Introduction
The purpose of this strategy is to discuss financial position of Apple Inc, marketing and human resource management analysis, SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats), PESTEL, Porter’s five forces analysis, and key strategies of the organization in order to recommend future strategies.
a) Main Markets of the Organisation:
A brief description of the major strategic business units or the operating market segments of Apple Corporation are given in the following table –
Table 1: Main Markets of Apple
Source: Self-generated1
b) Profit Generation:
The key amounts of profits for the company come from the sale of some innovative products and services in range of different markets, which, for example, include iPhone, iPad, iPod, Apple TV, software-products, like Mac OS X, iOS, printers, storage-devices, computer-memory, digital-video, still-cameras, etc. 2
Internal analysis
Financial Analysis of Apple
Cash flow, balance sheet and income statement of Apple demonstrate that sales income of this company is increasing gradually, for instance, total sales revenue of Apple were $65,225 million in 20103.
Table 1: Main Markets of Apple. Source: Self-generated from Annex 18
However, the figure 1 shows financial position of the company –
Table 2 analyses key ratio of Apple to assess the performance of the company –
- As shown in the table 1, there has been a sudden decrease in the current ratio of the company. As this kind of fall in the ratio demonstrates the deterioration of the liquidity position of the business, it is notable that the liquidity position of Apple has weakened over these years
- Although the GPM of the company has increased from 2008 to 2010, it fell again in 2011 – it is notable that a decrease in GPM could indicate that variable costs have risen while selling price has remained constant; it could also mean that Apple has cut prices to make an augmentation in sales
- High net profit margin ratio shows how successful the firm is at changing sales into profit, and that the firm is capitalizing on some competitive-advantage, which can give it some additional capability and suppleness throughout the difficult financial periods – from 2008 to 2011, this ratio has increased constantly in the case of Apple, showing a positive trait for its operations;
- A high debt equity ratio commonly denotes that a firm was antagonistic in financing growth with debt; so, this can result in volatile earnings because of additional interest-expense; however; as Apple’s debt equity ratio has lowered than the previous year, its position has strengthened again
- From 2010 to 2011, the liabilities to assets ratio of Apple diminished from 0.364337683 to 0.352219085; this shows that Apple’s liquidity ratio has reduced than the previous year; which needs further amplification.
Conclusion: – The financial ratios of this company are quite stable.
Marketing Analysis of Apple
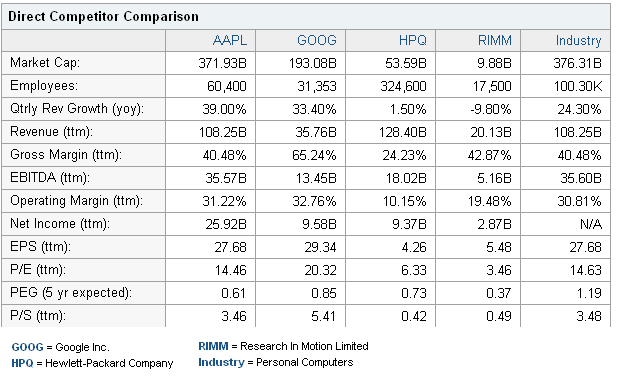
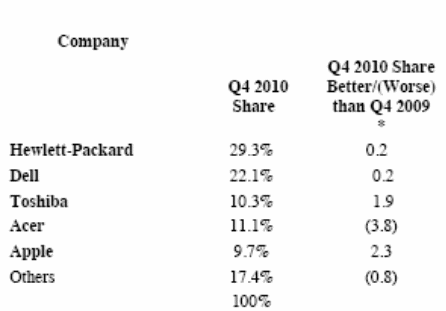
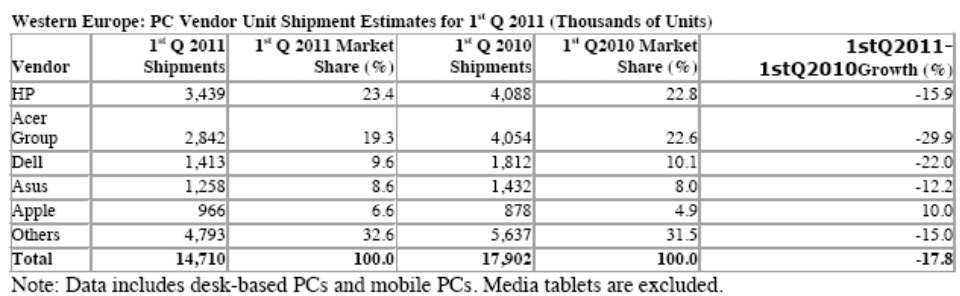
The competition in this industry is too high, but the performance of the company in stock market is outstanding as the figure number three, four and five demonstrate these issues more elaborately, for instance, figure three provides direct competitor comparison, and figure four shows the US market share. On the other hand, figures number six demonstrates the performance of Apple in European zone.
