Introduction
Company profile
Rocky Mountain Chocolate Company is one of the leading international confectionery firms, which operates in the United States, Japan, the United Arab Emirates, and Canada. This large confectionary firm has managed to capture a massive market share in the United Arab Emirates. Crail Frank established this company in 1981 in Colorado Springs. According to Dayal-Gulati (56), the firm was very successful in its first years of operation and would soon open franchise stores in various cities within the United States (McKnew 67). The fact that this firm was selling franchises enabled various other stores to open in countries other than the United States. Because of the good reputation this brand had acquired in the United States and Canada, it was easy to enter the Emirati markets. The brand was already known globally, and its products and packaging had been considered as being customer-sensitive (McKnew 78).
In the United Arab Emirates, Rocky Mountain Chocolate Factory did not meet a serious market threat. Although the market already had some competitors, the firm was able to experience limited competitive threats because of the strength of the brand name. Its packaging strategy became a hit in this country after a very short while (Leggett 67). This company was keen on the target market in this country, which includes the youth and women. To attract this market segment, the firm can up with attractive packaging with colors that would be appealing to the market segment (Dayal-Gulati 59). It worked. This firm is currently one of the leading chocolate manufacturers and retailers in this country. The brand of this firm has become very strong over the years, a fact that has helped it become more competitive. This research seeks to determine the importance of the brand name in making Rocky Mountains Chocolate Factory competitive in the market (McKnew 92).
Statement of the problem
The brand is one of the most important factors that always determine the success of a firm in the market. The brand offers a firm an identity in the market, which enables it to compete with other firms in the market. Some of the important elements of a brand include name, logo, tagline, shape, colors, sounds, and tastes among others. It is important to understand the value of a brand and determine its role in ensuring that a given firm is successful in the market. In this study, the researcher seeks to determine the importance of the brand name in making Rocky Mountains Chocolate Factory competitive in the market.
The objective of the study
In every research paper, it is always important to state the objectives of the study. According to Allison (18), at the end of research, it is always important to determine if the intended objective is achieved or not. The only way of achieving this is to have a set of objectives and counter-check these objectives against the outcome to determine if the intended objective is achieved. In this study, the researcher set some specific objectives that would help in determining the success of the outcome of this research. The following are the objectives.
- To determine the level of competitiveness of Rocky Mountains Chocolate Factory in the local market
- To determine the role of the Rocky Mountains Chocolate Factory brand in enhancing the competitiveness of this firm.
- To determine how well the local market understand the brand name Rocky Mountains Chocolate Factory
- To determine how this firm can use its brand to help it remain sustainable in its operations within this country.
Hypothesis
According to Aston (12), research hypotheses are always important in defining the path of a piece of research. Before a researcher sets forth to conduct research in a given field, it is always necessary to understand the topic under investigation. Out of this preliminary study, a researcher would develop some ideas of what the out of the current study can be. This would always form the basis of the research. The following are some of the hypotheses that the researcher developed based on the objectives set in the section above.
- H1o. Rocky Mountains Chocolate Factory is not competitive in the local market
- H1a. Rocky Mountains Chocolate Factory is very competitive in the local market
- H2o. Rocky Mountains Chocolate Factory brand does not play a key role in enhancing the competitiveness of the firm.
- H2a. Rocky Mountains Chocolate Factory brand plays a key role in enhancing the competitiveness of the firm.
- H3o. Rocky Mountains Chocolate Factory cannot use its brand to help it remain sustainable in its operations within this country
- H3a. Rocky Mountains Chocolate Factory can use its brand to help it remain sustainable in its operations within this country
- H4o. The local market does not understand the brand name Rocky Mountains Chocolate Factory
- H4a. The local market understands the brand name Rocky Mountains Chocolate Factory
The above hypothesis will help guide this research. The researcher seeks to reject all the null hypotheses and accept their alternative hypotheses using primary and secondary sources of data.
Scope and limitation of the study
In every research, it is always prudent to state the scope and limitations of the study. This will be of help to those who may be interested in using the material at a future date. The scope of collecting primary data for this research was limited to major cities in the United Arab Emirates. The researcher selected a sample population of those who will take part in this research from customers and workers of this firm in this country. The secondary data was used to help give further details on the topic in countries where this firm operates. The secondary sources of data came from books, scholarly journals, company websites, and other online sources of information. The research was conducted in the context of the United Arab Emirates. Any application of this paper in an environment, which varies significantly from that of this country, is beyond the scope of this research.
Significance of the study
This study is very important. As Cummins (6) observes, research is a complex and costly project that must have a justifiable basis to support the reason why it is necessary. This would help make the process sensible because of the costs associated with the process. A number of firms in the United Arab Emirates- especially the new start-ups- do not appreciate the importance of brand in the market. They operate without any brand name that can help them secure a solid market share in the local markets. This move has affected the level of competitiveness of these little start-ups.
