This research proposal, tackles the researcher’s interest in answering the research question of How to overcome the failure of knowledge Management implementation in Organizations. The proposal includes a brief introduction about the broad topic of the field, which is “Knowledge Management”. According to Gurteen, (1998) “Knowledge management is then defined as the coordinated, structured and supported use, creation and sharing of knowledge within an Organization” (p.45). Knowledge management is been pursued by most leading Organizations in order to achieve a world- class performance (Ruggles, 1997).
The proposal also includes a literature review of different scholars. It includes the perspectives of industrial organization, the voluntalistic view and different theory contributing to the failure in knowledge management. Accordingly, uncertainty is associated with Organization failure to predict the outcomes hence investing in wrong directions (Anderson & Tushman, 2001).
Mainly, the proposal covers the objectives of the research. Moreover, it contains the methodology that the researcher is suggesting to use while conducting the study. It will elaborate on the sampling techniques to be followed, the target technique, sampling technique, data analysis and data presentation. The research design to be used in this study will be descriptive survey and the sampling population size will be small in order to enhance the effectiveness of the study since it will be manageable and controllable.
The proposal also tackles some limitations and difficulties that are being faced while doing the research. The greatest advantage is that the research problem involves Organizations located here in the country.
Introduction to Knowledge Management
“Knowledge management is then defined as the coordinated, structured and supported use, creation and sharing of knowledge within an Organization” (Gurteen, 1998). Knowledge is dynamic and it management is critical in the competitive success of an Organization. The top management is involved in strategic perspective where Knowledge management is fundamental (Malhorta, 2002). They need to know how things work and how they should work to make improvements market share definitely grows with enhanced knowledge of both internal and external customers (Singh, 2011). Despite the fact that knowledge flows naturally, it should be managed implicitly to enhance change. KM is essential in all firms that operate in the 21st century because it necessitates viability of the form through its increased profitability.
Although knowledge is the most vital asset in the realization of set objectives, many leaders in businesses acknowledge that effective techniques are lacking. This includes the poor planning and management in the realization, distribution, Organization and creation of values, which require the use of appropriate intellectual assets and knowledge. Knowledge management is been pursued by most leading Organizations in order to achieve a world- class performance. This is so especially, where future plans are well stipulated and individual performance is measured hence, the achievements of long-term objectives (Ruggles, 1997).
The new forces of businesses today are demanding to Organizations to adopt additional knowledge management. This may include; the intensified information technology, rapid Organizational change, intensified knowledge on goods and services and high growth in Organizational scope to cater for changes in consumer demands and preferences. Thus, others can define knowledge management as an organized systematic procedure for attaining, communicating and organizing employee’s knowledge to allow for productivity and efficiency in usage within the organization (Davenport, Jarvenpaa, & Beers, 1996).
In addition, effective Organizations that are composed of complementary related entities put greater demands on the sharing of knowledge that is paramount to all (Ruggles, 1997). This will withstand in the event that Organization will increase continuously resources to be spent in consulting service of knowledge management. Hence, they can decide on either to utilize the already existing knowledge or to invest on a new knowledge. However, this is affected by inadequate sources of capital, lack in the willingness to learn, poor infrastructure in information technology and poor organizational structures (Lilleoere & Hansen, 2011).
Introduction to my research question
Due to the increasing failure of knowledge Management (KM) implementation in Organizations, as a researcher, I intend to find the ways appropriate in solving this. In the last few years, we have witnessed new knowledge management come and go. Majority of these projects have successful make Organization influence the benefits from their KM systems. Such achievements are enhanced by use-intensified technology. However, the failure of some technology should not be seen as drivers to KM in Organization as it only act as “catalyst” to either the failure or success. The lesson learnt here is that a balance is needed in technology, people, processes and instrumental contents used (Tsui, 2005).
During the 1990’s the technology used is discrete to the current one where to advance it there is change of systems, processes and may be even the location of the Organization. Operations in Organization were base on predictions, which is contrast to the current ones where everything is emphasized on adaptation and precognition. Everything including goals, processes, products, purposes and administration is reviewed and redefined in order to adapt to the new requirements. The study will seek to highlight the contribution of different approaches and their contributions to the failures being experienced in different Organization. It will concentrate on the models either new or old, tools, strategic thinking, technologies deployment, Organization structures and the attitude to knowledge management (Davenport, Jarvenpaa, & Beers, 1996; D’Aveni, 1989).
Hypotheses
This study seeks to fulfill three hypotheses as indicated below:
- Hypothesis 1: Knowledge Management failure can leave a positive effect on Organizations.
- Hypothesis 2: The size of the firm and the organizational culture are positively related with implementation of knowledge management in an organization.
- Hypothesis 3: Knowledge Sharing Culture can lower the rate of KM failure in organizations.
