Introduction
In the current competitive business environment, firms are keen to find a working solution to various problems they face. Action learning offers one of the best approaches of finding solutions to challenges that a firm may face in its operational processes. According to Fournier and Grey (2000), it is not possible to eliminate challenges that a firm may face. These challenges always set in when they are least expected, and unless they are dealt with appropriately, they may have serious consequences on the organization. The only way of dealing with any form of problem is to be ready to address these challenges when they surface within a firm. Critical action learning offers a systematic approach that can be used by a team of experts to formulate a policy that can help in addressing the problem in the best way possible. In this study, the researcher seeks to find a solution to a problem affecting an organization- as presented in the background to the case below- using critical action learning.
Background to the case
Employee motivation is one of the most critical management tasks that define how employees will address their tasks within an organization. At ABC Company, it is apparent that a problem exists with the approach the management has taken in motivating their employees. The management knows that it is important to motivate its employees. However, it does not know of the best approach to do this. According to Kilduff and Mehra (1997), the approach that is taken to motivate the technical staff is very different from that approach that is needed to motivate scholars. These are two groups of people with different perception when it comes to defining motivation. What a technical staff may find to be very motivational may mean little or nothing at all to the scholars. However, the management has failed to realize this fact.
It is using a common approach to enhance employee motivation for its entire staff. This strategy has worked in one way, but failed in the other. The technical staff seems to be happy with the approach taken by the management to motivate them, and they are loyal to this firm. On the other hand, the scholars are not pleased with the motivational approach that the management is using. This has seen a high employee turnover rate in this firm, specifically the intellectuals. As Jakubik (2010) notes, high employee turnover rate is a serious challenge that a firm should find a way of addressing in order to avoid its negative consequences. It takes time for an employee to learn about the systems within an organization and the culture that is common within such a system. When the rate of employee turnover is high, the firm may be affected negatively because it will be losing its employees at the stage where they have the right knowledge about the firm and are at their highest rates of productivity. This trend is unsustainable, and the management will need to find a lasting solution to this problem as soon as possible.
Steps taken to address the problem
According to Choo and Bontis (2002), the first and most important step in addressing an existing problem is its identification and definition. The case presented above clearly identifies the problem that is affecting ABC Company. It is important to find an effective solution that will be able to address the problem in an effective manner. The management has not taken a step towards finding a solution to this problem yet. That is why this critical action learning is very important. It will help in addressing the problem so that the scholars can be retained at this firm. The following steps are important when addressing a problem such as this one.
The first step has been addressed in the section above, which is problem identification. At this stage, the management will try to define the problem in very clear terms so that the experts who will be dealing with the problem will know how to approach the whole issue in order to come up with a lasting solution. The problem in this case is the high turnover rate of scholars at this organization because of ineffective employee motivation approaches.
The second step will be to identify the cause of the problem. Chia (1995) observes that when addressing a given problem, it is very important to get deep into its root cause. It is by addressing the cause that the problem will cease to exist permanently. The case presented above indicates that there is a problem within the management system at this firm. In the current world where knowledge about employee management is everywhere, one does not expect the management of any reputable company to use the same strategy when addressing the issue of employee motivation. This can clearly be defined using Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. According to this model, people at different ladders in life have different needs. A sweeper- who definitely belongs to the lowest social class within such an organizational setting as the one presented in the case- will have pressing needs that are very different from the scholars who belong to higher social class. When such a sweeper is given $ 1000 as a gift by the end of a financial year for exceptional performance, it will mean a lot to him or her because this is like a three-month salary given to them free. For the scholars, such an amount of money will mean nothing to them. In fact, what some require as a form of motivation may not be in the form of money. Some may require a better working environment where they can conduct their research without any frustrations. Others may require the management to support them in their individual research. The management of this firm comes out as ineffective, a fact that has resulted into the current stalemate.
The third step will be to address the problem. As explained above, the problem lies with the management strategies used in this firm. This will have to be addressed as soon as possible. The management strategies at this firm will need to change. In the new approach, different categories of employees will be handled differently based on their area of work, level of education, talents, special skills, and their relevance to the organization. The new system will drop the current motivational system used in the entire organization. It is demonstrated that the system is working among the technical staff. However, when the technical staffs realize that their motivational approach remains the same while that of the scholars have changed, they will feel devalued. For this reason, a completely new approach will be taken closely following the Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs as the guideline.
The last stage will be to evaluate the performance of the new system. According to Puga and Trefler (2014), when a new system is introduced in an organization to address a specific problem, it is not a guarantee that it may work magic. For this reason, it is always necessary to conduct a regular evaluation in order to determine if the proposed strategies have offered the expected outcome. In this case, the team of experts who will be implementing the proposed solution will have to conduct a regular review in order to determine if the existing problem has been solved.
