Abstract
This study attempts to explain the salient features of internal control and the benefits that could accrue to a company adopting a good internal control system. Internal controls are considered as extremely important to perform everyday operations of a company more efficiently. The major components of the internal controls system of a company include the control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication, and monitoring. These five components combined together enable a company operate smoothly and successfully. Any company having a strong internal control system in place is likely to avoid any financial mismanagement and at the same time will perform with its utmost efficiency. The structure and function of internal controls will also be exemplified in this study by examining the internal control system in operation in a specific company. The company studied is the Clothing Factory that produces apparels such as jeans, shirts, skirts and sweaters. Being a successful company it is considered worth studying the internal controls in this company. The necessary and possible improvements to the internal control system of this company will also be detailed within this study.
Introduction
Effective internal control systems form the foundation for the safe and sound working of any organization. A properly designed and consistently followed internal control system of operational and financial internal control enables the board of directors and the management of an organization to safeguard the resources of the organization. An efficient internal control system in place ensures that the organization produces reliable financial reports and helps the organization to comply with the laws and regulations governing the conduct of business of the organization. Another distinct advantage of a properly placed internal control system is that there is the possibility for the reduction of significant errors and irregularities. It also assists the organization in the timely detection of such errors and irregularities when they occur and to take necessary remedial action in time. It is also important for the board of directors of a company to ensure that a proper and effective internal control system is in operation.
It is not possible for the board to delegate this responsibility to anyone down the line. It is the duty of the board also to verify the integrity of the internal control systems every now and then. Internal control consists of systems, policies, procedures and process effected by the Board of directors and management and other personnel of the company to safeguard the resources of the organization, limit or control the risks expected to be faced by the organization, and finally achieve the objectives of the organization. Effective internal control provides the board of directors and other stakeholders of the company a reasonable assurance that the operations of the organization are efficient and effective, that the record of the transactions maintained by the organization are accurate, that the financial reporting system of the organization is reliable and efficient, that the risk management system in place for the company are effective and the organization complies with the laws and regulations governing the company, internal policies and procedures.
Aims and Objectives
The study on internal control is undertaken with the aim of analyzing the salient features of internal control system and the importance of having an effective internal control system in place for different organizations. In order to achieve this aim the study focuses on accomplishing the following objectives:
- To study the different components and elements of an effective internal control system
- To study the importance of the internal control system to be in place in any organization
- To study the operation of the internal control system in a specific company to report on the effectiveness of the system with respect to that particular organization.
By analyzing the internal control system being practiced in chosen organization ‘Clothing Company’ the paper will provide a detailed report on the role of the internal control system in any organization in enhancing the performance of the company.
Literature Review
This chapter presents a detailed review of the available literature on the topic of internal control. The objective of this chapter is to orient the readers to the subject of internal control by presenting various scholarly articles on internal control. In order to understand the need for an effective internal control, it becomes vitally important a detailed review of the available literature is undertaken.
Introduction
In the present day commercial world every organization is subject to the risk of being defrauded. Big accounting frauds have led to the downfall of large organizations causing enormous financial losses to the investors and other stakeholders of such organizations. Frauds of this kind have also resulted in huge costs of litigation apart from incarceration of key individuals. They have also led to the erosion of huge capital resources and to the lowering of investor confidence in the capital markets. Fraudulent behavior on the part of key executives has adversely affected the reputation, brands and images of many of the large organizations all over the world. In order to combat against the risk of accounting and other frauds several legislative measures like US Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, 1977, US Sarbanes-Oxley Act 2002 and US Federal Sentencing Guidelines 2005 have been enacted. These legislations have enhanced the responsibility of the management for having an effective fraud risk management in their respective organizations. One of the key instruments in the hands of the management and the board of directors of different organizations is the creation and putting in place of an effective internal control system in place in the organizations which will have the effect of putting the performance of the organization under check at every stage.
Sources for Review of the Literature
Contained within the literature review are the 39 sources that were used to develop this dissertation. First, I would like to discuss the literature review, and then I would like to give you the opportunity to review the sources that have been chosen for this dissertation. The literature review includes 3 books, 3 internet sources, and 35 articles found in academic journals. The sources discuss what internal controls are, what they do for the company, and the role that managers play in the development and implementation of the internal controls. One source that particularly aided in the development of this dissertation (The Globalization of Efforts to Improve Internal Controls) discusses the improvements that can be made on existing internal controls. This article aided in developing a plan to improve the Clothing Factory’s internal controls. However, all of the sources included in the literature review are sound and they offered important information in the formation of this dissertation. The sources consulted for the preparation of this dissertation are shown in the Bibliography section.
Risk Assessment and Internal Control
The first step in framing an effective internal control system is to study and make a realistic assessment of the risks associated with the business. Risk assessment is one of the major responsibilities of the management undertaken to reduce any unwanted surprises. Failure to detect and safeguard against these risks may result in the erosion of confidence and the organization may not be able to achieve its financial and other objectives. In evaluating the potential impact of the risks associated with the business it is vitally important that the qualitative and quantitative costs need to be addressed. Quantitative costs cover the cost of property, equipment or inventory, cash losses incurred by the organization, damage and repair cost, cost of legal cases etc. Qualitative costs may include loss of reputation, loss of customers and market share etc.
Internal Control Tools
After making a careful assessment of the risks and their magnitude the next step is to identify the appropriate control mechanisms to be instituted to manage these risks. It is for the managers to focus their attention on high risk and high priority areas. Just as the managers are responsible for identifying the financial and other risks it becomes their responsibility to design, implement and monitor the internal control system necessary for their functional areas. “Internal controls help keep a company on course to achieve goals, carry out management directives, reduce surprises, increase reliability of information, promote effectiveness and efficiency, safeguard assets, and comply with rules and regulations”
Some of the tools that may be of use to the managers in designing and implementing an effective internal control system are:
- Creation of a Control-Conscious Environment
- Separation of Duties
- Authorization/Approval
- Reviews
- Reconciliations
- Asset security
- Information and Communication
- Monitoring
The internal controls may either possess then character of a preventive control or detective control. While the preventive controls act to prevent the happening of undesirable acts, the detective controls attempt to detect the acts after they happen. Although the detective control mechanisms detect the happening of a loss they do not anything to prevent such incidents from happening.
Control Conscious Environment
The control environment is the control consciousness of an organization which encompasses an atmosphere where the organizational members conduct their activities ethically and they also understand their responsibilities towards the organization. It may be noted that an effective control environment is characterized by an environment where competent people who have a thorough knowledge of their responsibilities, limits to their authority and remain committed to the acts they are supposed to in the right way.
Conclusion
This chapter made a brief review of the literature. Detailed bibliographical details of the literature which formed the basis for this dissertation is provided in the Bibliography section.
Research Methodology
The objective of this chapter is to provide the readers a detailed insight into the various research methods and their relative features. The justification for the selection of a relevant research methodology that was used for conducting this research is explained within this chapter.
Introduction
The review of the available literature provided an in-depth insight into the issues that characterize the internal control system in general and also the need for placing an effective internal control system in any organization. The measures that the board of directors and the management of any organization have to initiate for the implementation of an efficient internal control system were also discussed. This chapter aims to detail the research methodologies that were used for collecting the required information and data for conducting this study. This chapter also highlights the relative features of various research methods undertaken.
Research Methods
According to White (2000), “the approach a researcher uses to investigate a subject is termed the methodology. Methodology refers to the philosophical basis on which the research is founded.”
For the purpose of gathering the necessary data and information for this study it is imperative that a suitable research method is selected and adopted. Academics and the literature on the research methods have recognized two important research methods being, Quantitative research, and Qualitative research.
There are several methods available for the purpose of collecting the data for any social research. However it is vitally important that an appropriate method that will fit into the purpose of the study is selected so that the research yields valid results. It is to be noted that the selection of a suitable research method and data collection method largely depends on the topic under study. The pros and cons of all available data collection methods were reviewed for choosing the best fitting method for the current study. Based on the analysis it was proposed to use both quantitative and qualitative methods of social research as they were found to be having the necessary features essential to complete the study. Both the quantitative and qualitative methods are found to be the most popular and widely used methods of data collection and social research. The later part of this chapter presents a detailed discussion on the salient features of these research methods.
Quantitative Research
White (2000) defines quantitative research as “In this type of research the results are given numerical values and the researchers use a mathematical and statistical treatment to evaluate the result of the research findings”. The quantitative research approach involves and employs an objective way of studying various issues. Since this approach is based on the idea that observation and measurement is the core of the scientific endeavour, this approach is also known as positivistic approach. In most occasions the quantitative research collects and makes use of numerical data as the basis for the research analysis.
Qualitative Research
The qualitative research follows the view that it is not possible for the researcher to stand back and await the collection of data and information and then forms the opinion thereon. According to Myers (1997), “qualitative research methods are designed to help researchers understanding people and the social and cultural contexts within which they live. The goal of understanding a phenomenon from the point of view of the participants and its particular social and institutional context is largely lost when textual data are quantified”. In general numerical data are not being used in the qualitative research methods for the interpretation and analysis of the information and data collected. However in some of the researches the quantitative information also forms the basis for formulating some of the theories for developing the hypotheses.
