Executive Summary
The company will be Lebanon most important microfinance institution. The core service portfolio consists of lending money to small enterprises and helping micro and small enterprises. The company will function on a national scale from a wide-ranging system of branch networks. The company provides a variety of specialist services intended for small businesses. The company will initially presented lending services all the way through Beirut.
The company should accept people’s behaviour in a particular way that they believe is in their best interest. Following a systematic approach to the study of human behaviour will bring to light important facts and relationships that will, in turn, serve as a basis for more accurate predictions of behaviour.
The knowledge about how a person perceives a particular situation can help predict his behaviour. Though a person’s behaviour may appear rather irrational to other, it may seem perfectly rational to him. This difference in perception arises because an outsider may not have access to the same information or may not perceive a given situation in the same way as the person whose behaviour of every individual. However, certain consistencies can be defined in the behaviour of every individual. These consistencies are significant since they make room for accurate prediction of other’s behaviour in specific situation.
One of the challenges to the study of Organizational behaviour is to overcome the belief that behaviour is either the outcome of intuition or is based on common sense. Moreover, what might be common sense to one person may not be so to another. A best option to gain better practical knowledge about the above discussed theory would be to study an organization in particular.
Vision, Mission and Corporate Objectives
The microfinance firm not only limits it to thrive in the domestic market of Lebanon but it aims to flourish and expand internationally in Middle East and Africa. Even though the microfinance firm will be established in the Lebanon, which is an established market for microfinance services. The microfinance firm will be the strongest in performance in the business by generating $ 2 million in the first year in business. Therefore, to pick up return on investment to shareholders, the company should prefer to stress on lending business and look for methods to develop it abroad (Ball 2008).
Vision
The vision of the company is to benefit from acquiring business dealings operating in overseas markets. For instance in Africa or the Middle East, the accessibility of new clients or cheaper costs of hiring people may provide competitive advantage.
Mission
The mission of the company is to move strategically and extend across the globe. It believes in providing local public liability for handling the markets they know best. It has a decentralized approach. The company provides the greatest opportunities owing to the strategic fit factors. One of the major aims of the company is to augment the turnover of the existing business.
Corporate Objectives
Trading has will be continued extensively in proportion to the trends that have are observed in the similar microfinance institutions. The profits will maintain at an equivalent level. As anticipated, the trading performance of the company proved to be flexible. The market conditions in the Lebanon business and in Middle East and Africa remain more or less similar in comparison to the reports produced in the year of 2008.
However, the operating profits of the other business ventures have increased three percent against the period starting from January 2009 until September 2009 at constant exchange rates. In summary, this microfinance firm is making good advance and now the Board of Directors observes the consequence for the year of 2010 in a more optimistic light. With its strong free cash flow and balance sheet, the Board will consider that the microfinance firm well positioned to gain from its market expansion.
Description of Business
Phase 1 (Internet Platform):
Why?
It is difficult for Micro-Finance Institutions/NGOs to source funds to be lent to borrowers. It is also difficult for such institutions to let the lenders know who they are lending to. Such institutions rely mostly on donations, and donators are not always informed as where the money is really going.
What?
We wish to connect the lenders directly to the borrowers through Micro-Finance institutions/NGOs. To achieve our objective, we are creating an internet based lending platform through which the profiles of the individuals in need of funding will be uploaded by the Micro-Finance Institutions/NGOs who we intend to partner with. Due to their strong presence in rural areas of under-developed nations, Micro-Finance Institutions/NGOs are experts in identifying & screening potential borrowers. However they are mostly short of funds; the internet platform can bridge that gap through the MENA region, by rigorously working towards identifying the lenders.
How?
We plan to market our platform to attract the attention of corporations as well as individual lenders who can lend to the borrowers after studying their profiles on the platform. We realize that a close partnership between us & reliable Micro-Finance Institutions/NGOs can make the lending become more effective & more transparent.