Dayal-Gulati (56) notes that the only way a firm can compete with others in the market is by developing a name that would help it identify itself in the market. The brand offers a firm this much-needed identity. The brand will be fighting for a favorable position in the market. This research focuses on how Rocky Mountain Chocolate Factory has used its brand name to gain a competitive edge in the market. This research would bring out the importance of developing a strong brand, by making it clear how this firm has used its brand locally and globally (Sager 40). This research will help users understand how the brand name can help a firm distinguish itself from other firms in the market. This will help emphasize the need to develop and protect a brand in the market.
Definition of the terms
Gilboy (74) says that the purpose of research is to develop an understanding of an area of interest so that it can enhance the development of that particular field. In every research, there may be complex terms for nonprofessionals who do not have detailed knowledge about the topic under research. At times using alternative simpler terms may make the explanation lose its real meaning. For this reason, it may force the researcher to use terms that some users may find complex. To help this group, these complex terms are explained in the section below.
- Brand name: specific words used in identifying a product, service, concept or a company
- Brand logo: the image or visual trademark used in identifying the brand
- Brand Colors: specific colors and the way they are arranged to help identify a brand.
- Brand shape: the unique shape that helps in identifying the trademark of a given brand.
Literature review
Issues concerning brand have attracted the attention of several scholars who have written numerous kinds of literature about it. According to Kratschmer (38), the world market is increasingly getting competitive as new firms get into existence. This is forcing various players in different industries to come up with ways of remaining competitive. Liew (26) says that firms that cannot remain competitive in the market are always forced out of the market by other firms, which are more competitive. For instance, Fujifilm managed to outsmart Kodak, which was considered as the giant in the film industry. Coca Cola on the other hand has managed to remain the leading beverage company in the world. Rocky Mountain Chocolate Factory has experienced massive growth both locally and in the international markets. To achieve this level of competitiveness, it is necessary to have identification. It is necessary to have a name that will help the market have a clear way of distinguishing the products of one firm from those of another. It is only through this that a firm can benefit from all the efforts it takes to deliver quality in the market.
According to May, George, and Roper (82), in the current competitive market, a firm cannot afford to operate in the market without a specific brand name that helps in its identification. The current global market demands that a firm operates with a clear identity that would help it compete against other firms successfully. Mercer (37) warns that developing a strong brand is not an easy task. Some of the current firms with strong brand names took years and many resources to gain the current position. Mishra (68) argues that it is easier to destroy a brand name than to develop a strong name. This means that firms should take the process of developing a brand name very important because this is always the image of the firm in the market. Narayan (29) observes that in the American market, Blue Band had become a very strong brand in the market that most shoppers were asking for Blue Band while they meant other brands of margarine. To them, Blue Band and margarine meant one thing. This is a clear demonstration of how a strong brand name can give a firm an advantage in the market. Some scholars have come up with a number of theories related to a brand and its elements.
Theoretical study
Shahi (46) says that it is important to come up with theories that can help in understanding the model in a given field. In marketing, it is always important to come up with models that can be used by various stakeholders in order to enhance various activities. Theories have been developed to help explain the importance of a brand and it can be used to make a firm competitive in the market. One of the main theories that have been widely used in this field is the Theory of Brand Loyalty. This theory is very popular among marketers (Klimchuk 112). It seeks to explain the relationship that exists between customers’ psychology and a company’s brand. This theory holds that the following three factors that will influence a positive relationship between a brand and a customer (McLaughlin & Aaker 78). They include emotional attachment, behavioral aspects, and brand evaluation. For a firm to create a good relationship between its brand and customer behavior in the market, it is important to ensure that these three factors are observed very keenly. For instance, the firm should find a way of evoking the emotions of customers to its products positively. It should find a way of making customers have favorable memory of the brand in the market. Snider (48) says that a firm should find a way of dealing with likes and dislikes. It should try to minimize dislikes while encouraging customers to like the brand.
According to Srinivasan (52), another popular theory is the branding theory. This theory seeks to offer guidance on typical brand management components. This theory helps to explain how to select an appropriate brand name and logo for different products. It also seeks to explain how to develop an awareness of the brand among the selected market. Stuart (78) says that this theory is important in making a firm provide customers with what they need, and how to strike a positive relationship with customers on the first time of encounter. This theory has been used heavily by new start-ups that seek to develop the new brands in a competitive market. Researchers have also developed a number of other theories relevant to this field.
Related study
According to Tedrick (9), the brand is one of the most important factors within a firm. This scholar says that brand is the actual garment and the ornament that a firm wears in the market in order to look attractive to society. An attractive garments will always attract attention a positive way by creating admiration. On the other hand, a bad garment will attract the attention of the public negatively, by attracting rejection. Others would want to strike a middle ground, which attracts neither too much positivity nor negativity in the market. Budelmann (47) says that the approach taken by the firm will vary, but one fact that should always remain clear is that the approach taken would always determine the strength of a brand in the market. According to Kotler (78), marketing has become so important that firms can no longer ignore it. Successful firms are those that are able to come up with appropriate marketing strategies.
Schematic diagram
MacLennan (37) says that in order to be able to understand the brand, one should be able to understand brand elements. The following schematic diagram shows the brand elements.