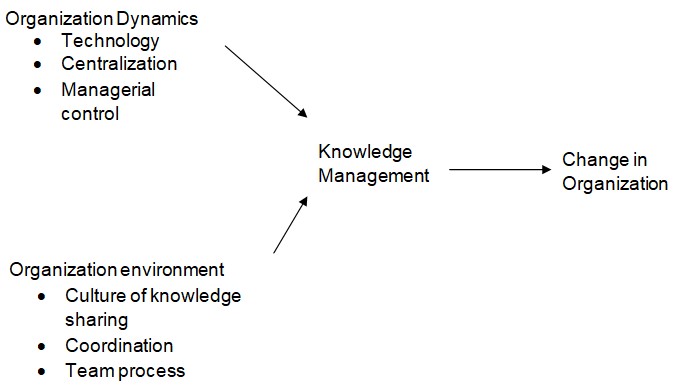
A structure showing knowledge management in organization change
The study will have different variables, which includes; knowledge management as a dependent variable, organization as an independent variables and culture, technology, process and people as key moderators. It is perceived that successful organization implement knowledge management, I will seek to identify whether there exist a relationship between success and knowledge implementation. Knowledge management to be successful with a support from information technology there should be a balance between process, leadership and people management (Amburgey & Hayagreeva, 1996). Knowledge management should be enhanced by cultural support, where Organizations will invent environmental conditions that will lead to increased desire by employees for knowledge. Assumption to this is that employee has the willingness to share knowledge to enhance its continuity in the organization. The hypothesis will statistically be tested.
Research Question and Motivation
Researchers found out that approximately 50% to 70% of knowledge management initiatives and projects fail to meet its objectives (Ambrosio, 2000). There are so many reasons that scholars have pointed out of why does knowledge management projects fail in Organizations which is tackled in the literature review section of this proposal. Therefore, as a researcher I am interested to come up with solutions to lower the knowledge management failure in Organizations. The study should answer the following research questions;
- Does insufficient knowledge awareness leads to failure of knowledge management implementation in Organizations?
- How does the liability of newness contribute to failure of KM?
- Is there a there a link between the Organization size, culture and failure of knowledge management implementation in Organization.
- Does industrial life cycle theory and awareness contributes to failure of knowledge management implementation in Organizations.
Literature Review
According to the industrial Organization perspectives, knowledge management is fixed in Organizations. Thus, the external forces bring up failures. These are created by a revolutionary change in technology innovations and increasing Organization order that lead to new entrants to share the market (Scott, 1992; Nelson, 1995). Since the new entrants will adapt quickly to changing technology to meet the demand, the incumbent will be forced out of the market hence the failure in the knowledge management (Baum, 1996). The entrants will initiate competence in the production and consumer satisfaction causing the incumbent to be discontinued.
There are various three assumptions underlying the failure in knowledge management by Organization. First, constraints and pressure in Organization is assumed to be externally influenced. Secondly, Organizations are perceived to be using similar strategies. Third, decision makers in Organization are assumed rational and that they make decision in the interest of it (Sheppard, 1995).
There are other suggestion that demand structures cases the knowledge management failure due to consumer changes in tastes and preferences, brand change by core customers, recurring demand decline and strategic competition from new and existing rivals (Sheppard, 1995). In addition, process and product innovations due to technological uncertainty lead to failure of knowledge management (Slater & Nayver, 1994). Uncertainty is associated with Organization failure to predict the outcomes hence investing in wrong directions (Anderson & Tushman, 2001)
There exists a positive correlation relationship between failure in knowledge management and resources availability being the complexity in the environment (Anderson & Tushman, 2001). Organizational complexity can be termed as the intricate linkages within the Organization and outer bodies such as other institutions, stakeholders and competitors (Dess & Beard, 1984).
The other school of thought views failure of knowledge management implementation in Organization in a voluntaristic approach (Hambrick and Mason, 1984). This approach assumes that managers are key or principal decision makers in the organization and that they are rational actors who are powerful. Thus, models within the organization and its environment influence actions from the mangers. This is constrained by the powers of the managers, their commitment and implementation capabilities (Mone, McKinley, and Barker, 1998). Failure of KM is highly caused by the management decisions and actions. According to Kroll, Toomb & Wright (2000), the arrogant and self-confidence managers lead to KM failure because they refuse to listen to advices from other people. Management changes can lead to failure or success where the successors adopt new ways (Malhotra, Gallettra & Katz, 2003).
To illustrate the failure of knowledge management implementation in Organization, I will center on the four theories developed by different scholars. First, the Theory of Group thinking, which articulates that knowledge management in Organization, is dependent on the number of people working in the Organization (Turner & Pratkanis, 1998). The more the number the more it is easy to implement the knowledge in the Organization as decision will be made by all. Managers can make decision that adversely affects the Organization if they do not actively listen to the advice from the other key decision makers (Arling, 2010). Second is the theory of upper echelon where decision on knowledge management are made and influence by key decision makers in the Organization. Research has showed that managers who are serving a long tenure tend implement knowledge less as there adopt in the systems (Barnett, Greve, & Park, 1994).
The third theory is the feedback of success. This is from the point of view that the success curse is failure. Most Organization has knowledge management implemented to the extent that they succeed (Miner, Kim, and Haunschild, 1999). At this angle, they are more conversant with the appropriate knowledge to use. The break even of the knowledge implementation in the Organization is experience if the management becomes arrogant to the employees. Thus cautious is needed in order to maintain the same growth of the knowledge management. The last one is the theory of threat rigidity effect. Under this, most Organization wishes is to retain the status quo of the knowledge management. However, manager’s attention can be diverted if a crisis happens, where the manager would consider the most relevant information concerning the organization. Noise created by the crisis is considered after looking at the environmental source of it and it effect (D’Aveni, 1989). Thus, there is little implementation of the knowledge to the Organization.