Phase 2
After 1 year of operating the Internet Platform, we intend to raise an initial Fund of $5M, which will be dedicated to MSEs. This Fund will operate in 2 core activities:
- Private Equity Investments in MSEs
- Green Field Investments in MSEs
Private Equity Investments in MSEs
Within the Private Equity Investment we will make substantial, sometimes controlling, investments, generally in MSEs and typically with a view toward divesting in 3 to 5 years. The Company’s investment activities intend to contribute to the development of the infrastructure within the region and acts in different fields. Within the Private Equity investments we will apply a dual investment strategy where 50% of the allocated capital will be invested based on internal screening processes and 50% will be co-invested with Private Equity MSEs partners around the MENASA region.
Green Field Investments in MSEs
Through the Internet Platform exposure and an extensive network of partners, multiple green field and start up opportunities in MSEs will be presented to us. A first class team of researchers and analysts with the analytical screening capabilities needed is tasked to recommend the best investment targets. The research is fact based and must follow a predefined screening methodology. Every investment decision must be approved by the investment committee. Similar to the private equity strategy investment will be taken in a wide field of industries and markets.
Business Strategy
Business model for the internet platform (Year 1)
Our intention is to give borrowers the access to funds that are otherwise not accessible.
Once the lenders (Corporations & Individuals) decide on which Micro-Finance Institution they wish to lend to, they can remit the funds to our platform. We in turn will transfer the funds to our Microfinance Partners who will then release the funds to their borrowers.
The lenders will open a live account on the Internet Platform and they will be able to track the activity of their account every time they access the site.
The Micro-Finance loans are usually from 12 month tenor up to 24 month tenor. Once the loan is returned to the lenders, they can decide whether they intend to re-lend. The interest that is earned on the loan will be passed on to the lenders @ 2-3% per annum.
Business model for the incubator (Year 2)
We aim to become a world-class investment company in MSEs driven by clear values and principles, which focus on foresight, innovation and prudence. Independent of each business unit at our company (Private Equity or Green Field), every investment has to follow the investment manual which can be summarised within the following steps:
- Stage 1 – Screening focuses on assessment of the investment size of the prospect, the revenue multiple and returns, industry check, the development stage of the prospect and the potential exit options.
- Stage 2 – Evaluation analyses the prospect management, market, product and services, technical aspects and the financial opportunity.
- Stage 3- Due diligence focuses on developing full prospect profile in four segments; operational/strategic, financial, legal and technical.
- At Stage 4– Closing focuses on legal transaction and final financing structuring.
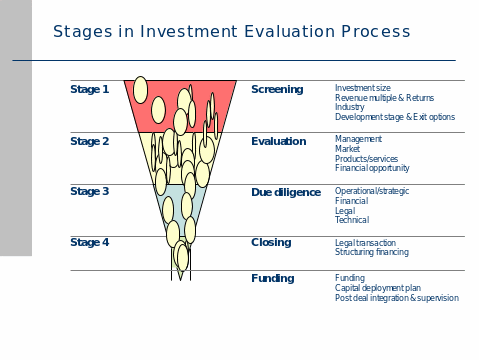
Both of our Business Units have slightly different screening processes which are being adapted to best practices. However, the main elements for screening, evaluation and approval always prevail.
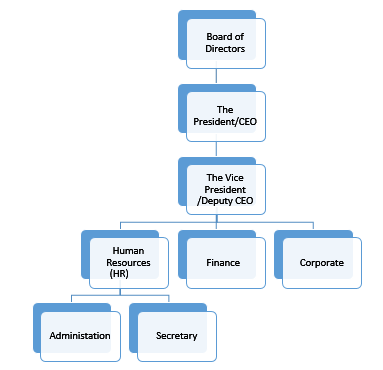
Organizational chart (Phase 1)
Internal Risk Management (Phase 2)
In consideration of the Company’s investments, we will install a comprehensive risk management process to monitor, evaluate and manage the principal risks assumed in conducting the Company’s activities. These risks include market, credit, and liquidity, operational, legal and reputational exposure (International Business Publications 2009).
We seek to be able to monitor and control our risk exposure through a variety of separate but complementary financial, credit, operational and legal reporting systems. It is indispensable to implement high priority, effective procedures for evaluating and managing the market, credit and other risks to which we –along with our partners- will be exposed. Due to the complexity of the structure and the desire to be fully operational in the shortest time possible, consideration could be given to partnerships with large international players, primarily during the initial phases of activity.