Action Learning Research
Action research study is a field that has been in existence for some time, and it is always very useful in addressing various forms of problem, especially if they exist in the context of a learning environment. The case presented in this study can be addressed very appropriately through action learning research. It is important to review literatures in order to understand what others scholars are saying about action learning. It will be beneficial in guiding the process of finding a lasting solution to this problem using this strategy.
Action Learning Set Discussion Literature Review
The concept of action learning has been in existence since 1982 when Revans Reg theorized it (Schultz, 2010). This scholar applied this concept in many organizations as a way of finding solution to business development problems. This concept was further enhanced to address leadership problems, and teamwork challenges. Sewell (2005, p. 76) defines action learning as “An approach to solving real problems that involves taking action and reflecting upon the results.” It is important to appreciate the fact that different problems in an organizational setting are unique in different ways. Developing a universal solution to a given set of problems could have worked in the past. However, the current business environment is very different from what it used to be in the past. Competition has gotten so stiff those organisations are keen on identifying any form of competitive advantage that they can use in order to remain sustainable. Sometimes the competitive edge may be brought by the tiniest of the information that an organization has over its market rivals. This makes it undesirable to use a given conventional method of solving problems. Every firm would want to find a solution that is unique to its own system. A strategy may work for company A may not work for company B because numerous internal factors make these two firms unique even if they are operating in the same market. Moreover, an innovative firm would want to develop a unique solution that is not currently used by the market rivals. This makes action learning one of the best approaches that a firm can use when addressing a given problem.
In the current business environment, it is important to have a customized solution to every problem that an organization faces. Action learning makes it possible to use teams within an organization to come up a solution based on a practical context. As Tomi (2009) says, when faced with a problem, the management will find the right individuals who have the capacity of generating the desired solution. These individuals will be organized into groups and the management will task them with the assignment of finding a solution to the problem. The solution generated will be tested to determine if it has the capacity of solving the existing problem. In the case presented above, the scholars who are affected in the strategy used by the management should be involved in finding solution to this problem. They can form teams and each team will be tried to develop an effective solution to the problem. The results obtained from these teams can be integrated to develop an effective approach to addressing the problem.
Knowledge Creation
Knowledge is an important tool in the current world because it defines the ability of a firm to make informed choices. Tomi (2009) says that many organizations have realized the relevance of having the right knowledge at the right time among the right people. For instance, human resource management is one of the most important managerial functions. The human resource manager will need the right information about its workforce, and the emerging trends in the management of the employees. This can only be achieved through knowledge creation. For this reason, firms are very keen on spending in order to create knowledge that will be useful in the normal running of a firm. Knowledge creation refers to developing new information about a given aspect of an organization that can help improve the current system.
According to Tavallaee, Soofi, Sadaghiyani, and Salehifar (2012), knowledge can be created through two main approaches. The first approach of knowledge creation in an organizational context is through experience. When a firm is faced with a given problem and it goes through it successfully, it will amass a wealth of knowledge about the problem and the best way of addressing it in case of future occurrence. Anderson, Heriot, & Hodgkinson (2001) calls this as a reactive approach to knowledge creation. In some cases, the experience may have serious negative impact that an organization may not recover from it. This makes it a very dangerous approach of creating knowledge that a firm should not consider using. Learning through experience has brought many organizations down, especially when they realize that they lack enough resources to sustain them through that expensive learning process. This means that the second approach of creating knowledge- learning through research- is the best way that a firm can use to amass knowledge.
A firm should always be proactive when it comes to creating knowledge. The management unit should be in a position to predict the future, and create a means of managing these futuristic challenges in the most efficient manner possible. Learning through research makes it possible for a firm to avoid problems even before they occur. For instance, there is a heated debate among scholars and various stakeholders about the use of genetically modified foods. Many large corporations are using ingredients obtained from genetically modified organisms because they are cheap and have reliable supply. It is not known how the future of genetically modified organisms will be in the society, but many of these corporations hope that it will be in their favor. However, Sewell (2005) says that relying on hope is a very dangerous approach because sometimes things may not go as hoped for because of the uncontrollable environmental factors. For this reason, a proactive firm will initiate a research to come up with an alternative before this issue turns into a serious problem.
The government may issue strict laws that criminalize the use of such ingredients and if a firm were to wait for such a time, it may be too late to salvage the situation. The same case applies to this organization. The management failed to understand the fact that their approach to motivating employees was wrong. It failed to come up with effective knowledge on how the issue can be address and the result was a mass flow of scholars out of the firm. This was a serious blow to the firm. Tacit and explicit knowledge are the two main forms of knowledge. Both are important in different ways to the success of an organization. Lambe’s Wheel of Knowledge shown in the figure below helps in explaining how the firm can find both tacit and explicit knowledge relevant when addressing various organizational issues.