Having considered the relative merits and demerits of the qualitative and quantitative research methods, this research has adopted both the qualitative and quantitative research methods for the completion of this study. Since the topic under study is more subjective where the opinions and information collected from the samples provide the basic criteria for the discussion and conclusion, the choice of qualitative research method was considered more appropriate. In addition the research also collected data on the basis of questionnaire distributed among the employees for arriving at their opinions. These data are tabulated and analyzed statistically to answer the research questions. For achieving this, the research has adopted the quantitative research method also.
The process of qualitative method comprises of analyzing the perspectives of the participants in detail. This method also takes into account the behaviours and life experiences of the participants narrated by them in a natural setting. Thus this method considers the total perspectives of the individuals taking part in the process of research.
The quantitative method takes employs mathematical models and other tools involving measurements of variables embedded in the research. But in contrast to quantitative method, the qualitative method does not employ any of these models. The qualitative method depends mostly on the information and data collected based on human experiences and a logical deduction of views and opinions on the basis of the information either assimilated by the informants or the researcher on the basis of the collected information and data. Qualitative method of research is often considered as expensive. It usually deals with a very small number of samples and in this method measurements of variables is impossible. The qualitative method mostly uses non-quantitative methods of collection of data and depends more on the human interaction. (Lofland & Lofland 1984) One important feature of qualitative method is that its main focus is on the qualitative aspects of research instead of on mathematical analysis or measurements. Therefore qualitative method is to be considered as one based on a subjective methodology. Thus this method engages the skill and expertise of the researcher as necessary instruments for conducting the research. (Adler and Adler; 1987)
Results of qualitative research methods are considered thoughts of themes. They cannot be represented as percentages or subjected to statistical analysis. Since the samples are relatively small and do not make up a randomly selected representative samples they cannot be related to a broader population. Moreover since the participants are asked different questions the researcher gets different viewpoints of the participants.
Features of Qualitative Research Method
The important features of qualitative research method have been discussed from different angles and thus a body of characteristic features has been evolved for this method of social research. This method of research can at best be described as one having a naturalistic approach. (Bogdan and Biklen, 1982; Lincoln and Guba, 1985; Patton, 1990; Eisner, 1991) These research scholars and academicians have drafted certain distinct features of qualitative research which have been adopted by recent studies.
According to Patton (1990) it is necessary to find a natural setting for conducting the process of qualitative research. It is also important that the researcher maintains emphatic neutrality continuously through the process of the research while using the qualitative method. Then only it is possible for the researcher to gain the maximum advantage of using the method and collecting the required information and data. Here the researcher is regarded as a human instrument as far as the collection of information and data is concerned. Inductive method of analyzing the data usually is associated with the qualitative research method.
Eisner (1991) is of the opinion that use of descriptive reports forms the basis of qualitative research. This aids the researcher by enabling him to have the advantage of using an expressive language and the presence of an eloquent voice in the text of the study. Hoepfl (1997) states the qualitative research is based purely on the element of trustworthiness and this enhances the value of the results of any research. The qualitative research insists on the researcher to possess a character of interpretative nature. This provides the researcher the capability of exploring the meaning of the narratives of the participants to the extent that the participants narrate the events and the contexts under which the events happened. Lincoln and Guba (1985) identify the interconnectivity of the different characteristics of the qualitative method of conducting a research. They also apprise the method to possess an emergent nature which helps the researcher to a large extent. Patton (1990) has observed that the researcher can evolve his strategies only on the data collection process is started since it is for the researcher to pursue a systematic way of observance. It is also necessary that the researcher interprets the meaning of the information collected from the participants only with reference to the contexts and circumstances under which the information were passed on to the researcher. The process of conducting qualitative research requires the researcher to specify the primary questions involved in the research in advance so that they can be explored in their proper perspectives. This also facilitates the planning by the researcher of the research strategies at a later stage for the successful completion of the research.
Rationale behind the Selection of Research Methods
By comparing the qualitative and quantitative approaches and taking into account the nature of this study, both the qualitative and quantitative research methods are chosen for gathering and analyzing data. This research being an exploratory and subjective one, the concepts, processes, or variables that have been identified and used in the previous studies have been adopted for conducting the study. The research objectives have been derived from a review of the available literature. In this study the views of the senior managers of the chosen organization about the practice and effectiveness of internal control systems through the survey method have been considered to accomplish the research objectives. For this purpose the qualitative method has been chosen. As the subject under study also could accommodate numeric data or information for analysis on the basis of questionnaire circulated, the quantitative method of research was also chosen. This is further supported by the fact that although the research questions are more subjective in nature finding out answers for the questions required the adoption of questionnaire method of quantitative research method. According to Marshall (1987), qualitative research approach is used in research studies which aim to analyze the reasons for the differences in the policies evolved and the common perspectives of such policies. Thus the method aims to indulge in assessing the strengths and weaknesses of informal and unstructured links and processes that are being followed in different social settings. The qualitative approach is also employed in conducting those researches which cannot be undertaken on an experimental basis due to several constraints imposed by the political and ethical considerations.
This is so because the study begins with a flexible plan for the purpose of exploring a phenomenon rather than with hypotheses which are to be either proved or disproved. Further since the qualitative research attempts to understand the world through the eyes of participants it necessarily has to be functional in informal and unstructured linkages. Since the qualitative research must occur in a natural setting it cannot be done experimentally.
Survey Method
Survey method is mostly widely used by the researchers for the collection of primary data from various sources of data that are well informed and properly organized. Denscombe (1998) makes an assessment of the purpose of the survey. According to the author the purpose is to assimilate a detailed and coherent view points on the information and data gathered which at a later stage could be used for completing the research process. Denscombe (1998) has identified three important characteristic features of the survey method. These characters are; (i) the coverage of the research is very wide and inclusive of all salient aspects, (ii) the method takes into account the particular point of time when the research is being conducted and (iii) the empirical nature of the research adds value to the research findings.
The survey method has been considered to be the most popular and useful one. The superiority of the method is brought out by the quantitative and numeric values derived from a fraction of the sample population. The samples are given the opportunity to provide answers to questions set in advance by the researcher. (Creswell, 1994; Neuman, 2002; Fink, 1995) The survey method provides the chances for making generalization of the opinions and views expressed by the samples who took part in the survey. The survey method also has a distinct advantage of providing the chances of a large number of participants to take part in the survey. However the method suffers from the bias of having a low response rate which may vitiate the results of the survey results. This happens due to the fact that most of the respondents do not wish to take part in surveys. (Aaker, Kumar & Day, 1998)
With a view to arrive at a comprehensive result for assessing the effectiveness of internal control systems the survey method has been chosen. The survey method has been chosen for the purpose of making a complete description of the study and also to compare and explain the attitude and behaviour of the samples. This will enable the researcher to arrive at some definitive conclusion of the research study undertaken.
Methodology used for Research in Clothing Factory
In the current study, due to the nature of the topic there was the necessity to collect some quantitative data for analysis, review, and comparison. The qualitative information on the effectiveness of internal control systems in ‘Clothing Factory’ was gathered using questionnaire survey method collecting information and data from the staff and officers of the Company. Since the study was focusing on the internal control systems of the particular Company there was no need to collect any other information from alternative sources for peer-review or comparison. Thus the analysis of the information gathered is limited to the extent of a comprehensive presentation of the inferences, opinions, and viewpoints of the respondents which are relevant to the study. As far as the context of the presentation of data is concerned, the issue of internal control systems was one of key issues for any organization. Due to this fact the information provided by the respondents from Clothing Factory can be considered as having been provided out of established practices and system of internal control. The questions were focused on some of the main issues concerning the internal control systems, for collecting the required information for completing the study on the effectiveness of the internal control systems in Clothing Factory.
Apart from the senior managers, questionnaires were distributed to 50 chosen employees of the Company to find out the effectiveness of internal control systems in ‘Clothing Factory’. The survey conducted among the chosen employees presents the viewpoints of the employees on the effectiveness of the internal control system. The survey results go to present the views of the employees on the level of control on the variance functional areas of the organization. Since the information and data is collected directly from the employees the study to this extent has found the precise impact of the internal control systems.
Sample
In order to pursue this research study it was necessary to select a target population. For the current research the population covers employees of Clothing Factory, especially who have been working with the company over varying periods. The sample population required for the survey has been selected randomly on the basis of the years of service the employees have put in the company. On collection of all the required information on the samples the information on the potential target population was then stratified by the various demographic parameters to arrive at an appropriate random sample population. The target population was then randomly chosen to reduce the sample size down to 50 different individuals. This approach was necessary for brevity as well as to have an effective follow up with the samples for collection of information on the effectiveness of internal control systems in ‘Clothing Factory’
Questionnaire Development
It was decided to collect the primary data through a self-administered questionnaire distributed to the selected sample population in this research through an ‘Online Survey’. A questionnaire is a document containing questions and other types of items designed to solicit information appropriate for analysis. This involved drawing on existing research in the area of the effectiveness of the change management practices, to identify aspects relevant to the current research. Questionnaires are the instrument of choice for many researchers working in various fields, theoretical traditions and research designs (Creswell 1994), no doubt because they are seen as the most appropriate tool to obtain systematic and comparable data from a large number of individuals and analyze it economically. The following section will describe and explain the format, structure, and content of the questionnaire developed for the purpose of collecting information from the employees of ‘Clothing Factory’.