- Product: The prime strategy of Apple is to produce wide range of products targeted at different market segments. Key products of Apple are iPod, iPhone, Apple TV, iTunes, ipad, icloud, MacBook and so on;
- Price: This company’s pricing strategy includes perceived value pricing; moreover, it sets the price high at the initial stage of launching a new product though it changes price considering geographical location;
- Promotion: Apple has successfully applied IMC campaign projects to develop brand image in global market;
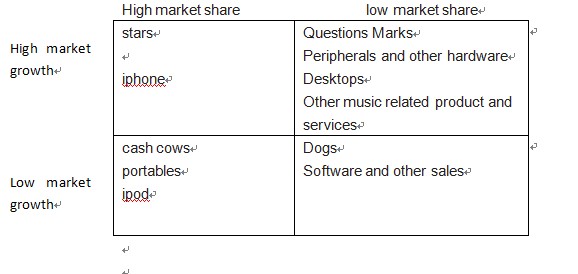
- Place: Apple’s strategy is to make the product available in all the major stores of a country, so that all customers can buy them easily. However, figure 15 shows BCG matrix for the SBUs
HRM analysis of Apple
Apple’s HRM policy is based on the philosophy of equal opportunity; its core competency is that it consists of the finest HR in the industry to assure that the best performers are working with it in terms of production and innovation, which help the company to diminish staff turnover5. They also pointed out the result of survey report, which was carried out among the US technology professionals to know the cause to work for Apple and the HR departments found following reasons –
As the performance of the company mainly depends on the human resources of the company, the aim of the employers to retain potential employers for a long-time to gain competitive advantages; however, the following figure shows employers preference in job sectors –
Operations analysis
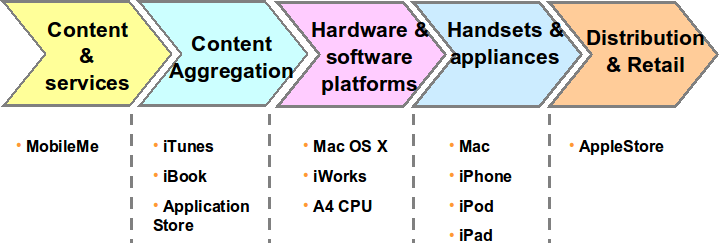
According to WordPress (2010), Apple controls all the major elements of the value chain system; the value chain of Apple is analyzed in figure 16 of the appendix.