Nonetheless, the effectiveness of policies and procedures for managing risk exposure will never be, as for all existing Investment Companies, completely or accurately predicted or fully assured. For example, unexpectedly large or rapid movements or disruptions in one or more markets, or other unforeseen developments can have a material adverse effect on the result of operations and financial conditions. The consequences of these developments can include losses due to adverse changes in inventory values, decrease in the liquidity of trading positions, higher volatility in earnings, increases in credit risk to customers and counterparties and increases in general systemic risk.
To limit risk and to monitor adherence to best practices, we will institute the following committees and management groups.
Control, Milestones and Corrective Action
The most important aspect to open up the business in a new country is that the company should have an adequate control system in place. We are taking the period of 5 years as the milestone for microfinance firm. Let us analyze the milestones of the company in this regard.

The company should follow the milestones depicted in the chart above. The analysis points out an exciting prospect for microfinance in Lebanon. With proper corrective measures, company will be successful in Middle East.
Situational Analysis
The situational analysis is the snapshot study of what the company is facing regarding the external opportunities and obstacles. Here, the company is looking to open its business in Lebanon. Let us analyze the factors it has to face to set up a business there.
Macroeconomic Analysis
The Company is opening up its business in Lebanon. To start business in a completely new environment needs a complete analytical study of the place. For that purpose, the PESTEL analysis is the most suitable.
- Political- In comparison to the other countries in the Middle East, Lebanon is safe and stable. The Government encourages healthy competition in the industry. Another promising fact is that Middle East remains unaffected by terrorism or the country is surrounded by countries in loggerheads now and then( Spero and Hart 2008).
- Economic- The economy is one of the developing in the world. The country sits on a GDP of $ 30 million (as in 2009). Lebanon is a member of WTO. She has free trade agreements with almost every country in the Middle East region. There were worldwide fears that their currency would fall in the wake of global recession. But it managed to hold fort. It is a very stable currency raised in the backdrop of a stable economy. The economy is dominated by mining and agricultural activities, which traditionally have been stable sectors (Thatcher 2009).
- Social- The social system of Lebanon is quite similar to that of Saudi Arabia. The language of the people is also multicultural in nature, however Arabic is more common. In addition, the population of Lebanon is primarily a working force, which will serve a good market for microfinance firm.
- Technological- Lebanon, being one of the developing countries in the world is not technologically advanced. Most of the banks in the world have set up shop in Middle East and this has led to a new healthy environment for business. This in turn, has led to the development of technology to support these businesses.
- Environmental- Lebanon gives a lot of importance to preserving the flora and fauna of the country. This preserves the ecological balance of the system.
- Legal- The Lebanon legal system is differentiated into territorial systems, and one federal system. The legal system for business purpose is highly efficient and Ombudsman is there for any grievances in every state.
The Macroeconomic analysis shows that Lebanon is one of the sought after place to do business and it is a great opportunity for a microfinance company to start there. In the long-term, trends in the business environment continued favoring Microfinance business. With the continuation of globalization, there is the hope of growth for the institution. Middle East economies have continued growing, offering opportunities for the bank’s growth.
There was a continued gain in capital markets all over the world as a way of linking investors and issuers throughout the world. These were characteristics of a situation where constraints on capital limited traditional lending by banks. Asset investment continued growing while individuals planned for retirement. New wealth was also continually being created within the fast-developing economies. The microfinance sector’s positioning as a global business leader for the poor enabled it to exploit these opportunities and survive the hard (Ebony Magazine 2007)
Industry Analysis
Industry analysis is a way of analyzing the industry in which the company is working. The microfinance is working in an industry, which is prone to recession attacks.