Construction of the Questionnaire
Based on the observations gathered from the literature available in respect of various change management practices the questionnaire was constructed to collect the information and data from the employees of ‘Clothing Factory’. The purpose of the questionnaire was to find out the effectiveness of effectiveness of internal control systems in ‘Clothing Factory’. It was also necessary to find out the impressions of the employees and the factors that influence the implementation of internal control systems.
The questions have been constructed as closed end questions giving different options to the respondents to express their opinion about particular issues numerically indicating the degree of effectiveness and intensity of the management practices.
The first section of the questionnaire is devoted to the demographic information about the participating individuals. The information about the age, gender, years of service, and current income are some of the questions included in this section. This basic information was collected to tabulate and present the information pertaining to the demography of the participants. This gives the reader an idea about the homogeneity of the samples to represent the bulk of the informants.
The second part of the questionnaire is devoted to find out the viewpoints of the employees and also their responses as to what according to them will be the impact of internal controls on the functioning of the organization. Questions have been framed in this section to find out the opinions of the employees on the effectiveness of internal control systems.
The rest of the research done for this dissertation came from the books, professional and academic journals.
Findings and Analysis
Introduction
The objective of this chapter is to present a detailed report of the findings of the research gathered on the basis of the responses received from the survey (n=49) Out of the 50 questionnaire circulated among the employees of Clothing Factory, 49 of the samples responded to the questionnaire. The questionnaire sent to the employees is appended to this report as Appendix I. The responses received were tabulated and analyzed to present the findings in a comprehensive form to the readers. The findings are followed by a detailed analysis and a review of the various views expressed by the respondents.
Findings
This study made an assessment of the effectiveness of the internal control system in Clothing Factory. As observed form the review of the literature it is quite likely that the provision of proper and efficient internal control system is an essential prerequisite for the detection and prevention of frauds and for ensuring an efficient functioning of the organization. The analyses indicate that there is a positive correlation between effective internal control system and the overall efficiency of the organization.
Questionnaires were distributed to 50 employees of Clothing Factory being the Company chosen for research during regularly arranged meetings and through the internal mailing system to enable them to feed the responses via mail. The participation of the employees was made voluntary and anonymous. The selected samples were briefed with an overview of the purpose and layout of the survey to enhance their understanding of the survey. Employees who were willing to participate were assured that the information they provide will be kept confidential and the study intends to present only a summary results of the findings. The questionnaires were completed by 49 individual yielding a participation rate of almost 100 percent. The findings are discussed in the following sections.
Demographic Information
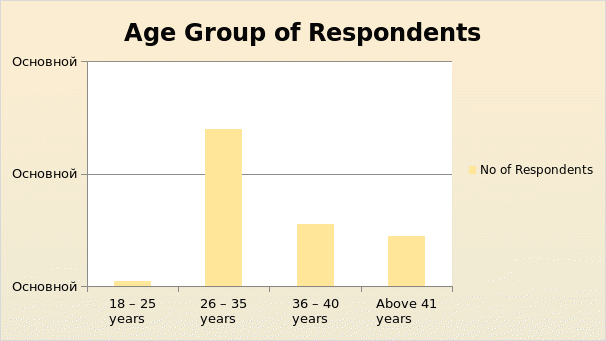
The survey incorporated all categories of positions including management staff. Demographic information on the age of the participants was obtained by collecting information on four different age groups. The majority of the participants at 28 out of 49 (57.14 percent) were belonging to the age group of 26 to 35 years. There were 9 participants in the age group of above 41 years. The distribution of the samples according to age is shown below:
Table: Age-wise Distribution of Samples.
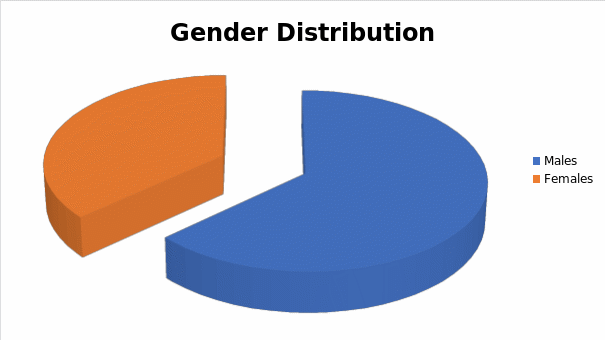
The majority of the respondents were males. The number of male participants out of the total 49 people was 31 representing 63.26 percent. The gender distribution is presented in the following table:
Table: Gender Distribution of Samples.
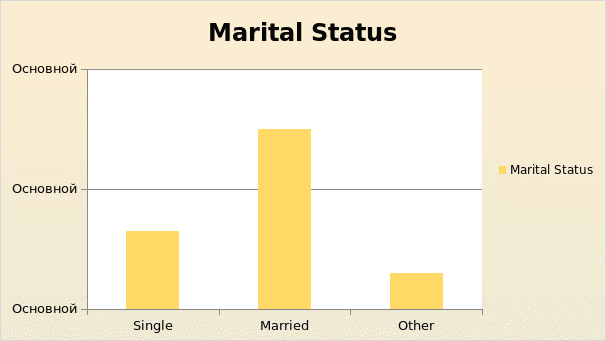
The marital status of the individual employees does have an impact on the ethical values the employees carry towards the organization as those who have a family to take care would think twice before committing any fraud and hence they remain more loyal to the organization. Out of the total 49 respondents 13 were single, 30 of them were married and 6 belong to other categories. The percentage of married people to the total number of respondents represents percentage.
Table: Marital Status of Samples.
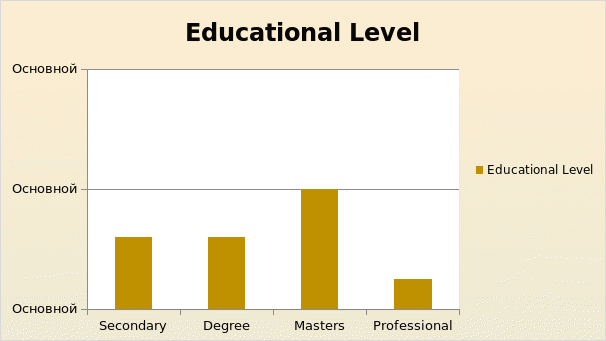
The next question in the questionnaire was concerning the education level of the participants. The demographic information on the education level was collected under four different categories like secondary, degree, masters and other professional education. A majority of 20 out of 49 respondents were having education at the masters’ level while 12 of them were degree holders. The percentage of people holding masters degree was 5 out of 49 participants were having other professional qualifications. The graphical representation of the educational level of the participants is appended below:
Table: Educational Level of Participants.
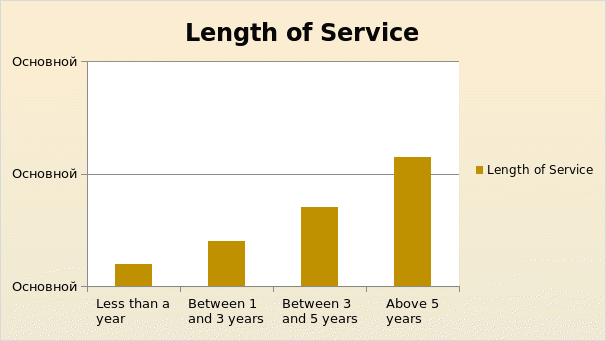
The period of employment with any particular organization also has an impact on the ethical standards and loyalty of the employees towards the organization. In order to determine the level of employee commitment a question on the number of years of service by the respondents was asked. The responses to this question indicate that a majority of 23 employees out of 49 respondents have worked with the company for a period of more than 5 years. This shows the level of organizational commitment the employees have on the company Clothing Factory. While 14 of them were with the company between three and five years only 4 of them were having less than one year service with the company. The pictorial representation of the period of service with the company is shown below:
Table: Length of Service with the Company.
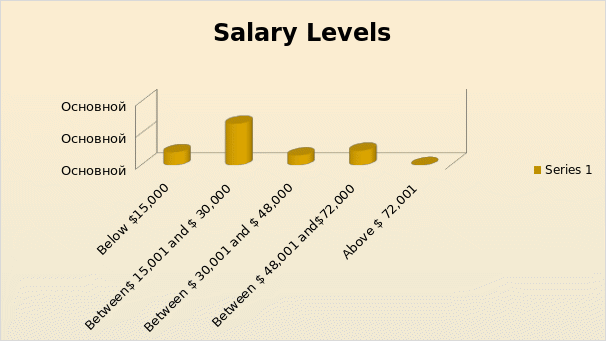
In the questionnaire the next question related to the levels of salary being drawn by the respondents. The information on the salary levels was gathered by making five distinct groups of salaries starting from below $15,000 and above $ 72,001. Out of the responses received it is observed that 26 out of 49 respondents belong to the category of $ 15,001 to $ 30,000. There were 6 people in the range of between $ 30,001 and $ 48,000 and 9 people in the range between $ 48,001 and $ 72,000
Table: Salary Levels.
