence communities in positive ways (Martin, 2010). To this level, Yahoo Company recognizes that innovation is apparent if it develops strategies for minimizing the impacts of the flaws of its commodities to get a negative response from the people who utilize them. Likewise, the Amazon Company needs to focus on reducing any weakness in its products through product modifications to add extra unique value.
Conclusion
Innovation is critical in ensuring the long-term success of any company, including Amazon. Models for assessing innovation seek to establish the necessary areas of improvement or gaps to develop better processes. The adjustments involve restructuring an organization’s development strategic plans, incorporating training and development, and establishing linkages among other concerns. The Amazon Company experiences competition, although it is the world’s leading online retail organization. Although the necessary areas of improving innovation at the company have been identified, the paper confirms that the reason why the company has emerged as a global brand in the online retail market is linked to its commitment to innovation, value proposition, and mission statement.
Reference
Baden-Fuller, C., & Morgan, M. (2010). Business Models as Models. Long Range Planning, 43(2-3), 156-171.
Baird, H., & Gonzalez-Wertz, C. (2011). How top performers achieve customer-focused market leadership. Strategy and Leadership, 39(1), 16-23.
Bullinger, J., Kuhner, M., & van Hoof, A. (2002). Analyzing supply chain performance using a balanced measurement method. International Journal of Production Research, 40(15), 3533-3543.
Dorner, N., Gassmann, O., & Gebauer, H. (2011). Service innovation: why is it so difficult to accomplish? Journal of Business Strategy, 32(3), 37-46.
Hansen, M., & Birkinshaw, J. (2007). The Innovation, Value Chain. Harvard Business Review, 85(6), 87-98.
Kanter, R. (2006). Innovation: The Classic Traps. Harvard Business Review, 84(11), 72-83.
Kim, J., & Wilemon, D. (2007). Sources and Assessment of Complexity in NPD Projects. R&D Management, 33(1), 16-30.
Martin, K. (2010). Innovation, Ethics and Business. Sidney: Institute for Corporate Ethics.
Morris, L. (2008). Innovation metrics: innovation process and how to measure it. Innovation White Paper, no.2. London: Routledge.
Reference for Business. (2015). Amazon.com, Inc. – Company Profile, Information, Business Description, History, Background Information on Amazon.com, Inc. Web.
Tidd, J., & Bessant, J. (2009). Managing Innovation: Integrating Technological, Market and Organizational Change. The International Journal of Educational Management, 21(1), 6-25.
Von Stamm, B. (2009). Leadership for Innovation: what can you do to create a culture conducive to innovation? Strategic Direction 25(6), 13-15.