The financial industry in Lebanon is devoid of any big player of the size of the proposed company. The market is largely unorganized and there are small companies scattered in different states. The best option to start in Lebanon in the microfinance business is to start organically because the market is devoid of too many big players and the competition is light. Lebanon is a small country and most of the companies are restricted to some urban only. The microfinance can open its operations in the Southwest coast because it is the economic center of the country. The main companies, which have a major percentage of organized sales, are
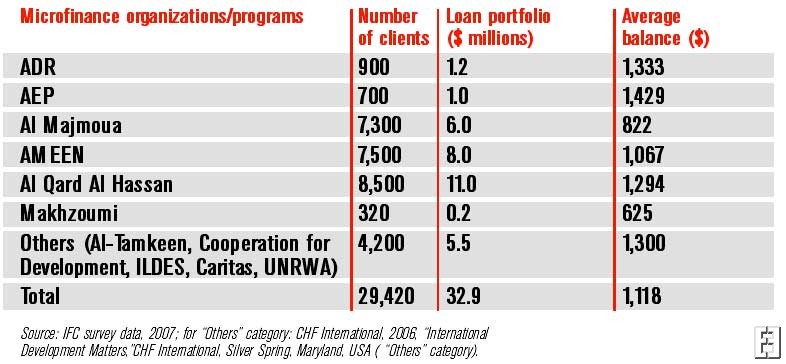
The leading players do not operate on a wide scale. The company has the expertise and experience on their side to develop their business. Their logistics, being much improved will be able to serve all over the country and even in the other countries of the Middle East. The PIMS (Profit Impact on Marketing Strategies) shows the company in good light.
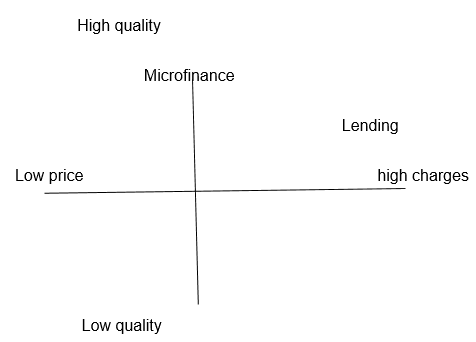
The map shows that microfinance company is the best in terms of quality and charges and has a high chance of success in Lebanon markets. From the discussions above, we can infer that company can start from scratch in Lebanon and capture the huge market there. The absence of any real competition here makes the job even easier. The company has to start operations in an area where demand prevails, e.g. Southwest coast. The expertise in mobilising funds and servicing and improved logistics will help the company to cater to the whole country in the days to come. For the moment, the company should look forward to open branches in city centres. The time span is five years during which the company will look to lead business in the Southwest and the northern region.
Porter’s Five Forces
Threat of New Entrants
- Economies of Scale: It is important to notice that the industry is growing to maturity and the company have to invest more to provide the market with innovation. If the number of companies is increased, the ratios would remain stable. Thus, as the industry is in its maturity stage and economies of scale have been reached. This proves that the capital has been more productive, allowing the industry to achieve economies of scale, making the barriers of entry high. The high degree of technology used in this industry also has an impact on lowering the cost. Thus, economies of scale exist, making the threat of new entrants low, making the industry attractive (Tong 2008).
- Brand Identity; Brand identity is not particularly important for this industry. The buyers are not concerned about brand identity; they are more concern about good quality along with good prices. Buyers are looking for products that will satisfy their needs more than looking for a specific brand. In conclusion, brand identity is not a barrier to entry, the threat of new entrants is high, and the industry is unattractive.
- Access to Distribution: New entrants into this industry are able to tap into these existing channels of distribution. This reduces the barriers to entry which increases the threat of new entrants and makes the industry unattractive.
- Expected Retaliation: There has been no evidence of retaliation in this industry against firms attempting to enter. Many firms have been acquired or have merged with larger companies but in most cases they have been to their benefit. This indicates low barriers to entry which increases the threat of new entrants. The industry is unattractive.
- Conclusion: In conclusion, the industry is attractive because of the economies of scale and absolute cost advantage. On the opposite, the industry is unattractive because of the non possibility to differentiate proprietary product, the non existence of brand identity and the easy access to distribution. According to the decision matrix, the industry is attractive because of the importance of the key factors and the high barriers to entry.
Suppliers
There are some other suppliers that are providing the industry with value added services, but that is not the trend for the industry. Many times, larger supplier firms acquire smaller firms if their prices are not competitive or if they are a threat to current business.
Supplier concentration, presence of substitute inputs, differentiation of inputs, importance of supplier volume, importance of volume to the supplier, impact of inputs on cost or differentiation, and the threat of forward or backward integration are not significantly applicable and can be ignored.
- Access to Capital: The profitability of this industry has been consistent over the past several years. This trend is expected to continue due to the growth rate of the industry. The growth of the industry will provide opportunities to increase profitability by expanding operations. Because the industry is profitable on average, this increases the possibility of being able to obtain debt financing on attractive terms. The low cost of debt financing for expansion makes the industry attractive.