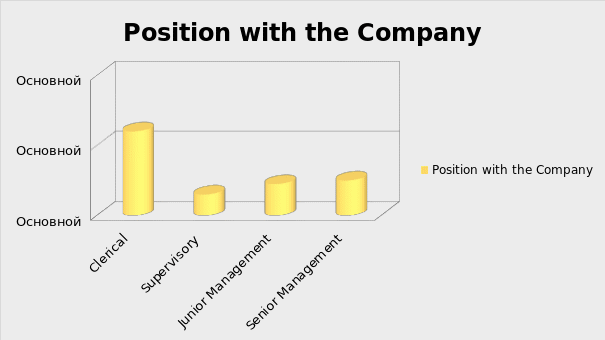
Since the samples included different levels of employees, a question on the respective positions of the respondents was inevitable. The responses received indicate 24 out of 49 respondents representing 48.98 percent belong to clerical cadre. 10 of the respondents were in the senior management category and 9 belong to junior management category. The graphical representation of the position with the company is shown below:
Table: Position with the Company.
Internal Control System
The second part of the questionnaire contained questions on internal control systems in practice in Clothing Factory and the knowledge of the employees on those practices. The questions were devised to extract the viewpoints of the employees on the effectiveness of the internal control systems being implemented by the company.
Awareness of Internal Control System
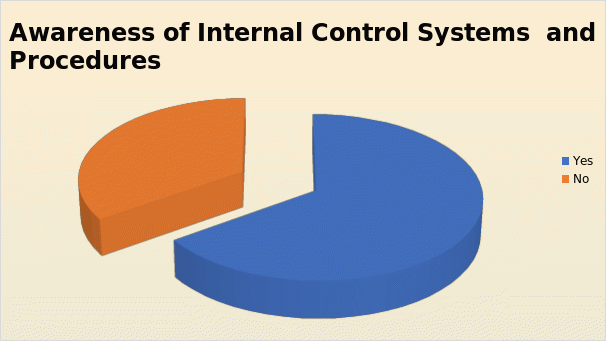
The first question related to the awareness of the chosen employees on the concept of internal control. For the question on the awareness of internal control, 32 out of 49 participants had replied that they are aware of internal control principles. This constitutes 65.3 percent of the sample population. 17 of the respondents were not aware of internal control principles. Perhaps this 17 people would be belonging to the clerical cadre who might not be aware of the internal control systems and procedures. The chart showing the awareness of internal control is shown below:
When the respondents were asked to comment, whether the existing internal control systems presently in practice in the company are effective enough to control the organizational functions, 36 out of 49 representing 73.47 percent answered in the affirmative and confirmed that they are effective. 13 of the participants did not believe that the existing systems are effective enough.
Need for Internal Control Systems
Next question on the questionnaire concentrated on the opinion of the participants on the need for the internal control system in the organization. Seven different options where there is the need for internal control were provided in the questions and respondents were asked to rank them in the order of priority in their opinion. Since each of the 49 participants chose to attribute different ranking to the different attributes stressing the need for internal control, the mean value of the responses was calculated taking into account the weighted average of the rankings given by the employees. The mean values are shown in the following table:
Table: Need for Internal Control.
From the above table it can be observed that the employees feel that the detection of frauds and preventing them is the prime objective of instituting internal control systems. The employees have found that the improving the profitability of the company is another important objective of internal control. The respondents have also opined that improving the efficiency of the operations of the company is also another function of internal control. However, the employees are of the opinion that accurate financial reporting forms the last need of internal control mechanism.
Areas of Internal Control
On the question of the vulnerability of different functions to which internal control is to be applied varied opinions have been expressed by the chosen employees. Just as in the case of the responses for organizational issues, here also the responses received from the participants have been averaged on the basis of ranking given by them. The mean values arrived for various aspects mentioned in the questionnaire are tabulated below:
Table: Areas of Internal Control.
From the above table it is clear that cash disbursements is an area which has been found to be more vulnerable requiring more attention in the internal control systems. The respondents have also identified the accounts payable and purchases as the second more vulnerable area as there might be underhand dealings and commissions inbuilt in purchase prices.
Review Procedure
Researches of this kind normally have the objective of expanding prior studies on to the finding the exact procedure that is being followed in reviewing the existing internal control systems. However this study attempts to bring about the opinion of the selected samples on the review procedures for the internal control systems to improve their effectiveness. The opinions expressed by the respondents have been tabulated below on the weighted average basis attributing the mean value to each of the aspects.
Table: Review Procedure.
From the responses of the samples it is seen that the employees are of the opinion that the follow up by the management on unexpected results or unusual items would throw light on the effectiveness of the exiting internal control systems and procedures. Building some sort of performance indicators has also been identified as one way of reviewing the internal control system in practice.
Responsibility for Internal Controls
On the question of the authority who should take the responsibility for the implementation of the internal control systems the respondents have indicated the following results:
Table: Responsibility for Internal Control.
It can be observed from the responses that the employees feel that the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) has more responsibility to take for the implementation of a proper system of internal control, closely followed by the Chief Financial Officer (CFO). This response implies the unawareness of the respondents of the ultimate responsibility of the board of directors for the implementation of the internal control procedures.
Suggestions for Improvements
The last question in the questionnaire requested the respondents to offer their ranking for the suggestions mentioned in the questionnaire for improving the effectiveness of the internal control systems and make it more beneficial to the organization as well as to the employees. The ranking offered by the respondents weighed to the number of respondents offering the same rank has been taken into account to arrive at the following mean values:
Table: Suggestions for Improvement.
As expected the selected samples have expressed the opinion that it would be better for the company to prepare and circulate all the procedural formalities relating to the internal control systems.
Analysis
A detailed analysis of the findings of the study is presented below:
What are internal controls?
The implementation of internal controls is the foundation of a solid company. Without cohesive internal controls, the company will suffer. In the Findings and Analysis section of this dissertation, I will delve into what internal controls are, what they are not, how they can be used most effectively within an organization, and the requirements of management with respect to the system of internal controls over financial reporting.
In 1992 the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations (COSO) of the National Commission on Fraudulent Financial Reporting published a document entitled Internal Control-Integrated Framework. The document defined internal controls as, “a process affected by an entity’s board of directors, management, and other personnel.” (AICPA, 2008: 41) Internal controls consist of the following categories: effectiveness and efficiency of operations, reliability of financial reporting and compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Components of Internal Control
Internal controls can be judged as effective in these categories if the board of directors and the management teams understand the extent to which the company’s operational objectives are being achieved, the financial statements are being prepared reliably, and the laws and policies governing the organization are being followed. The COSO framework consists of five related components and they are as follows:
- Control environment: The control environment covers the integrity and the ethical values possessed by the employees. The environment also encompasses the competence level of the employees. By evolving the control environment the management would be able to assign the role and responsibilities for individual employees at all levels. It also leads to the organized development of employee skills. The supervision and control from the board of directors is also encompassed in the control environment along with the structure and discipline to be followed by the employees.
- Risk assessment: Risk assessment is a process that identifies the risks associated with the firm’s business. It also involves the analysis of such risks identified. The purpose of risk assessment is to facilitate the achievement of the objectives of the company. The risk assessment process takes into account the assessment of both internal and external risks associated with the firm. It is necessary to establish and set the objectives for risk assessment before undertaking the process of assessment and such objectives should be interlinked with the different functional levels of the organization.
- Control Activities: Under this process the established organizational policies and procedures are being carried out so that the organizational direction as provided by the management is followed effectively. It is to be noted that the control activities are present at all levels of the organization to pursue the directives of the management. Some of the control activities in an organizational context are (i) approvals and authorizations, (ii) verifications, (iii) reconciliation of the results of different functions, (iv) a comprehensive review of the operating results of the organization, (v) provision of security for the assets of the entity and (vi) defining the duties and responsibilities for different functional areas
- Information and Communication: In any organization there is the need for identifying, capturing and communicating relevant information to the people at the right positions. This is necessary to enable the organizational members to carry out their responsibilities effectively. Information system that is existing within the organization is of primary importance for ensuring the promptness of this step in the total internal control system. It is important that both internal information system as well as the external communication methods is properly assessed and set in order for the management to take right decisions at the appropriate time. This will also enable the management to make an effective external reporting of the performance of the organization.