Knowledge is supposed to enhance smooth cooperation between leaders in the Organization, People involved in the factors of production and process of satisfaction to all including internal and external customers (Scott, 1992). The process in knowledge management should encompass support in information technology, organization structure and culture as well as the monitoring done for improvement. It should also focus on the best performance, that is, proper alliance, advanced programs for learning and training, effective organization and perceived culture change in the organization. More relevantly, employees should have mentors who instill a virtue of teamwork, sharing and trust. Hence, the need to have good communication within the organization, compliance measures to risk, efficient and advanced organization structures (Baum, 1996).
According to Malhorta, there is a gap between relevant knowledge and information technology, especially that which is disruptive (2002). Slater & Narver, (1994) shows that Organization are willing and wishing to be digitalized where delivery of service to prospective customer is possible for anything at any place in a given time duration. They have shown also that choosing technology careful can lead to success in organization prospects. However, failure in the same organization can be caused by the use of the most sophisticated technology. Thus, the study intends to show the correlation between the two knowledge management and organizational failure.
There is a gap in strategic execution and knowledge application. From the above definitions of knowledge management, different scholars have come up with different definitions without reaching into a common consensus of the right definition. According to Damodaran & Olphert (2000), scholars ought to come with the specific explanation of whether it is strategy pull or technology push that leads to organization failure. This can be analyzed by looking at the inputs in the product, processing and the expected outcome of the same. The findings of the study will help to bring some light on this looking at the variables including dependent, independent and moderators in the questionnaire. It will show whether a relationship exist.
More so, insufficiencies in capital have led to poor infrastructure in Organization’s information technology as explained by Chua & Lam, 2005). In the industry, capital is power and key in game theory. This is the main contributor to failure of knowledge management in different Organization and depends on the size of the Organization and the market share. Malhotra, Gallettra & Katz, (2003) shown that new entrants and small Organization fails in KM since they are unable to raise sufficient capital. Thus, the study will show the relationship between the variables with respect to KM to enable management team contribute fully. I will look at all the moderators of KM and their relationship to enable come with an appropriate conclusion.
Discussion
There are various reasons that have led to failure by Organization in the implementation of knowledge which are subjected by both internal and external factors. Different scholars have came up with definition of Organization failure being; Organizational bankruptcy, exit, downsizing, mortality, declining, death and retrenchment. (Davenport, Jarvenpaa, & Beers, 1996) I believe that each has a proportion in the failure of different Organization. Failure can however be defined as, “deterioration in an Organization’s adaptation to its micro niche and the associated reduction of resources within the Organization” (Tsui, 2005).
Accordingly, there are two assumptions to be noted in the definition failure. First, it is assumed that failure leads to negative consequences even though there are positive effects where Organizations learn from a fault. Second, there is no specification for the causes of failure. Hence, it be caused by environmental or Organization factor (Miner, Kim & Haunschild, 1999). Thus, knowledge management should be examined as a learning process, which is systematic and flexible in focusing Organization’s wants. It includes subjects associated to implementation, development and infrastructure in an Organization.
The failure of knowledge Management implementation in Organizations is brought about by the lack of key aspects in knowledge management being the adaptability, integrative and flexibility. Three factors attributed to the failure of implementation of knowledge management in organizations include culture, perception and awareness. If there is deficiency awareness of knowledge management in Organization then failure will felt. Researches has showed that majority of staffs do not have right information on the availability of knowledge within the Organization (Singh, 2011). It is thus suggested that there should easy access and availability of knowledge to the right people at the needed moment. For this to hold, the top managers should actively influence the employees to access knowledge and use it appropriately (Nonaka &Konno, 1998).
The perception of the Organization towards knowledge management can lead to failure or success. More so, the culture of knowledge management by Organization can lead to its failure (Davenport, Jarvenpaa & Beers, 1996). It should be equally shared and freely available to ensure that efficiency and implementation is adhered. Management panel have an advanced and a first hand to knowledge as compared to their juniors. Their willingness, commitment and readiness to effect change highly affect the growth of the Organization (Tsai & Lee, 2006).
Insufficient time during the implementation of KM in organization is another factor that has led to failure. Most Organization has a culture of their performance and their way of doing things. They have to set targets and Organization strategies to meet them. In some, evaluation and monitoring is done to ensure workers meet their expectations (Guptara, 1999). It is the tight timetable and strategic planning that lead to a failure in knowledge management since amplifiers to this are discouraged. Thus, Organization that have supported the sharing of ideas through trainings, enhanced teamwork, creation of trust and sharing the vision have ended up being giants in the market.
There is cautionary approach in knowledge sharing and investing new idea. To maintain the stiff competition, majority of the Organization considers knowledge as an asset, which is not to be shared by other competitors. Similarly, Organizations have adapted the contractual employment where employees will be under an oath of secrecy and confidentiality. The advancement of knowledge has seen growth in ideas and most Organization tend to move slowly because the fear being the leader in the market. Being a follow in that case has disadvantage that sees Organization into losses due to the curse of not investing when there is a chance (Damodaran & Olphert, 2000).
Lastly is the lack of managerial support. Knowledge management is directly related to management of the Organization, especially where managers are key decision makers. Most failure are contributed by arrogant and non visionary leaders who refuses to take advise from other people or are not ready to be risk takers. Management of various Organizations should lead by examples supporting knowledge sharing and recognizing their employee’s effort (Bantel & Jackson, 1989). The motivation factors to employees enhance the willingness to implement and advance knowledge hence the company benefits. This will see the aging employees pass relevant knowledge to the upcoming generation.