- Conclusion: – The industry is attractive because the suppliers are not concentrated; the inputs have substitutes and can not be differentiated – which has a direct impact over the cost structure of the suppliers. This allows the industry to have power over its suppliers. Furthermore, there is no threat of forward or backward integration, and the easy access to capital and abundant labour are playing in favour of the industry.
Buyers
- Buyer Concentration vs. Industry Concentration: – No particular buyer has influence over the product or price and most follow similar channels of distribution. Therefore, the buyer is in a weakened position, shows low amounts of concentration, and has little power over the industry. To this point, the industry has power over the buyers and would be considered attractive.
- Buyer Switching Costs: – buyers experience little, if any, switching costs, therefore buyers of have power over the industry, making it unattractive.
- Buyer Information: – we behave as if we are a potential buyer and search for information on the Internet and requesting prices from companies. By doing so, the buyers can compare the competition’s offerings and choose the most favourable one.
- Threat of Backward Integration: – There is no threat of backward integration as the buyers have no will or strategy to acquire their supplier’s suppliers. Thus, the buyers are not in a power position, making the industry attractive.
- Pull through: – Considering that there is almost no advertising expense, we can conclude that there is no pull through within the industry. Since there is no pull through, the buyers have the power over the industry; therefore, the industry is unattractive.
- Brand Identity of Buyers: – The industry does not impact the brand identity of its buyers. He said that the buyers are looking for a combination of quality and prices in order to give the consumers the best product that meets their needs, and since their customers are not aware of the different brands available in the market, brand identity does not play a major role. Considering that there is no brand identity of buyers, the buyers have the power making the industry unattractive.
Substitute Products
The microfinance industry does not have any substitute products as they are the substitutes of the banking industry products.
Rivalry
Degree of Concentration and Balance among Competitors
Because 20% of firms control more than 80 percent of the market, concentration exists, increasing the chances of rivalry. Because these firms have market shares within 20 percentage points of one another, the industry is considered balanced, also increasing rivalry. In total, the industry is concentrated and balanced; therefore, making it unattractive.
Diversity among Competitors
The different firms within the industry have been using the same strategies. Most of the biggest firms are doing some strategic acquisitions in order to have access to new technology. While using diversification as a strategy, firms were able to purchase smaller companies in order to expand into different products.
Innovations and investments in R&D are also a major strategy being followed within the industry. Along with innovations, high quality and low prices are other strategies that firms are being forced to follow. Insurance companies have been forcing the companies to have lower prices (Donohue 2007).
Even tough the firms are following the same strategies, they offer different services. Taking that into consideration, the level of rivalry is low which makes the industry attractive for other firms to enter.
Market Analysis
The market in which the company operates is characterized by stable demand. The market structure in Lebanon is to the liking of the company as competition is low here and the market has tremendous growth potential.
The market does not have huge competition as such. There Again, these companies are mainly regional players.
The company has a wide range of products at its disposal. To set up a new business it will not have to devote time to develop the products. What will require time is to understand the market and to develop it.
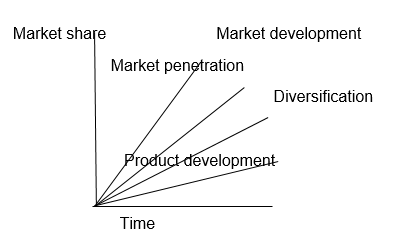
The above diagram on GAP analysis shows the factors of gaining market share against the period. For Sunlight, the two factors of market penetration and market development will take time.
Marketing Strategies
To operate in a new market and be successful needs a definite marketing strategy. Let us see what the microfinance can adopt to be successful in Lebanon.
The Ansoff’s Matrix gives us a clear picture of what needs to be done in a new market like Australia. (Ansoff’s Matrix n.d.)