- Monitoring: There should be a continuous monitoring of the internal control system by the top management and other executives to secure the effectiveness of the system. The monitoring aspect is usually interlinked with the internal audit function of the organization. Monitoring is also carried out as a part of general management and other supervisory activities. It is considered important that the deficiencies found in the internal control systems are reported to the management as normal routine and serious deficiencies are brought to the attention of the top management and the board of directors for a timely intervention and follow up action to improve the effectiveness of the system.
These five components make up the internal controls of a company.
Management develops a system using these components as a foundation, and brings these components together to form a reliable system by which their company is kept in check. In other words, the internal control system that is put into place by management is basically a regulatory system (the internal controls is the system that is used to keep the company in check).
Responsibility for Internal Control
Everyone within the company has a role to play in the company’s internal control system. Here is a list of the roles that each one in the company is responsible for.
- Chief executive officer (CEO): It is usually the CEO who is finally responsible for the effective implementation of the internal control system in any organization. It is for the CEO to evolve the principles and practices in an organization in such a way that the integrity and ethical values are taken care of to result in a positive environment for implementing the internal control system effectively. While the tone of the internal control system is set by the CEO the setting up of other operational elements of the system are left to the executives and officers at various levels under the direction and guidance of the CEO.
- Chief financial officer (CFO): The CFO controls the financial reporting and accounting. The audit committee works with the CFO to determine if the reporting is true and accurate. The CFO uses leadership skills to oversee all of the financial reporting.
- Controller /director of accounting or finance: The controller is responsible for most of the workings of the internal control system that are put into place by the CEO and the CFO. The controller understands the need for the internal control system, is committed to the system, and communicates the importance of the system to all of the employees within the company.
- Internal audit: One of the major functions of the internal audit department is to check and ensure the effectiveness of the internal control system in operation in the organization. The internal audit has also to contribute to the effectiveness of the internal control by pointing out the deficiencies. Since the internal audit reports are submitted to the audit committee of the board of directors and the senior level organizational members the part being played by the internal audit is quite significant in monitoring the internal control system.
- Board of director/audit committee: It is one of the important functions of the board of directors to ensure the effectiveness of the internal control system. The involvement of the board of directors becomes crucial when the management of the organization is entrusted to a team of executives or managers. The scope of oversight of the board of directors with respect to the effectiveness of internal control system extends to financial reporting, operational control and compliance with the applicable laws and regulations.
- All other personnel: The internal control system is only as effective as the employees throughout the company. Employees throughout the company understand that their role in the control system is an important one. The employees in the company are the ones who actually implement the internal control system.
Internal Control System in the Clothing Factory
Now attention will be given to the internal controls of one specific company in order to demonstrate the implementation of internal controls. The company is called the Clothing Factory and it is a company that operates within the garment industry. It was established in 1982. It started out as a small company with only 1 warehouse and 10 employees. Over the years this company has expanded and it now consists of 3 warehouses, 1 factory and 4 retail shops in Hong Kong. In addition, the Clothing Factory has 2 factories and 2 retail shops in Shenzhen and 1 factory in Dongguan (China). The staff has over 300 employees in Hong Kong and 3,000 employees in China.
The goods that are produced by the Clothing Factory are jeans, coats, jackets, trousers, shirts, skirts, dresses, shorts, sweat shirts, overalls…(etc.) The Clothing factory is experienced in producing woven fabric (denim and non-denim) knits and so on. The internal controls of the company consist of operational functions, financial reporting and following international laws and regulations.
Operational Functions
The operational controls of the Clothing Factory include receiving fabric, weaving cloth, and packaging them to be sent to retail outlets. All of the suppliers of the Clothing Factory directly deliver the fabric to each warehouse. Storekeepers classify the stored material and then report the material for entry into the i-netGarment System. The i-netGarment System provides a comprehensive inventory system for the Clothing Factory.
By using the i-net Garment System management is assured that the inventory is counted and that the fabric the suppliers send to the warehouse is not wasted. Whenever the cloth is delivered from suppliers the Fabric inspection Machine is used to inspect the quality of the cloth. This guarantees that the quality of the cloth that is purchased is up to the standards of the company. If the fabric is in good condition, then the storekeeper will sign the delivery note to the suppliers. The same process is put in place for accessories. If the accessories are in good condition, then the storekeeper will also sign a delivery note to the suppliers.
Only the fabric that is needed to fulfill customer orders is taken from the warehouse to the factory for production. The material will be signed out of the warehouse and signed into the factory. That way the company can keep track of the cloth and no money will be lost.
The operations involved in making clothes have many steps. The steps include design, paper sample, cutting, sewing, dyeing, printing, embroidery, washing, ironing, packing, and final quality control, etc. Not each step is processed by our factory. Some of the steps are outsourced. Some of the processes that are outsourced are washing, dyeing, discharge print, reactive print, pigment print, pattern grading, print, and embroidery.
The company uses quality control procedures; however, the quality control procedures are not professional. If the quality of the clothing is unacceptable to the customer than the goods are returned to the company and a loss is reported. The clothing is replaced within 14 days.
Marketing and Sales
The designers at the Clothing Factory recently won the Overall Winner Award and the Lectra Award for the best technology from the New Hong Kong Fashion Collection Award. The Clothing Factory also sells their clothes to be used in Television and film. The marketing and sales department uses aggressive marketing tools to sell the clothes.
The Clothing Factory uses the Point of Sales (POS) system record to ensure a sufficient supply of clothing and the designers know what will sell and what will not sell. The supply of clothes from the factory is continuous. The POS system with a Barcode provides a simple and quick payment procedure and decreases the time with which the customer must spend shopping and selecting their clothing. The Clothing Factory keeps financial records for every purchase that is made everyday, week, month, and year.
Technology Development
The IT system that is used by the Clothing Factory is the i-netGarment system. The i-netGarment system can follow network links from offices and factories and the system can also overcome any obstacle that arises. The staff uses the internet in order to monitor the entire production and operation process. The POS system ensures that payments are made quickly and accurately. The IT department provides strong support to the staff. If anyone on the staff has a problem wit the computer software or hardware, the IT department provides the solution.
Human Resources
The human resource department is very involved with its employees. The human resource department is responsible for staff training, career development, performance management and development, succession planning, key employee identification, and organization development. At the Clothing Factory 60% of the employees have a degree and the entire management team is professionally qualified. Employees are also trained and this is important because it produces staff that are familiar with the operations at the Clothing Factory and all of the employees have the opportunity to advance together.
Firm Infrastructure
The Clothing Factory departments include the Sales & Marketing Department, Accountings & Financial Department, Humane Resources Department, Internal Audit Department, Purchases Department, IT Department, and the Product Development Department. Household bank (HSBC) provides strong financial support. They have loaned the Clothing Factory over 1 billion dollars since 1982.
The internal audit department ensures that financial reporting and other systems run smoothly. The system must be followed by all employee or their will be waste and money will be lost. The internal audit ensures that there will be no waste and no embezzlements of money.
Quality Control
The quality control procedure consists of two steps. First of all, the quality of the merchandise is controlled. Specifically, the fabric and the colors of the fabric are inspected. Then the quality of the fabric and assortments of materials are inspected. The patterns, designs, and packaging are then inspected. After the pre-production quality is assessed to meet the company’s standards, then the production lines and accessories are reviewed for quality. When the productions lines are inspected the cutting of fabric is assessed, the sewing line is inspected, and finally the packaging is inspected once again before shipping.
Sustain Competitive edge Advantages
There are plans to build a new factory in early 2009. When this new factory is build, there will be no need for outsourcing. The dyeing, printing, embroidery, and washing etc. will all be done at the new factory. Although these working procedures may be difficult tasks, the new factory will have all of the equipment necessary to do these tasks. Staff will be challenged to learn new skills and a campaign to bring experienced employees on board as well. With the end of outsourcing, profits will increase and losses will decrease.
Conclusion
The Clothing Factory has many competitive advantages. The reason that this company can progress is because of the internal controls that are in place. The operation of this company is smooth, the financial reporting is simple and accurate, and all laws and policies within the company are followed. The i-netGarment system is used to help staff with financial reporting and to keep up with the stock so that there is no waste. The POS system is used because it is an easy system for customers to utilize, and it is an accurate system for keeping track of sales, therefore, the staff is not burdened with the difficult task of manually keeping track of sales. All of the sales and the record keeping is done on the internet. This company has a competitive edge over other companies because their internal control system is simple, straightforward, and up-to-date with the modern era.
Conclusions and Recommendations
This chapter contains certain concluding remarks on the study on internal control recapitulating the issues discussed in the text. This is followed by few recommendations for an effective implementation of an efficient internal control system. The chapter also describes certain limitations this study faced.
Conclusion
Internal controls are the foundation of every business. Good internal controls ensure that the company’s operations run smoothly. Internal controls consist of the following components: the control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication, and monitoring. The proper implementation of each component is important in keeping the company running smoothly. In addition, every individual within the management team has a specific role to play in ensuring that the internal controls are implemented correctly. One of the most important results of a good internal control system is the prevention of fraud. The most unlikely individuals commit fraud. Those who commit fraud include those who may have an alcohol or substance abuse problem, a gambling problem, financial problems, they also may be a disgruntled employee or they might simply like to live on the edge. Whatever the reason for committing fraud, the perpetrators is rarely caught. Therefore, it is very important to implement a strong internal controls system within the company.