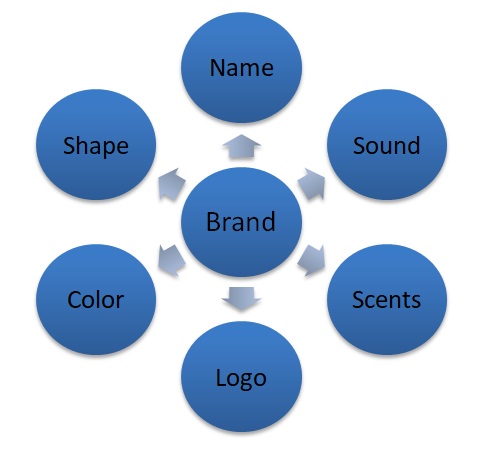
The above schematic diagram shows some of the common elements of the brand that one should understand when developing a new brand. It is important to understand the relevance of each of these elements in the context of the market (Plunkett 58). For instance, a scent that is attractive in the American market may not be very attractive in Emirati society. Most of the people in this country do not eat pork due to religious factors. It is important for a firm to avoid scents that are associated with pork in this market. Understanding these facts would help a firm grow in the market.
Synthesis
It is clear from the above discussion that a brand is a very important element of a firm in the current global market. In order to become competitive, a firm needs a strong brand, which customers can identify with through strong emotional attachments. According to McKnew (62), a brand gives a firm identity in the market, which helps in all the operations in the market. Rocky Mountains Chocolate Factory faces strong competition in the local Emirati market. For this firm to remain competitive, it must use its strong brand name positively.
Works Cited
Allison, Melissa. “Starbucks Struggles with Reducing Environmental Impacts.” The Seattle Times, 5.1 (2013): 1-18. Print.
Aston, Robert. “Corporate Social Responsibility Could Swamp Social Enterprise in 2013”. The Guardian, 5.5 (2013): 1-12. Print.
Budelmann, Kevin. Brand Identity Essentials: 100 Principles for Designing Logos and Building Brands. Beverly: Rockport Publishers, 2010. Print.
Cummins, Anna. “Challenging Starbucks”. Chicago Fair Trade, 1.1 (2013): 1-7. Print.
Dayal-Gulati, Anuradha. Winning Strategies for the Indian Market. Evanston: Northwestern University Press, 2010. Print.
Gilboy, George. Chinese and Indian Strategic Behavior: Growing Power and Alarm. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012. Print.
Klimchuk, Marianne. Packaging Design: Successful Product Branding from Concept to Shelf. Hoboken: Wiley, 2012. Print.
Kotler, Philip. B2b Brand Management. Berlin: Springer, 2006. Print.
Kratschmer, Philipp. Organizational Culture is highly Resistant to Change. New York: GRIN Verlag, 2011. Print.
Leggett, Ann. Insiders’ Guide to Boulder and Rocky Mountain National Park. Guilford, Conn: Insiders’ Guides, 2009. Print.
Liew, John. Employee training a study of education and training department in various corporations. Sydney: General Books, 2009 Print.
MacLennan, Janice. Brand Planning for the Pharmaceutical Industry. Aldershot: Gower, 2004. Print.
May, Steve, George Cheney, and Roper Juliet. The Debate Over Corporate Social Responsibility. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2007. Internet resource. Web.
McKnew, Natalma. Annual Franchise and Distribution Law Developments, 2008. Chicago: ABA Forum on Franchising, 2008. Print.
McLaughlin, Damien, and Aaker, David. Strategic market management: global perspective. Chichester: Wiley, 2010. Print.
Mercer, David. Marketing Strategy: The Challenge of the External Environment. London: Sage, 1998. Print.
Mishra, Sethi. Rethinking India’s Growth Strategy: Services Vs. Manufacturing. New Delhi: Concept Pub. Co, 2008. Print.
Narayan, Prasad. Strategy for Modernisation of the Indian Economy. Bombay: Economic Research and Training Foundation, 1987. Print.
Plunkett, Jack. Plunkett’s Retail Industry Almanac 2009: The Only Comprehensive Guide to the Retail Industry. Houston: Plunkett Research Ltd, 2008. Print.
Sager, David. Annual Franchise and Distribution Law Developments, 2007. Chicago: ABA Forum on Franchising, 2007. Print.
Shahi, Romes. Towards Powering India: Policy Initiatives and Implementation Strategy. New Delhi: Excel Books, 2007. Print.
Snider, Jamie. “Corporate social responsibility in the 21st century: A view from the world’s most successful firms.” Journal of Business Ethics, 48.2 (2003): 175–187. Print.
Srinivasan, Rose. Strategic Management: The Indian Context. New Delhi: PHI Learning, 2009. Print.
Stuart, Rogers. Marketing Strategies, Tactics, and Techniques: A Handbook for Practitioners. Westport: Quorum Books, 2001. Print.
Tedrick, Catherine. “Stakeholder Analysis”. Slide share, 2.1 (2011): 1-9. Print.