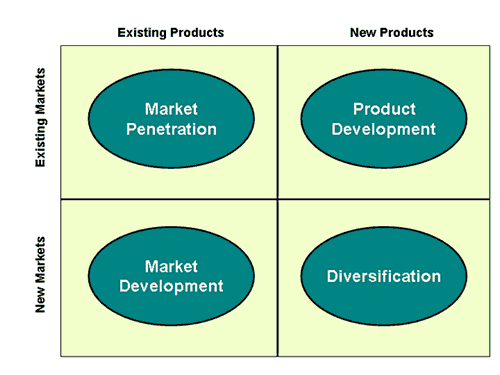
The microfinance is operating in a new market with the existing products. Therefore, it should devote its energy in the market development and penetration.
The market is very attractive in terms of growth and prospective customers. The initial period may be harder with the firm opening its activities.
With careful planning, the company may be a leader and should look forward to place itself at the top left corner where it may grow and penetrate. This is possible when the market is profitable and may yield high returns.
Segmentation, targeting and positioning
We can analyse the new market for the microfinance company by STP analysis. As the company is moving into a new market, it is essential that we do a STP analysis.
- Segmentation- the microfinance company offers financial products and solutions. These products will require differentiated marketing. The products cannot be pushed to all types of customers.
- Targeting- the microfinance company should target the small businessmen more as they are the ones to take up the services.
- Positioning- the microfinance company will be positioned as a premium service provider in financial services.
The microfinance company products are characterized by stable demand. Therefore, it does not follow the decline trend depicted in the PLC curve. With proper promotional and marketing strategies, the maturity period stretches to a long time.

Internal Analysis
The range of products, the improved logistics and the quality of service are its core competencies. The strategy of the microfinance company in respect of the Generic strategies may be discussed as follows-
- Cost leadership- the microfinance company has expertise in the field in which it is operating. The company with its essence in technology and expertise can deliver goods at a lower rate than the other companies in the industry.
- Differentiation- The Company can differentiate itself in terms of price or quality. The quality would be naturally higher than that of the others.
- Focus or Niche Strategy- The Company can opt for a niche strategy serving a group of customers in its formative years in Lebanon.
It may be noted that the microfinance company should opt for only one of these strategies. Otherwise, it would be stuck in the middle. For a company of the microfinance company’s stature it is the best to follow the Differentiation strategy.
The microfinance company has a developed value chain. The inbound logistics is taken care of at the Company headquarters and the outbound Logistics is seen over by the microfinance company Direct.
The 7S framework model if applied to the microfinance company gives a view that there is a high chance of the success. The system, skill, strategy of company is the best in the industry.
Employee Compensation
Employee compensation is one of the major determinants of HRM effectiveness in an organization. The compensation policy and the reward system that is followed by an organization are viewed by its employees as indicators of the management’s attitude and concern towards them. It is not just the compensation in Toto, but its fairness as perceived by the employees that determines the success of a compensation management system.
Hence, it is very important for the management to design and implement its compensation system with utmost care and tact. A good compensation system should be able to attract and retain employees, give them a fair deal, keep the organization competitive and motivate employees to perform their best. Once again, best performances of employees of an organization are definitely the proof of an effective HR function of the organization.
Conclusion
All the factors discussed above points out to the fact that a microfinance company will succeed in Lebanon. The strengths of the company are its core values, support system, logistics and the competencies. The weakness is that it will have to start from the scratch and build the business. The opportunities are the vast markets in the Middle East and Africa and the urge to grow. The competition is very less here and the market is virtually unorganized. Therefore, there are minimal threats here.
List of References
Ansoff’s Product Matrix (n.d.). Web.
Ball, L, 2008, Money, Banking, and Financial Markets, Worth Publishers, York.
Donohue, T, 2007, The Subprime Mortgage Crisis, US Chamber of Commerce, Washington DC.
Ebony Magazine, 2007, How the Mortgage Crisis Is Affecting You, November edition,Vol. 63, No. 1.
International Business Publications, 2009, European Banking System Handbook Vol. 1, International Business Publications, New York.
Model Use and Applicability (n.d.). Web.
Spero, E, & Hart, J, 2008, The Politics of International Economic Relations, Cengage Learning, New York.
Thatcher, M, 2009, Internationalization and Economic Institutions: Comparing European Experiences, Oxford University Press, New York.
The Product Life Cycle, (n.d.) Net MBA. Web.
Tong, H, 2008, Real Effects of the Subprime Mortgage Crisis: Is it a Demand or a Finance Shock? International Monetary Fund, Washington DC.