The stakeholders and public have shown sharp reactions to the recent corporate scandals with huge expectations from the organizations to take an attitude of not tolerating any fraud. Irrespective of the size or status of an organization the board of directors has been entrusted with the responsibility of ensuring an overall ethical behavior in the respective organizations under their control. This becomes applicable to the public, private, government or not for profit organizations. The role of the board of directors has been considered of specific importance as historically most of the frauds have been committed by the collusion of the senior management with other key officials. The public, stakeholders and regulators are provided with clear signals on the intentions of the board of directors and management towards facing the fraud risks and about the fraud risk tolerance of the organizations. In this respect the role played by internal control is of immense value as the organizations derive the maximum benefits in terms of control against frauds being committed by different individuals. This study has found out that with an effective and efficient system of internal control in place the organizations will be able to safeguard the resources of the organization against all possible risks of fraud.
Limitations of the Study
The small size of the sample may perhaps be viewed as the serious limitation of this study as it may weaken the results. The smaller size also has limited the use of more robust statistical analysis methods. It may not however be out of place to mention that field studies always include small samples. For instance the study by Cartwright and Cooper (1989) on the success of joint ventures between IT firms had only 68 participants representing a 41 percent response rate. Since the information and data for this study was collected from a single organization, care should be taken while making generalizations out of the study. A final limitation of the study is that the research has used self-report data and consequently the use of a common method to collect the data could vitiate the results to some extent.
Recommendations
When the internal controls of a company are changed or improved the entire company benefits. However, improving the internal controls of a company translates into a big change in the way the business itself is run because the internal control system is the backbone of the company. In order to change the internal control system and the way that business is run in general, top management must understand what type of business environment their staff is working in and then they must effectively communicate the changes within the company to their employees.
In order to understand the company’s environment top managers must understand that like individuals, companies have their own personality. With that said, top management needs to understand what makes their company tick, and what are the good traits of their company and what are the bad traits of their company. By understanding what type of environment the staff works in, top management will understand why their organization either rolls with the punches to consistently deliver on commitments and produce great results, while others fail to meet their commitments and produce poor quality products.
Changing the internal control system of a company also requires strong communication skills. Top management needs to communicate the changes effectively to their staff or the new internal controls system will fail. Most of the time, mangers communicate in order to transmit pertinent information about the job.
With all the benefits of communication, managers need to make communication a priority. Even with careful consideration to the way that managers communicate to their employees, some employees will never be reached. Many messages to the staff are too long and not of good quality. The messages are unfocused, rambling, and frequently irrelevant to the needs and concerns of the audience.
In addition to delivering the message carefully, mangers need to recognize that the same words mean different things to different people. Communication easily gets garbled and misunderstood. Individual words have different meanings when heard by employees with different backgrounds. When the communication process breaks down mangers should assess why the breakdown in happened.
Generally, people tend to see others as they see themselves and they develop a message that they would want to hear. But, this is not the way successful communication works. It relies on the manager’s ability to put himself or herself inside the heads of their audience. Communication and community have the same root. They imply a common bond that unites people.
With that said, we can now turn our attention to the specifics of the Clothing Factory. The Clothing Factory has a very good internal control system; however, improvements could be made. The Clothing Factory’s system for keeping track of its materials is very good. The i-net Garmet system counts inventory, keeps track of fabric, and is a reliable computer system. The POS system of sales is simple for the customer to use and easy for the staff at the Clothing factory to use. This system keeps waste to a minimum and profits to a maximum. The Clothing Factory has a policy of trust with their employees. This can be very positive for moral and building relationships between staff and management. However, if an employee commits fraud against the Clothing Factoring, it could be extremely damaging, as it is a relatively small company. In the business environment today there is great risk of fraud occurring. Fraud and the embezzlement of money are common incidences today. Therefore, I would error on the side of caution and introduce more sound internal controls in order to prevent security risks. Finally, the Clothing Factory has very sound internal controls and a warm working environment. But, management must communicate effectively with their staff about the changes they plan to make. If improvements to the internal control system are made, the Clothing Factory will become a successful business.
Bibliography
Comptroller’s Handbook ‘Internal Control’ Comptroller of the Currency Administrator of National Banks
Controlling Joint Venture Risk
Controlling Joint Venture Risk is an article that focuses on the risks involved in joint partnerships. The article discusses the difficulties small businesses face, and describes situations that lead to fraud and embezzlement. This is a good article for small business owners to read.
COSO
COSO is an article that discusses internal controls in general and describes methods of preventing fraud. This article outlines the reasons it is important to have a strong internal control system. This is a good article to read for general information about internal controls.
The Tally Stick: the first internal control?
The Tally Stick: the first internal control is an article that describes operational internal controls. The article also focuses on fraud prevention and keeping the company secure. This is a good article for entrepreneurs who are interested in finding out more about operating a company.
Reporting on Internal Control over financial reporting
This article discusses how internal controls are used to regulate financial reporting. It also describes the ways in which Internal controls are used in the day-to-day operations of the company. This is a good article for people in management positions to read.
Board-level Risk Committees: Implications and opportunities for risk Managers
Board-level Risk Committees: Implications and opportunities for risk Managers is an article that focuses on the role that Managers play in controlling the risks of the company. This article examines management responsibilities pertaining to the internal controls of the company. It is a sound article with many strong points to make about the role that managers play within the company.
Internal Control Weakness and Information uncertainty
Internal Control Weakness and Information Uncertainty is an article that discusses the pitfalls of weak internal controls. When the internal controls of a company are weak the company suffers. The operations of the company become disorganized and the information that is communicated within the company breakdowns. Once there is uncertainty within the company, the company begins to lose profits and may eventually fail. This is a strong article that informs the reader about the significance of sound internal controls.
The Benefits of Early Controls Assessment: Prevention is better than a Cure
The Benefits of Early Controls Assessment: Prevention is better than a Cure is an article that focuses on planning the internal controls system before the company is in business. This article also emphasizes the importance of internal controls in general. This is a good article for anyone who is in the development stage of planning a business, as well a business student.
Controlling Internal Controls
Controlling Internal Controls is an article that focuses on the job of the CEO, CFO, director of accounting and the internal auditor. This article describes the role that top management plays in developing and implementing internal controls. Controlling Internal Controls clearly outlines the job that management does and it is a good article for those who are planning a career in management to read.
Assessing the Control Environment Using a Balanced Score Card Approach
Assessing the Control Environment Using a Balance Score Card Approach is an article that focuses on accurate and honest financial reporting. In this article, internal controls are regulated by using a balance sheet to keep track of finances. This is a good article for those business students who are studying to become an accountant.
Controlling Internal Controls: It’s not about eliminating risk but making sure your existing rules are followed
Controlling Internal Controls: It’s not about eliminating risk but making sure your existing rules are followed is an article that describes the real world structure of internal controls. It exemplifies real companies working in real environments. This is a good article for all entrepreneurs to read.
Strong Internal Controls are the best defense against Financial Fraud
Strong Internal Controls are the best defense against Financial Fraud is an article that delves into issues related to fraud and embezzlement. This article focuses on how to develop and implement the best security systems. The article is a strong source for understanding the structure of internal controls as it relates to fraud.
Knowledge is Power
Knowledge is Power is an article that discusses the risks involved in running a business. It delves into to topic of fraud and embezzlement and explains many of the reasons why employees commit these crimes. It is a sound research tool and it backs up many of the other sources I found on fraud.
Improving the Effectiveness of Audit Committees
Improving the Effectiveness of Audit Committees is an article that gives good insight into the workings of audit committees. This article defines what audit committees do and how they can be improved. This is a good article with some very good information to disseminate.
Internal Control differences between community health Centers that did or did not experience Fraud
Internal Control differences between community health centers that did or did not experience Fraud is an article that discusses the affect that internal controls has on health centers. In this article, it was discovered that those health centers that did not have good internal controls experienced a high rate of fraud. This is a strong article with important insights to disseminate.
Internal Controls
Internal Controls is a general article that discusses internal controls and how they affect businesses. This article describes the inner workings of fortune 500 companies and offers advice on planning a strategy for developing and implementing internal controls. Internal Controls is a good article for business students to read.
Building an Antifraud Framework: Culture, Risk Assessment and Oversight together can Combat Fraud
Building an Antifraud Framework: Culture, Risk assessment and Oversight together can Combat Fraud is an article that focuses on fraud prevention. Fraud and embezzlement create tremendous problems for corporations. This article focuses on ways in which fraud can be detected and prevented. It is a good article for business students to read before they enter into corporate world.
The UK Approach to Corporate Governance
The UK Approach to Corporate Governance is a report on the way in which companies in the UK implement internal controls. It details the operational systems and the laws that govern companies within the UK. This is a good article to examine because it gives one insight into how business is conducted in other countries.