Research Methodology
The methodology of research will cover the processes and procedures of data collection and analysis to be followed. It will elaborate on the sampling techniques to be followed, the target technique, sampling technique, data analysis and data presentation. The research will use both primary and secondary data sources. The primary data will entail observation and face-to-face interviews, which will use a combination of semi structured and unstructured forms of questions in the form an interview guide that will contain the pertinent issues under scrutiny on knowledge management. Secondary data will entail library searches, internet searches, books and journals (Dess & Beard, 1984). The research will therefore be quantitative so that the study can generate numerical data for statistical and deductive analysis. This methodology is also the most ideal to test or verify the theory (Freeman, Carroll & Hannan 73).
The unit of analysis will be team of management, organization staff and the team of information support systems. Teams of management are those responsible in planning the strategies for the organization. All decision of the organization comes from them. Teams of information support systems are staffs responsible for supporting and implementing the knowledge management systems. The implement what has been passed by managers and ensue that it works to the optimization. Finally, the organization staffs directly support knowledge management at it implementation. They include, customer service staff, research specialists, marketers, engineers and other supportive staff within an organization (Damodaran & Olphert, 2000).
Study Design
This research will take a deductive approach that will entail the researcher working from a known hypothesis. Thus, the study takes a top down approach as compared to the inductive approach that takes an up down strategy. To realize the use deductive approach, quantitative tools of collective and analyzing data like questionnaires were used. Quantitative tools were preferred as compared to qualitative tools because they enable the researcher to come up with facts. This is unlike qualitative tools that first come up with an abstract idea that is followed by creation of theories and concepts about the idea. The data in quantitative research is hard and reliable as compared with qualitative research where data that is rich and deep (Quinn 170).
This type of research is positivist. This is because it is dealing with facts that are positive and phenomenon that can be observed. The goal of the study is to explain the failure of knowledge management implementation in organizing which is not only descriptive but also explanatory and predictive. Thus, the study will also be quantitative since it will draw conclusions on measurable evidence.
Research validity
Validity is the extent to which a given instrument is designed to measure. The validity of a study can vary in different samples used. In one situation, a study can be valid while in other scenarios, it may not. The validity of a study is measured by what the study claims to and the availability of logical errors in the conclusions drawn from the study.
According to scholars, internal validity is the extent to which it is possible to make independent reference from the findings of a study especially if the independent variable influences the dependent variable. In the study, organization structures and other moderators influence knowledge management. Internal validity will be strong since the study will include a survey in different organization in order to test hypothesis, thus it will be experimented. In addition to this, random sampling of the sample will be efficient is ensuring a strong internal validity.
On the other hand, external validity is the general application of the findings of the study to other settings. This might not exist in the study because results may change given the same circumstance under a different organizational setting. It is my assumption that information from different respondents will be similar under a different setting. The sampling unit will be divided into different strata in different departments where it will be easy to detect logical errors.
The measurement of the theoretical construct of the study will be measured using construct validity while convergent validity makes comparison between the scores that are obtained from different instruments that are used in the study. Unlike convergent validity, divergent validity compares the instruments used in the study that measure opposite concepts. Given the above validity and reliability, the study is valid and reliable for use by any person or organization (Quinn, 179).
Thus, I am expecting to have a validity of level one after collecting data and following the right procedure. This will be so after collecting data in a random method, fully covering the potential respondents and ensuring that they answer questions after fully understanding it.
Research Reliability
The performance of any research tool is usually measured in terms of reliability, validity and sensitivity as well as specificity. These concepts will also be applied in this study by the researcher to ascertain the reliability of the study. Reliability is the ability by which a study is able to produce results that are consistent and stable over a given period of time and given similar circumstances. Various types of validities exist that include internal validity and external validity. Internal validity relates to the correlation between items when measured on a scale. Whenever a study provides the same results after the application of two different measures, the outcome is said to be equivalent (Yin 99).
To make sure that the research is reliable, the questionnaire used will be similar and biasness will be reduced by ensuring that right wordings are read accordingly. Proper sampling and analysis techniques will be followed to the conclusion. I will also ensure that sub population of the sample will be equal and that all questionnaires will be administered in following the timing schedule where organizations close to each other are interviewed the same day.
Type of research designs
Deductive (Theory testing empirical research)
The research design will use survey where questionnaire will be used to collect data needed on the study. It will comprise a control systematic variance in order to ensure there is internal validity between organizational strategy, conflict, leadership style and power. It has the advantage of easy in administration, can be statistically analyzed, flexibility and standardized. More so, it can be used to collect factual data, measure internal like attitudes, beliefs, values and perception of events, objects or attitudes. It is however faced with the problem of biasness since the interviewer may influence the respondent by directing the answer, that is, influencing on what he or she wishes to answer. The research design is a cross-sectional research design since is comprises of different department and different organization under a different setting. Results from the five different organizations will be analyzed and a finding on the relation between the variables will be established.
The scale of measurement is interval. This is because there is the use of questionnaire where the study is quantitatively designed and there is the use of likert scale of measurements. It can also be used to measure the modes and the attitudes of the respondents. In addition, the findings can be statistically measured and determined.
Focus group discussion
Focus group will be formed in each organization, which will comprise of six respondents. It will assist in defining the problem more precisely, obtaining more relevant information and testing the accuracy of information provided. The discussion will also be useful in formulating a questionnaire for the consumer.