- Positive Factors: Stronger issues of operations including high revenue generation from iTunes music store, hardware and software, restoring notebook and desktop, technological sophistication, low debt and so on;
- Negative Issue: On the other hand, weaker factors are less integration with Intel and Microsoft, backward globalization, high operating costs, little returns from products6;
Strengths and weaknesses
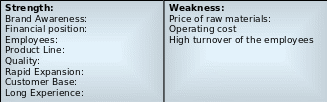
- Historical background, strong brand awareness, loyal customer base and market stability of Apple for exclusive products are the main strengths of this company;
- According to the income statement and balance sheet of Apple, strong financial position due to increase sales and net profits by 83% and 95% was one of the major strengths of the company8;
- In addition, efficient and high qualified employees help the company to achieve long success; however, it had more than 5,500 employees in 1986, and about 14,600 employees in 1990s, but now Apple has more than 46600 full-time permanent staff and an additional 2800 full-time temporary workforce and contractors9;
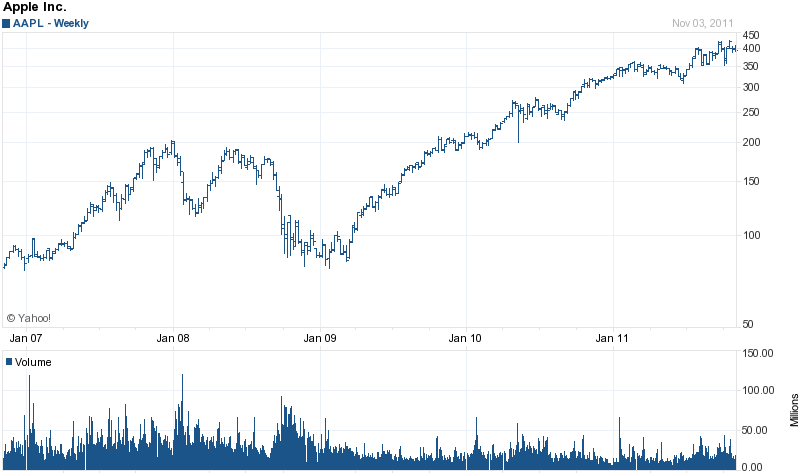
- The performance of the company in stock market is outstanding now as share of the price is increasing day-by-day;
- It had total 357 retail stores including 56 stores in international market;
- Customer relationship management, supply chain management system, high quality products and after sales services, internal administrative control, decision-making power, and technology of the company are the key strengths.
Weakness:
- The contribution of Steve Jobs who solved long-standing troubles of the company and remained at the centre of all decision-making, for instance, in 1997, he planned to spend $110 million to acquire the assets of the leading clone maker. Therefore, this company has to face leadership problems for his unfortunate death to develop new products10;
- Apple has to spend huge money for legal issues due to increase of competition in the market11;
- The financial position of resellers is not good enough because of high production costs;
- High operating costs, high price and volatility of raw materials.
External analysis
PESTLE Analysis of Apple
- Political:
Political factors impose a substantial amount of pressure over the multinationals; in recent years, the unrests in Middle East countries, like Egypt, Libya, Syria, as well as European nations like Greece have put severe impacts on its sales, for instance, Apple may experience lose from the operation in Asian Zone due to unstable political position in Middle East countries.
- Economic:
The external economic factors of the countries in which the companies operate causes sudden boosts or slowdowns in its financial positions, for example, the graph number nine shows how external economy influences the share prices for years on Apple.
- Socio-cultural:
Throughout its operating areas, the companies of electronic products try to ensure higher involvement of the community in order to provide more jobs standing on the principle of equal opportunities disregard of any ethnic background. As a result, Apple follows an ethical code of conduct as part of its corporate governance to ensure job satisfaction.
- Technological:
It is one of the most important factors in this industry because competitors always eager to invent new products with new features. In this industry, Apple is presumed to be a technological icon due to its contribution in the civilization through the launch of some pioneering products. It possesses a highly passionate R&D team that is capable of delivering advanced technologies for years.
- Legal:
In order to operate in such a wide range of markets, the payers of this industry need to comply with the corporate and environmental laws of different countries, for instance, Apple has to consider the rules of national and international market;
- Environmental:
Most of the companies of this industry try to reduce carbon emission; thus, Apple has planned to contribute on environment by reducing CO2.