Managing internal controls
Managing internal controls is an article that focuses on fraud and embezzlement. The prevention of fraud is the most important element of a company’s internal controls system. This is a good article for students and professionals alike to read.
Focus on high-risk controls : the PCAB’s auditing standard no.5 enables publicly listed companies to narrow the scope of testing for sarbanes-oxley compliance
This article focuses on companies who must comply with sarbanes-oxley
practices. The article describes sarbanes-oxley practices and helps guide entrepreneurs through its policies. I would recommend this article to international business students.
Restoring trust in American business: the struggle to change perception
Restoring Trust in American business: the struggle to change perception is an article that discusses fraud and the ethical implications associated with distrusting one’s employees. This is a good article because it describes the types of environments that breed distrust between staff and management. This is a good article for business students to read.
Integrating Entrepreneurship and Strategic Management Activities to Gain Wealth
Integrating Entrepreneurship and Strategic Management Activities to Gain Wealth is an article that discusses strategically developing internal controls in order to ensure the success of the company. The role that top management plays in the development and implementation of the internal controls within the company is also discussed. This article aids in the understanding of the managements responsibilities within the company. It is a strong article and a good source to use in examining the scope of what internal controls do and how they affect business.
Managing Risk with internal controls
Managing Risk with internal controls describes how internal controls are implemented and maintained. After the internal controls are implemented they need to be managed. This article gives good insight into how to go about keeping track the internal controls. Managing internal controls is a strong article that all entrepreneurs should read.
ISO
ISO is an article that describes the specific laws and requirements that North American Company’s have to comply with. This article emphasizes the importance of following the law and standards that exists in the company’s country. ISO is a strong article with a lot of examples of good internal controls.
Strategic Management System Enhancement and Strong influence Strings
Strategic Management System Enhancement and Strong Influence Strings is an article that discusses the relatively recent recognition of the importance of sound internal controls within a company. This article also provides a comprehensive plan for the development and implementation of strong internal controls. This is a strong article with sound advice and it includes a good strategic plan for developing internal controls.
Documenting Internal controls: Identifying and recording organizational controls has become practice for many audit professionals
This article discusses recording organizational controls such as financial reporting, inventory, other company records. Documenting Internal Controls is a strong article that disseminates a lot of information about documenting internal controls. I would recommend this article to business students and entrepreneurs.
Procedures to Prevent Fraud and Embezzlement
Procedures to Prevent Fraud and Embezzlement delves into how fraud is committed, what drives employees to commit fraud, and how to prevent fraud from happening. This book also gives insight into how the internal controls of a company can be used to prevent fraud and how management can detect fraud within the company. The employees who commit fraud according to this book are often the most seemingly unlikely people to commit a crime. However, Procedures to Prevent Fraud and Embezzlement underlines the many reasons that employees step over the line and commit fraud. This is a sound source that gives its readers insight into the ugly world of embezzlement.
Delivering on Your promises: an Effective Control Framework
Delivering on Your Promises: an Effective Control Framework is an article that discusses the role management plays in developing and implementing internal control systems. It reinforces the philosophy that top management has made promises to their staff. Specifically, the promise that the business will run smoothly, be successful, and keep them employed. This is a good source that aids in the understanding of the ethical value of developing a sound internal controls system.
Internal control: help for small business has arrived in the form of Cosco’s latest guidance on internal controls over financial reporting:
This article discusses Cosco’s guidance of internal controls for companies. Many companies have faulty or poor internal controls because those in top management positions do not know how to develop or implement internal controls. This article goes into detail about Cosco’s new guidance system for those types of companies. This is a good article for management, entrepreneurs or business students to read.
Are your Internal Controls helping you?
Are your internal controls helping you is an article that focuses on innovative ways to operate a business. This article challenges management to think outside the box. It gives the entrepreneur the scope to think creatively about internal controls. Are your controls helping you is a good article for all businessmen and businesswomen to read.
Building a research model for internal auditing: insights from literature and theory specification cases
This article includes many examples of strong internal controls working for companies and making them better. The article also demonstrates weak internal controls and how they adversely affect companies. This article is a good article for anyone who is interested in internal controls to read.
Make risk management and internal control work for you: by tailoring an integrated, business-process-based template solution, small companies can address risks and controls in a cost-effective manner, whether or not Sox compliance is mandated.
This article focuses on managing risk through pre-planning and strategic development. The article also emphasizes a business-process-based template solution. These articles give the entrepreneur insight into business plans that they can use in the real world. Mangers, entrepreneurs, and business students should read this article.
Trends shaping tomorrow’s world: forecasts and implications for business government, and consumers
This is an article that describes future trends for companies. It focuses on internal controls and innovative ways to detect and prevent fraud. This is a good article for all business students to read.
The Risk of being Global: How to Manage overseas Opportunities
The Risk of being Global: How to Manage Overseas Opportunities is an article that discusses international business. In the article, Siciliano and Zuvich talk about the importance of internal controls within the community of international business. Developing sound internal controls is key to keeping the operations of international companies thriving. This is a sound source for research into the workings of internal controls.
The Managers Guide to Compliance
The Manger’s guide to Compliance gives a lot of insight into the pitfalls of fraud and explains the process involved in detecting and preventing fraud. This is a very detailed book and it gives a lot of important information to the reader on the subject of internal controls. It is a sound resource for research into the area of planning and executing internal control systems.
The Globalization of Efforts to Improve Internal Controls: Why Much of the World Thinks SOX sucks
The Globalization of Efforts to Improve Internal Controls is an article that discusses how to improve existing internal controls. This article impresses upon the reader the importance of improving the company’s internal controls periodically. The article aided in my understanding of how to improve on existing internal controls such as those at the Clothing Factory.
Incentive to defraud
Incentive to defraud is an article that delves into the world of stealing, lying, and cheating corporations out of their money. This article describes many of the different motives behind embezzlement. This is a good article for people in top management positions to read.
Account reconciliation: an underappreciated control: this procedure has become even more important since Sarbanes-Oxley’s passage
This article focuses on account reconciliation and the importance of maintaining accurate financial reporting. The article describes Sarbanes-Oxley’s passage and emphasizes the significance of following the laws pertaining to individual companies. This is an important article for business owners and management to read.
Beyond COSO: Internal Control to Enhance Corporate Governance
This book approaches the internal control for corporate entities from the perspectives of implementation of corporate governance measures
Managing the Business Risk of Fraud: A Practical Guide
Sponsored by the Institute of Internal Auditors, Institute of Certified Public Accountants and Association of Certified Fraud Examiners available online from website
References
Aaker, A. David, V. Kumar and George S. Day (1995), ‘Marketing Research’ 5th edition, John Wiley and Sons, New York, NY.
Adler, P. A. & Adler, P. (1987) Membership roles in field research Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publications.
Applegate, D.B. (2001) Controlling joint venture risk, Journal of Managerial issues, 58(3) p.44.
Applegate, D. & Willis, T. (1999) COSO, Internal Auditor, 56(6) p.60.
Apostolou, N. & Crumbley L.D. (2008) The tally stick: the first internal control? The Forensic Examiner, 17(1) pp. 60-63.
Agami, A (2006) Reporting on Internal Control over financial reporting. The CPA Journal, 76 (11) pp. 32-35.
Atkinson, W. (2008) Board-level risk committees: Implications and opportunities for risk managers. Risk Management, 55(6) pp. 42-46.
Barra, R. A. & Kenneth, G. (2007) Internal controls: Lessons to be learned from fire. International Journal of Service and Standards, 21(2) pp. 87-89.
Beneish, M.D., Billings, M.B. & Hodden, L.D. (2008) Internal control weakness and information uncertainty, Accounting Review, 83 (3) pp. 665-704.
Bogdan, R. C., & Biklen, S. K. (1982) ‘Qualitative research for education: An introduction to theory and methods’ Allyn and Bacon, Inc. Boston.
Bronson, S.N., Carcello, J.V. & Raghunandan, K. (2006) The benefits of early controls assessment: prevention is better than a cure, The CPA Journal, 76(11) pp. 6-9.
Candreva, P.J. & Roberts, N. (2006) Controlling internal controls, Public Administration Review, 66(3) pp. 463-469.
Callaghan, J. H., Savage, A. & Mintz, S. (2007) Assessing the control environment using a balanced sore card approach, The CPA Journal, 77(3) pp. 58-62.
Cheney, G. (2008) Controlling internal controls: It’s not about eliminating risk but making sure your existing rules are followed, Investment Dealer’s Digest, 27(3) pp. 30-35.
Cambell, D. R. & Cambell, M.V. (2006) Guidance for small public companies reporting on internal controls: an overview and assessment of the COSO exposure draft, The CPA Journal, 76(9) pp. 22-26.
Cash, J. I. (1993) Corporate information systems management. Illinois: Business One Irwin.
Clancy, K. (2008) Strong internal controls are the best defense against financial fraud, US Business Review, 9(3) pp. 16-18.
Clark, M.J. (2008) Knowledge is Power, The Risk of being global: How to manage overseas Opportunities. Risk Management, 55(6) pp.58-59.