Patrick Lambe Wheel of Knowledge
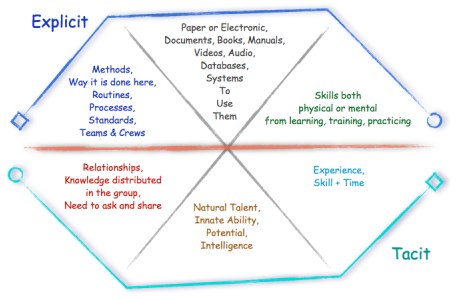
Explicit knowledge involves the methods, rules, routines, processes, and standards put in place in an organization to guide the stakeholders in various operational processes. It defines the organizational culture and practices of a firm. When trying to come up with a solution to an existing problem within a firm, the stakeholders will rely on explicit knowledge in order to come up with an acceptable based on the existing rules and regulations. If the existing explicit knowledge is the problem affecting the organization, then it may be necessary to redefine them so that they can reflect the current environmental factors. On the other hand, tacit knowledge involves experience and skills that one has in handling a given issue. When developing new knowledge on how to address an existing problem, the experience and skills will be of great importance. It is for this reason that the researcher argues that the problem ABC Company is facing is because of limited tacit knowledge at the management level. The management should have known that the strategy it was trying to use could not work for the scholars.
Motivating Scholars in practice environment
The case presented about ABC Company reveals that scholars are not adequately motivated at this firm, and this has forced most of them to leave after a short stay. In order to solve this problem, it is necessary to develop mechanism through which they can be motivated in order to retain them at the firm. Motivation may take the material or non-material forms. Some people feel motivated when they are given attractive package at the workplace. It is essential that the management rewards its employees based on their relevance to the organization. The scholars should be made to feel that their earning is a true reflection of the value of input they have to the organization. Sometimes financial reward at the end of a financial period may help boost their moral and feel appreciated.
According to Sewell (2005), financial rewards may not necessarily be the best motivational approach that a firm can use. It will be important to identify non-material motivational strategies that can boost the morale of the scholars while working for this firm. According to Puga and Trefler (2014), scholars like to be given academic space so that they can develop new knowledge without any forms of restriction. This can be the first step in addressing the issue of motivation. These scholars should have academic space where they can engage in research besides their normal work at this firm. This will make them feel respected. They will feel that they have a position that is recognized by the management. Basing promotion on one’s level of knowledge and output within the organization may also be another important approach. The management may develop a system where promotion is based on an open process of employee’s performance. The performance measure should be accepted to all the stakeholders so that do not feel cheated when one is promoted based on these parameters. Other motivational strategies such as get together parties at the end of the year, team-building retreats, and external academic forums among others may also help in motivating the scholars.
Critical Action Learning Results and Conclusion
As it is, ABC Company is losing valuable scholars that can help it achieve success in the current competitive environment. The scholars are citing lack of motivation as their main reason of moving away from this firm. Based on the critical action learning conducted in this study, it is apparent that this problem can be solved easily when the management changes its human resource management strategies. It should avoid using a universal approach in motivating its employees. The approach used in motivating the teaching staff should not be the same approach used in motivating employees. The discussion reveals that the management will need to design material and non-material strategies of motivating the employees. It is also clear that all stakeholders should be involved when coming up with managerial decisions. When using action learning, the management of this firm will need to involve these scholars in finding solutions that is acceptable to all the stakeholders.
References
Anderson, N., Heriot, P., & Hodgkinson, G. (2001). The practitioner-researcher divide in industrial, intangible assets and knowledge creation. Journal of Knowledge Management, 7(13), 36-52.
Chia, R. (1995). From modern to postmodern organizational analysis. Organization Studies, 16(4), 579-604.
Choo, C., & Bontis, N. (2002). The strategic management of intellectual capital and organizational knowlegde. New York: Oxford University Press.
Fournier, V. & Grey, C. (2000). At the critical moment: conditions and prospects for critical management studies. Human Relations, 53(1), 7-3.
Jakubik, M. (2010). Emerging knowledge creation spaces: Why should HR managers participate in knowledge creation? International Journal of Learning and Intellectual Capital, 6(2), 362-362.
Kilduff, M. & Mehra, A. (1997). Postmodernism and organizational research. Academy of Management Review, 22(2), 453-481.
Puga, D., & Trefler, D. (2014). Knowledge creation and control in organizations. Cifar, 5(7), 1-36.
Schultz, J. (2010). The Scholar-Practitioner A Philosophy of Leadership. Scholar-Practitioner Quarterly, 4(8), 54-90.
Sewell, D. (2005). Tip Focus Group On Energy Innovation System Country Report Upstream Oil and Gas in Norway. Pan-American Advanced, 5(90), 1-36.
Tavallaee, R., Soofi, J., Sadaghiyani, J., & Salehifar, M. (2012). Developing a Model of Knowledge Networks in Organizations Case Study: Petroleum Industry of I.R.Iran. International Journal of Social Science and Humanity, 2(5), 375-379.
Tomi, H. (2009). Reconfiguring knowledge management – combining intellectual capital, intangible assets and knowledge creation. Journal of Knowledge Management, 7(14), 36-52.