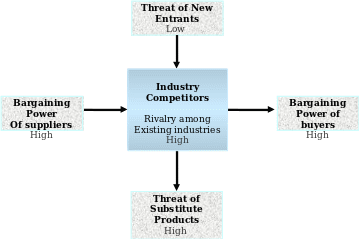
Porter’s 5 forces model
Bargaining power of buyers:
- The presence of many alternate products;
- consequently, the switching costs are lower
Strong force: Due to high bargaining powers
Threats of new entrant:
- High costs and skills required to enter the market
- Weak force: because of high barriers to entry
Bargaining power of suppliers:
- Highly specialised suppliers are not in large numbers;
- Higher price and inferior quality of raw materials;
- Communication policy with the third party and technology suppliers
Suppliers have moderate bargaining power
Threats of substitutes
- Several substitutes are available at competitive prices both in national and international market of the companies;
Strong force: Due to availability of substitutes
Industry rivalry:
- Oligopoly market;
- High legal cost;
- Diversification of the business;
- Coping software or other technology;
- Market expansion
Strong force: Due to coping technology and existing strong competitors
Critical Success Factors:
- The contribution Steve Jobs as co-founder, chairman, and CEO of Apple was one of the most successful factors for the company;
- Technological development in develop new products such as Apple develops the features of iphone;
- Proven ability to develop production processes;
- The distribution network of Apple Inc. is enough strong to generate competitive advantages as Apple has distribution channel in more than 89 countries to sale i-phone;
- According to the Annual report 2010, creating innovative, and high-quality products are the key success factors to develop i-phone segment.
Opportunities and threats:
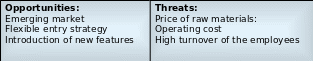
Prioritised opportunities of Apple includes:
- Emerging markets of Apple’s products would enhance the operation system and help the company expending business outside the US with its existing pricing strategy;
- Flexible rules and regulations of foreign countries assist to enter new market with new products;
- However, the management has scope joint venture with similar company to develop the software of other company by using its resources and capabilities of research team, such as, joint venture agreement between Apple and IBM was to form Taligent to introduce revolutionary new operating system;
- It has opportunity to include more features in single devise in order to increase sales and meet customer’s demands.
Prioritised threats of Apple includes:
- The markets for the Apple’s products and services are highly-competitive because of frequent product introductions and rapid technological advances
- Competition in the industry of information technology increased lawsuits and this company previously charged for unlawfully using Xerox technology, and Nokia wins Apple Phone Patent Case 13;
- However, many companies produced similar products without patents and ask relatively lower price, such as, Microsoft copied the graphical user interface;
- Continuous change of technology along with the risk of global financial crisis
Current strategies
The strategic position of the Organization
According to the annual report 2010 of Apple Inc, this Company is committed to ensure the best quality products and services to its customers by innovative hardware, and software as it has unique ability to design and develop its own operating systems for its customers. In order to do so, the management of this company decided to invest more on research and development to introduce new products and it would like to spend additional fund for marketing along with advertising of its key products like iTunes Store includes the App Store and iBookstore, iPhone, iPod, iPad, and so on14.
A) Description of Strategy/Strategies introduced to Date:
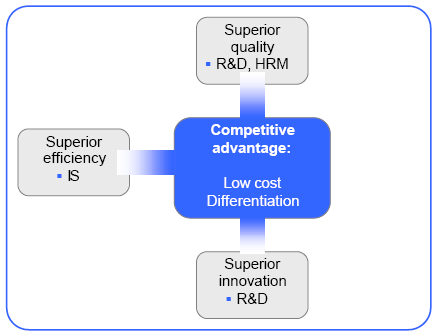
Functional strategies are targeted at recuperating the functions of the firm’s value chain by implementing four key issues such as the best quality, efficiency, innovation, and responsiveness of the customers; therefore, Apple’s ensures paramount quality products and HRM team of this company controls high-skilled employees to create value for the customer15. However, the following figure shows the functional strategy of Apple –
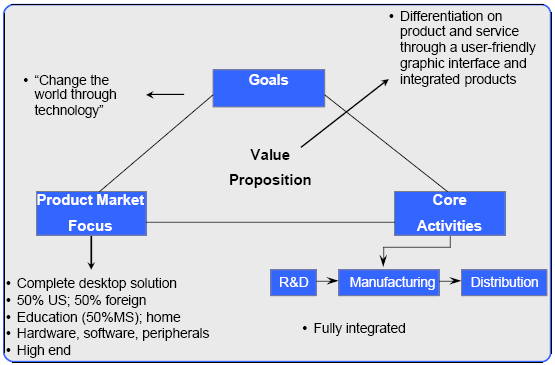
However, the following figure illustrates overall Business-Level strategy of Apple and it explains the success of the strategies to gain competitive advantages and this figure concentrates on three factors such as customer needs, target customers and distinctive competencies.