Creswell, J. (1994) ‘Research Design: Quantitative & Qualitative Approaches’, Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks, CA.
Davidson, B. A. & Ebersole, C. (2002) Improving the effectiveness of audit committees Bank Accounting & Finance, 14(1) pp. 68-88.
Denscombe, M. (1998) The Good Research Guide. Open University Press.
Fink, A. (1995). ‘How to ask survey questions’ Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications.
Dietz, D.K. & Snyder, H. (2007) Internal control differences between community health centers that did or did not experience Fraud. Research in Healthcare Financial Management, 20(1) pp. 43-47.
Douthett, E. B. Duchac, J.E. & Warren, D.L (2001) Internal Controls Journal of Accountancy, 64(3) p.13.
Durbin, N.R. (2006) Building an antifraud framework: culture, risk assessment and oversight together can combat fraud. Bank Accounting & Finance, 20(1) pp.43-48.
Eisner, E. W. (1991). ‘The enlightened eye: Qualitative inquiry and the enhancement of educational practice’ Macmillan Publishing Company New York, NY
Fraser, J. (2008) Managing internal controls Internal Auditor, 65 (1) p.11.
Goldberg, D.M (2007) Focus on high-risk controls: the PCAB’s auditing standard no.5 enables publicly listed companies to narrow the scope of testing for sarbanes-oxley compliance. Internal Auditor, 64(6) pp. 65-69.
Goldsmith, M. (1997) The Organization of the Future. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass Publishers.
Goodman,M.B. (2005) Restoring trust in American business: the struggle to chance perception. Journal of Business Strategy, 26(4) pp.68-88.
Hagen, A., Tootoonchi, A. & Hassan, M. (2005) Integrating entrepreneurship and strategic management activities to gain wealth: CEO’s perspectives Advances in Competitiveness Research, 13(1) pp. 48-64.
Hockley, C.A. (2001) Managing risk with internal controls. Journal of Property Management, 66(5) p.18.
Hoepfl, M. C. (1997). Choosing qualitative research: A primer for technology education researchers’ Journal of Technology Education, 9(1), 47-63. Web.
Huber, G. P. & Glick, W. H. (1993) Organizational Change and Redesign: Ideas and Insights for improving Performance. New York: Oxford University Press.
Kerzner, H. (1999) Project management: a systems approach to planning scheduling and controlling. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Koch, A.J. (1999) Strategic management system enhancement and strong influence strings. Emergence: Complexity and organization, 1(4) pp. 43-71.
Koutoupis, A.G. (2007) Documenting internal controls: identifying and recording organizational controls has become practice for many audit professionals. Internal Auditor, 64(5) pp. 35-37.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (2000) ‘Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences’ In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 163-188). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Lofland, John and Lyn H Lofland (1984) ‘Analyzing Social Settings: A Guide to Qualitative Observation and Analysis’ Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
McMillan, E.J. (2006) Policies and Procedures to Prevent Fraud and Embezzlement: Guidance. Internal controls and investigation. New Jersey, John Wiley & Sons.
Myers, M. D (1997) ‘Qualitative Research in Information Systems’ MIS Quarterly, 21(2), (1997) 241-242.
Neumann, Iver. (2002) “Returning Practice to the Linguistic Turn: The Case of Diplomacy.” Millennium 31.
Patton, M. Q. (1990). Qualitative Evaluation and Research Methods (2nd ed.). Sage Publications, Inc. Newbury Park, CA.
Pooter, M.D. (2008) Delivering on your promises: an effective control framework helps management achieve organizational objectives and create value for stake holders’. Internal Auditor, 65(5) pp. 65-69.
Rittenberg, L.E. (2006) Internal control: no small; help for small business has arrived in the form of Cosco’s latest guidance on internal control over financial report. Internal Auditor, (63)5 pp. 35-40.
Rubinfeld, A. & Hemmingway, C. (2005) Built for Growth: Expanding your business around the corner or across the globe. New York: Wharton school of publishing.
Salerno, P. (2006) Are your Internal controls helping you? Financial Executive, 20(1) pp.21-22.
Sarens, G. & Beelde, I. D (2006) Building a research model for internal auditing: insights from literature and theory specification cases, International Journal of Accounting Auditing and Performance Evolution, (3)4 p. 452.
Schwartz, M. (2006) Make Risk management and internal control work or you: by tailoring an integrated, business-process-based template solution, small companies can address risks and controls in a cost-effective manner, whether or not Sox compliance is mandated. Strategic Finance, 301(3) pp. 35-43.
Scheumann J. (2008) Trends shaping tomorrow’s world: forecasts and implications for business government, and consumers. The Futurist, 42(3) pp.35-51.
Tarantino, A. (2006) Manager’s guide to Compliance. New Jersey, John Wiley & Sons.
Thomson, C. (2000) The incentive to defraud. Internal Auditor, 57(5) p.63.
Vorhies, J.B. (2006) Account reconciliation: an under appreciated control: this procedure has become even more important since sarbanes-oxley’s passage. Journal of Accountancy, 202(3) pp.59-63.
White, B. (2000). ‘Dissertation skills for Business and management students’ Martins printer Ltd: London.
Appendix I Questionnaire
Questionnaire
This questionnaire is presented to you as a part of a research study in presenting a dissertation leading to ——– Degree from the ———- University. All the information you provide will be kept as strictly confidential. Please try to answer all the questions with the options provided against each. A ‘remarks’ column is provided at the end of the questionnaire to enable you to supply any additional information that you would like to add to the answers you have made against any of the questions. Thank you for your cooperation.
General Demographic Information
- Age Group:
-
- 18 – 25 years
- 26 – 35 years
- 36 – 40 years
- Above 41 years
- Gender:
-
- Male
- Female
- Marital Status:
-
- Single
- Married
- Other
- Education Level:
-
- Secondary
- Degree
- Master’s Degree
- Professional
- Employment Period with the Company:
-
- Less than a Year
- Between one and Three Years
- Between Three and Five Years
- Above Five Years
- Salary Level:
-
- Below $ 15,000
- Between $ 15,001 and $ 30,000
- Between $ 30,001 and $ 48,000
- Between $ 48,001 and $ 72,000
- Above $ 72,001
- Position with the Company:
-
- Clerical
- Supervisory
- Junior Management
- Senior Management
Internal Control Systems
- Awareness of Internal Control Systems:
Are you aware of the concept of change management?
-
- Yes
- No
- Impact on the Organizational Functions:
Are you of the opinion that the internal control systems presently in practice in the company are effective to control the organizational functions?
-
- Yes
- No
- Need for Internal Control Systems:
Please indicate your choice of priority on the need for implementation of internal control systems for accomplishing the organizational objectives mentioned. Please rank your choice on a scale of 1 to 5 where 5 indicates ‘Extremely Necessary’ and 1 indicates ‘Need is Negligible’
- Improve the ethical values
- Safeguard the assets of the organization
- Improving the profitability
- Detection and Prevention of Frauds
- Effectiveness and efficiency of operations
- Accurate Financial Reporting
- Compliance with laws and regulations
- Areas of Internal Control:
In your opinion which of the following area poses as most vulnerable for frauds necessitating strict internal control systems? Please rank your choice on a scale of 1 to 5 where 5 indicates ‘Most Vulnerable’ and 1 indicates ‘Least Affected’
- Cash Receipts
- Cash Disbursements
- Accounts Receivable
- Petty Cash funds
- Accounts Payable and Purchases
- Payroll
- Review Procedure:
In your opinion which of the following action will review the internal control system for assessing its effectiveness. Please rank your choice on a scale of 1 to 5 where 5 indicates ‘Extremely Positive’ and 1 indicates ‘Negative’
- Comparison of Budget with actual
- Comparison of current period results with prior period
- Building Performance Indicators
- Follow up on unexpected results or unusual items
- Studying the internal control reports
- Responsibility for Internal Controls:
In your opinion who shall be the proper authority to take responsibility for the internal control system. Please rank your choice on a scale of 1 to 5 where 5 indicates ‘Extremely Positive’ and 1 indicates ‘Negative’
- Board of Directors
- Chief Executive Officer
- Chief Financial Officer
- Internal Auditor
- External Auditor
- Suggestions for Improvements:
What according to you should the management do to make the internal control systems more effective and positive? Please indicate your choices with ranks on a scale of 1 to 5 where 5 denotes ‘Most Desirable’ and 1 denotes ‘Undesirable’
- Communicate to the employees that fraud, embezzlement, stealing etc
Will not be tolerated and will be severely punished
- Prepare and circulate all internal control procedures pertaining to
Various functional departments
- Monitor the internal control system on an on-going basis with
A periodic review for improvement
- Send employees to training programs on ethical practices and internal
Control procedures
- Evaluate personnel based on performance related to internal
Controls
- Take severe disciplinary actions for non-performance of duties
Relating to internal control activities
Remarks:
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
I take this opportunity to thank you for spending your time in filling up this questionnaire which will greatly help me in my efforts towards getting my degree.