Study Population and Sampling
The study population will involve organizations having different departments and sectors. The subjects of the study will be drawn from this population. The survey will target five government organizations in the United Arab Emirates, which are, Dubai Municipality, Dubai Police, Dubai Water and Electricity Authority, Dubai Transport and Road Authority and Dubai Courts. This size will be valid for purposes of this study and due to resource constraints. Stratified random sampling will be used to select categories from a complete list of the target population. The sample will be divided into “strata” with different of them forming stratum. Three hundred and sixty respondents will be interviewed. Each stratum will have a distinct difference since it would come from different departments in different organization. This size will enhance the effectiveness of the study since it will be manageable and controllable. This size will also be cost effective and above all, will assist in quality control since an equal chance will be provided to every member in the population to be included in the study.
Data collection methods and instruments
Primary Data
This will entail mainly face to face interviews through a combination of semi structured and unstructured forms of questions with the use of an interview guide and organization will be selected on a stratified random sampling. This will also ensure that the interviews are not restrictive. The study will use a detailed administered questionnaire in which research instrument will be constructed using open and closed ended questions. Semi- structured questions are open and elicit an individual’s response while unstructured questions provide the researcher with an opportunity to ask broad questions. Questionnaire will be formulated to check KM components including knowledge responsiveness, dissemination and acquisition. This provides a high degree of objectivity, probing and clarification. Unstructured interviews will also enhance the study because the interview will be directed by the relevant questions in the guide. The questionnaire will be piloted before being implemented to re-examine the research instruments from the additional feedback about the questionnaire instrument (Sheppard, 1995).
A letter of identification will be prepared to serve as an introductory document when conducting the research. This will reduce suspicion among the officers who will be assured of strict confidentiality of the information to be provided. As a researcher, I will continuously monitor the progress made in answering the questions and giving clarification when required.
Face to Face Interviews
The research will be conducted through open interviews with use of interview guides on relevant issues concerning the research problem. The interviews will therefore be focused and will combine semi structured and unstructured forms of questions. This will be important, as it will help the researcher interact closely with the respondents and get as much information as needed to enhance the research. The down side is that a lot of time will be required in this exercise but the researcher will overcome this through proper planning.
Observation
Observation will be used as a research tool to collect supplementary data. This will be through the technique of participant observation since the researcher will participate with the subjects. This will be through hearing, seeing, testing and personal intuition. This will avoid bias, will give the researcher the opportunity of observing natural behavior and it can also be carried out anytime. Observations will be recorded on notebooks and will be used to supplement the findings of the descriptive statistics.
Secondary Data
This data will be obtained through analysis and review of books, journals, papers, magazines and previous lectures on knowledge management in Organization implementation. We shall also rely on the past surveys and observation within the scope of the study.
Questionnaire Design
The questions that are commonly used in surveys and questionnaires are usually open ended, closed-ended questions and likert scales. Open ended questions do not always give answers that a respondent can choose from but allow participants to answer freely. On the other hand, closed ended questions provide answers for the respondent to choose from. Likert scale questions requests respondents to respond to the question along a given continuum from the given responses.
The questionnaire will be used to test validity of the research hypotheses and model. It will be inclusive of variables like technology, organization process, knowledge management, organization structure, organization culture and respondent background information. In some instances, dependent and independent variables will be assessed using likert scale that would array from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree”. The questionnaire to be used in this study will contain questions having process, people and leadership structures. The development of the questionnaire will consider questions that will give rise to information that is relevant to the importance of strategic innovation in Tata and Jaguar organizations.
Data analysis methods
The information collected will be analyzed in numerical and descriptive perspectives since the questionnaire was quantitatively and qualitatively designed. Scholars will also undertake an analysis of the secondary data through a review of published books, journals and articles who have examined the research problem before. This process will help in thorough enumeration of the research and presentation of the findings. Before analysis, the data collected will be checked for completeness and consistency by editing, coding, classification and tabulation.
Analysis will be carried out with the help of SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Scientists) and Stata. The two are programs that assist in data entry and analysis of the results. All statistical measurements including the correlation are automatic calculated. They ease the load of manually calculating these measurements. The Descriptive statistics such as frequency and percentages will used to analyze the data in some section. The results will then be presented in form of charts and tables.
Factor analysis will be used to analyze the various variables like mean and standard deviation. Factor analysis is a method for decomposing information in a set of variables for meaningful factors that are underlying latent dimensions of the problem. It is used to analyze variables in the questionnaire and check the variance with their likelihood effect on the data. Regression analysis was also be used to come up with the model expressing the relationship between the dependent variable and independent variables. Thus, it will help in the hypothesis in the study. All will be calculated using SPSS.
Data Constraints
The research problem is one that has not been entirely explored especially in the country owing partly to the unavailability of data. I hope to overcome this hurdle in the course of the research once authority is obtained to access the relevant data. My strategy is to conduct face to face interviews and use observation as a method of data collection. The greatest advantage is that the research problem involves Organizations located here in the country and that I happen to work in one of the subject organization.
Scope of Study
The research will be undertaken in the entire country. However, Field Officers will travel countrywide to seek findings through interviews with different Organization and citizens. Face to face, interviews will also be conducted with government officials, members of the civil society and humanitarian agencies. The data collection process is envisaged to cover three months.
Mechanisms to assure the quality of the study
The quality of data will be assured by the use of survey as a type of research design. Observation will give the researcher an opportunity of observing natural behavior and it can be carried out anytime hence reducing biasness. Raw data will be analyzed and publication done after validating the results; it will be stored in digital libraries where information is archived in document form. To increase the validity of the study, stratified random selection method for the respondents will be used (Burns, Acar & Datta, 2011).