B) Key Issues Relating to the Future of the Company:
- Success of the business depends on the supply chain management system, but it has to consider pricing risks and various agreements for the supply of component;
- Global financial crisis could materially adversely affect the Company;
- Innovative products or technology of the competitors can create hindrance of this company, such as, Xerox Corporation charged Apple to unlawfully using its technology for the Macintosh software;
- Good relationship with product manufacturing and logistical services provider and outsourcing partners;
- Apple is Vigorously defending infringement actions as plaintiffs seek injunctions and substantial damages;
- The performance of the third-party software developers;
- High price of its products for the customers of developing countries;
- Pressure of local competitors and clone technology are also significant factors for the future development of the company.
Identification of New Future Strategic Directions
Strategic Direction 1: Joint Venture
Apple can achieve competitive advantage by joint venturing with competitors to share their technology and enter new market; however, the following table illustrates more elaborately –
- Builds brand awareness: As a well-known company, Apple would gain key advantages
- Aligns with vision: It match would match with vision and help the company avoid legal costs
- Competition: Reduce completion in the global market
- Creation of unique experience: Meet the demand of target customers
- Target market: Positively, this strategy will increase loyal customer base
- Financial risk: Very low as without joint venture agreement, company needs to spend more for lawsuits
- Short and long-term Growth rate: It has also positive impact on short and long-term growth rate
- Think customer first: This strategy is not consider the customer but for the company
Strategic Direction 2: Pricing Strategy
Apple should require to restructuring pricing strategy in order to attract the customer of large populated area like India and China –
- Builds brand awareness: A reasonable pricing of the products would strengthen the image of the brand in global market
- Aligns with vision: the sales of the company can be boosted by a reasonable pricing strategy
- Competition: Local competitors and copied technology can decreased sales; thus, it should offer low price
- Creation of unique experience: It creates unique experience to the users of developing countries
- Target market: Positively, this strategy will increase loyal customer base
- Financial risk: This strategy meet the criteria of think customer first; thus, Apple should follow this strategy
- Short and long-term Growth rate: This strategy help the company to experience long-term growth;
- Think customer first: This strategy is not consider the customer but for the company
Strategic Direction 3: Leadership Development
- Builds brand awareness: A great leader can change the scenario of the company and can create good image of the brand, for example, Tim Cook should follow the leadership style of Steve Jobs as he was a great leader of Apple
- Aligns with vision: Match with the objective of the company
- Competition: Help Apple to compete with competitors
- Creation of unique experience: Apple has already served the best quality products; therefore, leadership would not create any problem
- Target market: It is also interrelated factor
- Financial risk: Many large companies have collapsed or suffered financial crisis due to mismanagement of the top-level management
- Short and long-term Growth rate: This strategy is an essential factor for the long-term growth of Apple;
- Think customer first: This strategy is many concentrate on the company’s internal factors
Future strategies
Suitability, Acceptability and Feasibility
Recommended strategic directions are suitable for Apple Inc. to increase sales using core competences and these directions also feasible as the top-management can easily implement these strategies and acceptable to all customers irrespective of the customers of national and international market. However, this report suggests Apple that “Strategic Direction 2: Pricing Strategy” would be the “winning strategy” as it would help the company creating lifetime value and increasing sales in the future.
Description of Recommended Strategy
This report recommended that combination of strategic direction number one and two can bring outstanding success in the global market as company faced huge challenge in the local and international market for the competitor’s technology and low price offerings. On the other hand, strategic direction number three has less significance than two other options to increase sales in the global market though a leader can play significant role in decision-making process and reduce internal conflicts.
Key Issues in Implementing the Strategy
- The decision-making process of top-management
- Corporate governance and corporate social responsibility
- External and internal environment, structure of the company and so on.
Reference List
- Anon (2011) Can Anyone Take A Bite Out Of Apple?- The Prospects and History of the Apple Corporation. New York Times, 6(1).
- Apple Inc (2011) Annual report 2010 of Apple Inc. [pdf] Web.