The method of Stratified random method will be the best in this study because there are distinct numbers of categories from the population ranging from municipality, police, water and electricity authority, transport and roads authority as well as courts in Dubai. All the organizations deal with different goods and services with a common interest of consumers’ satisfaction. The population sample will be divided into “strata” with different of them forming stratum with each stratum having a distinct difference since it would come from different departments in different organization. Thus, stratum will enhance the effectiveness of the study since it will be manageable and controllable. This size will also be cost effective and above all, will assist in quality control since an equal chance will be provided to every member in the population to be included in the study. The method will also ensure that sampling units will be utilized differently depending on the subpopulation. More so, it will give room for efficiently focusing by ensuring that planning is done to the right sub population and unwanted ones being eliminated.
Study period
The table below shows the duration of time each activity should take.
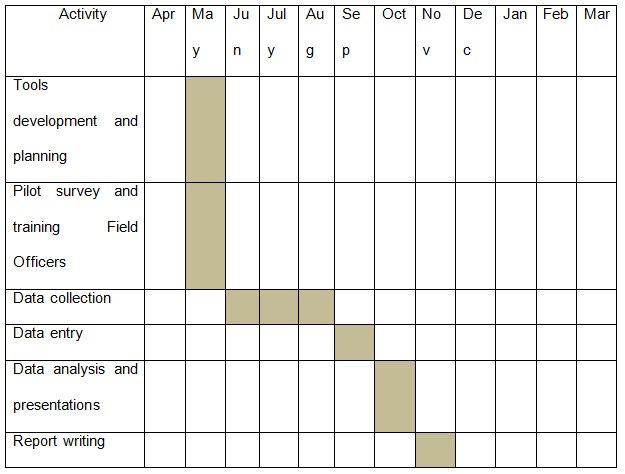
The first month will see the questionnaire been piloted before implementation to re-examine the research instruments/gains from the additional feedback about the questionnaire instrument. This will give sufficient time to re-evaluate the research design. After this, data collection is expected to take three months while data entry to take a month. The data analysis and presentation will thereafter take place. It is after presentation that report will be written on the findings of the survey. Finally, the results will be published and proper storage will take place.
Participants in the study
The study will be enhanced with proper coordination and support of the parties involved. The project will have two principal advisors and one expert from KM field. The principal advisors will guide me as a researcher in order to reach my goals and objectives.
Research contribution
The study provides various aspects that when followed would lead to growth and advancement of the existing knowledge. It acknowledges the existence of failure and explains different ways of overcoming it. After carrying out the survey, it will be possible to prove mathematically the validity of the study. Thus, it will show whether failure is contributed by lack of culture awareness, perception of Organization at its employees, poor implementation of policies, lack of objectives definition and the use of poor strategies. Hence, the study will assist in knowledge implementation, advancement, sharing and ownership (Sheppard, 1995).
The study will advocate for knowledge sharing, that is, directly sharing what is known to one to best known by the other. To maintain the stiff competition, majority of the Organization considers knowledge as an asset, which is not to be shared by other competitors. Organizations have adapted the contractual employment where employees will be under an oath of secrecy and confidentiality. The advancement of knowledge has seen growth in ideas and most Organization tend to move slowly because the fear being the leader in the market. The study will try to advocate for a common ground in order to advance the existing knowledge and reduce the cost of running organization due to the advantages of economies of scale in the use of similar knowledge management (Nonaka & Konno, 1998).
More so, the study will try to reduce the perceived image and advocate for knowledge sharing. Researches have shown that majority of the workers fear to ask or add knowledge because it might be perceived as an inadequacy sign. This is mostly where distillation of knowledge in some organization is minimal. A case especially where organizational mechanism is ineffective from discussing and debriefs. Thus, the study will tend to show the importance of knowledge sharing and dispersion. Hence, Organizations will improvise environmental conditions that will lead to increased desire by employees for knowledge.
Ethical considerations
In order to carry out the research, the researcher will ensure that a certain research philosophy framework is followed throughout the process. In particular; as the study made use of human participants for data collection purposes, ethical considerations will be taken into account. This is in line with the researcher’s aim of carrying out the entire process ethically. Among the significant ethical issues that need attention included respondents consent, confidentiality and data protection.
Implications
The expected output is that there will be a reduced failure of knowledge Management implementation in Organizations. This will be made possible if knowledge management is viewed in three major areas: total representation, acquisition and recycle (Amburgey & Hayagreeva, 1996).
There are various benefits of knowledge management implementation in Organizations being cost and time saving in term of efficiency. Researches have reported that Organizations become more competitive if there is efficiency in knowledge management that lead to development in the internal capabilities (Arling, 2010). It shows that knowledge management leads to satisfaction to customers, maximum utilization of resources and advancement of new and existing business ideas. Most Organization look at knowledge management through information technology while only facilitates quick sharing of knowledge. There is the need to look at the other facilitators of knowledge management like video capturing, observation and gossips (Slater &Narver, 1994).
Conclusion: Identification of limitations
There were some boundaries found during the investigation. In fact, failure of knowledge management implementation in Organization is contributed by various factors. They include the following:
There is generalization of the study, which is based on theoretical approaches. Failure of knowledge management implementation in organization is theoretically explained and identified which might be different if the questionnaires are filled and analyzed. Validity depends mostly on data collected and analysis done which might be different depending on the ground of interviewing and influence on the respondents. This will be overcome by finally having a report and findings on the project, which will later be published. Hence, it will be effective in testing the identified hypothesis in the study, which will lead to the generalization of the theories (Storey & Barnett, 2000).
It is also difficult to measure the knowledge and its management. Indentifying and investigating the knowledge management on the development of product is difficult. There is no standard measurement in the different organization depending on the differential in the services or products being offered (Barnett, Greve & Park, 1994). The study however will measure this by looking at the impact in the resources, people, growth of the organization and budget of the organization. These factors are easier to quantify leading to an assumption that it effects is brought by failure in the knowledge development.
The presence of supportive and strong top management, who are listening without actively involving themselves with ongoing projects, is a limitation to failure of knowledge management. Managers with other supportive teams within the organization ensure that knowledge is availed to the right person at the right time. Any disintegration becomes a challenge to the failure of knowledge implementation in organization. Thus, for KM to be effective, cultural support is important as it will instill a culture of helping and trusting information availed other employee (Freeman, Carroll & Hannan 73).
Recommendations
Some recommendations and solutions would improve the implementation of knowledge management in Organizations. These include:
The creation of knowledge repositories, where knowledge can be kept to be viewed by many within a given the Organization. Example is the use of digital libraries where information is archived in document form and can easily be viewed. This ensures that successors have the appropriate knowledge to run the Organization in the right direction (Collinson & Wilson, 2011). There are various number of knowledge management project that are to be implemented to ensure easy access. The advancing information technology can be properly used to knowledge easily and efficiently (Chua & Lam, 2005). The motivation factors to employees enhance the willingness to implement and advance knowledge hence the company benefits. This will see the aging employees pass relevant knowledge to the upcoming generation.
Knowledge use should be enhanced by cultural support, where Organizations will improvise environmental conditions that will lead to increased desire by employees for knowledge. Researches have reported that successful Organization support knowledge management by ensuring there is continuity in application (Chen, 2010; Wang & Chang, 2007). Such will be enhanced if there are set targets to be achieved, adapting decision-making by participative model, increasing employee’s incentives and increasing commitment and having committed management. Thus, cultural factors are effective in achieving KM implementation in organizations, which includes the results oriented, process, recycling, job security and privacy security.
Organization should adapt long-term objectives and avoid short term planning, which are expensive and inconsistency with the modern developments. For proper knowledge management and implementation, a correlation has to exist between planning and management strategies (Gal, 2004; Storey & Barnett, 2000). However, the strategies are to be consumer satisfactory in efficiency and standards, process oriented and good leadership.
More so, knowledge should be managed like an asset in the Organization. According to the research it showed that only 4% of all the Organizations that acknowledge and are able to calculate it in measurements like other traditional assets. It is thus calculated as an intangible asset within an Organization leading to directing other resources toward it. Knowledge management is been pursued by most leading Organizations in order to achieve a world- class performance. This is so especially, where future plans are well stipulated and individual performance is measured hence, the achievements of long-term objectives (Ruggles, 1997).
Finally, for knowledge management to be successful with a support from information technology there should be a balance between process, leadership and people management (Amburgey & Hayagreeva, 1996). The three oversee proper and effective implementation of knowledge management leading to customer satisfaction, maximum utilization of resources and advancement of new business ideas (Chen, 2010).
Conclusion
In this global era, for organization to be competitive, they should support KM initiatives in management in order to enhance development competence. The study inspects factors leading to success and those contributing to failure of KM in organizations. Successful KM has led to growth in resources especially those attached to the projects like budget, people and processes. It has also increased projects survival where projects can be viewed as organizational efforts and not individual effort. Hence project can easily survive without support from particular individual (Storey & Barnett, 2000). The study intends to show the benefits of awareness of knowledge management within the departments by emphasizing integration between the teams. Knowledge sharing and retention in organization is a serious issue, especially in organizations having decentralized structures.
From the study, then main factors of failures in knowledge management implementation in organization is the lack of support and commitment by top managers, poor and traditional planning, culture within the organization, resistance from employees, lack of coordination between employees and team leaders and financial constraints. The manager should view KM as ways of understanding, focusing and managing systems explicitly in order to premeditate knowledge building, application and renewal. With proper planning, knowledge can be created, transferred and captured if organizations pursue incentives and efforts that are planned well. Management team that is strong and supportive will be able to encounter employee’s resistance on KM (Barnett, Greve & Park, 1994).
It is perceived that successful organization implement knowledge management, I will seek to identify whether there exist a relationship between success and knowledge implementation. Knowledge management to be successful with a support from information technology there should be a balance between process, leadership and people management (Amburgey & Hayagreeva, 1996). Knowledge management should be enhanced by cultural support, where Organizations will invent environmental conditions that will lead to increased desire by employees for knowledge.
The top management should thus view knowledge manager as a system. They should adapt the new technology where knowledge is converted into products and services that are profitable to organization. This would be by disseminating, acquiring and converting knowledge in the right manner. They can decide on either to utilize the already existing knowledge or to invest on a new knowledge. However, this is affected by inadequate sources of capital, lack in the willingness to learn, poor infrastructure in information technology and poor organizational structures
Finally, for knowledge management to be effective everything including goals, process, products, purposes and administration should be reviewed and redefined in order to adapt to the new requirements. The study has highlighted the contribution of different approaches and their contributions to the failures being experienced in different Organization (Chen, 2010; Wang & Chang, 2007). It has also concentrated on the models either new or old, tools, strategic thinking, technologies deployment, Organization structures and the attitude to knowledge management.