- Boykin, R. Fiorini, A. & Webb, M. (2008) Apple Inc. Case Study# 1: iPhone, [Online] Web.
- David, F. (2008) Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases. 12th ed. London: Prentice Hall.
- Financial Times (2011) Nokia wins Apple Phone Patent Case.
- Helft, M. (2011) Apple Unveils ‘Cloud’ Music and Storage Service. [Online] Web.
- Hill, C. & Jones, G. (2007) Strategic Management: An Integrated Approach. 8th ed. London: South-Western College.
- Ilive, V. Lindinger, A. & Poettler, G. (2004) Apple Computer Inc: Strategic Audit.
- Johnson, G. Seholes, K. & Whittington, R. (2008) Exploring Corporate Strategy: Text & Cases. 8th ed. London: FT Prentrice Hall.
- WordPress (2010) Apple integrated business model.
- Yahoo Finance (2011) Balance Sheet of Apple Inc. [Online] Web.
- Yahoo Finance (2011) Basic Chart of Apple Inc for last five years. [Online] Web.
- Yahoo Finance (2011) Cash Flow Statement of Apple Inc. [Online] Web.
- Yahoo Finance (2011) Direct Competitor Comparison. [Online] Web.
- Yahoo Finance (2011) Income Statement of Apple Inc. [Online]
- Yoffie, D. & Slind, M. (2007) Apple Computer 2006. Harvard Business School, HBS No. 9-706-496
Appendix
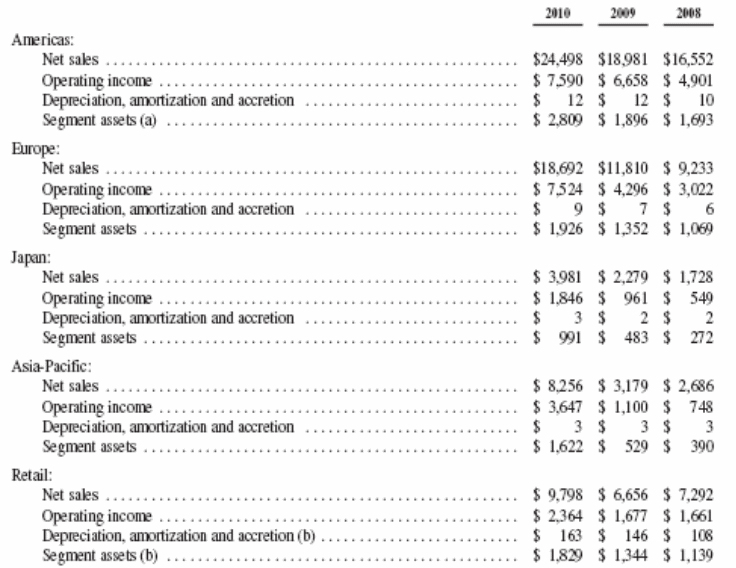
Table 2: Ratio Analysisю Source: Self generated 17
The following figure demonstrates the performance in European market –
Footnotes
- From case study Anon (2011)
- Yahoo Finance (2011)
- Yahoo Finance (2011) and Annual report 2010
- Boykin, Fiorini & Webb, 2008
- Ilive, Lindinger & Poettler (2004, p.89)
- Yahoo Finance (2011)
- David (2008)
- Yahoo Finance (2011)
- Apple Inc. (2011, p.15)
- Yoffie & Slind (2007, p.5)
- Apple Inc. (2011, p.15)
- Anon (2011)
- Financial Times (2011)
- Apple Inc. (2011, p.2)
- Hill & Jones (2007)
- Apple Inc (2011, p.36)
- Yahoo Finance (2011)
- Yahoo Finance (2011)
- Apple Inc (2011, p.27)
- Apple Inc (2011, p.27)
- Yahoo Finance (2011)
- David (2008)
- Ilive, Lindinger & Poettler (2004, p.136)
- Ilive, Lindinger & Poettler (2004, p.137)
- Ilive, Lindinger & Poettler (2004, p.137)
- Ilive, Lindinger & Poettler (2004, p.148)