References
Agarwal, R. Echambadi, R. & Sarkar, M.B. (2002). The Conditioning Effect of Time on Firm Survival: A Life Cycle Approach. Academy of Management Journal, 45(8), pp. 971-994.
Ambrosio, J. (2000). ‘Knowledge Management Mistakes’, Computerworld. 44.
Amburgey, T.L. & Hayagreeva, R. (1996). Organizational Ecology: Past, Present, and Future Directions. Academy of Management Journal, 39(5), pp. 1265–1286.
Anderson, P. & Tushman, M. (2001). Organizational Environments and Industry Exit: The Effects of Uncertainty, Munificence and Complexity. Industrial and Corporate Change. 10, pp. 675-711.
Arling, P. (2010). Facilitating new knowledge creation and obtaining KM maturity. Journal of Knowledge Management, 15(2), pp. 231-250.
Bantel, K.A. & Jackson, S.E. (1989). Top Management and Innovations in Banking: Does the Composition of the Top Team Make a Difference?. Strategic Management Journal, 10, pp. 107-124.
Barnett, W. P., Greve, R.H. & Park, Y.D. (1994). An evolutionary model of Organizational performance. Strategic Management Journal, 15, pp. 11-28.
Baum, J.A.C & Oliver, C. (1996). The Institutional Ecology of Organizational Founding. Academy of Management Journal, 39, pp. 1378-1427.
Bourgeois, L.J. III. (1984). Strategic management and determinism. Academy of Management Review, 9, pp. 586-598.
Burns, A. Acar, W. & Datta, P. (2011). A qualitative exploration of entrepreneurial knowledge transfers. Journal of Knowledge Management, 15(2), pp. 270-296.
Chang, T. & Wang, T. (2009). Using the fuzzy multi-criteria decision making approach for measuring the possibility of successful knowledge management. Information sciences. 179, pp. 355-370.
Chen, C. (2010). Knowledge management and innovativeness: The Role of Organizational Climate Structure, 31(8), pp. 848-870
Chua, A. & Lam, W. (2005). Why KM projects fail: a multi-case analysis. Journal of Knowledge Management, 9(3), pp. 6-17
Collinson, S. & Wilson, D. (2011). Inertia Japanese Organization: Knowledge management and routine and failure to innovate.
Crotty, Michael. The Foundations of Social Research: meaning and perspective in the research process. London, UK: Sage Publishers. 2003.
Damodaran, L. & Olphert, W. (2000). Barriers and facilitators to the use of knowledge management systems. Behavior and Information Technology. 19(6), pp. 405-413.
D’Aveni, R. (1989). The aftermath of Organizational decline: A longitudinal study of the strategic and managerial characteristics of declining firms. Academy of Management Journal, 32, pp. 577-605.
Davenport, T.H., Jarvenpaa, S.L. & Beers, M.C. (1996). “Improving Knowledge Work Processes”, Sloan Management Review, 37(4), pp. 53-66.
Dess, G. G. & Beard, D.W. (1984). Dimensions of Organizational Task Environments, Administrative Science Quarterly, 29, pp. 52-73.
Freeman, J., Carroll, G. & Hannan, M. (1983). The liability of newness: Age dependence in Organizational death rates. American Sociological Review, 48, pp. 692-710.
Gal, Y. (2004). The reward effect: a case study of failing to manage knowledge. Journal of Knowledge Management, 8(2), pp. 73-82.
Guptara, P. (1999). Why knowledge fails: How to avoid the common pitfalls. 9.
Gurteen, D. (1998). Knowledge, Creativity and Innovation. Journal of Knowledge Management, 2(1). pp. 5-13.
Hambrick, D.C., Cho, T.S. & Chen, M-J. (1996). the Influence of Top Management Team Heterogeneity on Firms’ Competitive Moves. Administrative Science Quarterly. 41, pp. 659-684.
Hannan, M.T. & Freeman, J.H. (1988). The ecology of Organizational mortality: American labor unions, 1836-1985. American Journal of Sociology, 94, pp. 25-52.
Lambe, P. (2011). The acknowledge parentage of knowledge management. Journal of Knowledge Management. 15(2), pp. 175-197
Lilleoere, A. & Hansen, H. (2011). Knowledge-sharing enablers and barriers in pharmaceutical research and development, 15(1), pp. 53-70
Malhorta, Y. (2002). Why Knowledge Management System Fail? Enablers and constraints of knowledge. Management in human enterprises. 42(3). pp. 56-93.
Malhotra, Y. Gallettra, F. & Katz, J. (2003). Role of Commitment and Motivation in Knowledge Management Systems Implementation: Theory, Conceptualization, and Measurement of Antecedents of Success. Proceedings of the 36th Hawaiii International Conference on System Sciences.
Mcgurr, P.T. & Devaney, S.A. (1998). Predicting Business Failure of Retail Firms: An Analysis Using Mixed Industry Models. Journal of Business Research, Vol. 43(3), pp. 169-176.
Miner, S.A, Kim, Ji-Yub, & Haunschild, P. (1999). Fruits of failure: Organizational failure and population-level learning. Advances in Strategic Management, Vol. 16, pp. 187-220
Nonaka, I. & Konno, N. (1998). The concept of “ba”: building a foundation for knowledge creation. California Management Review 40 (3), pp. 40-54.
Quinn, Michael. Qualitative Research & Evaluation Methods, 3rd Ed. USA: Sage Publications. 2002.
Ruggles, R. (1997). Why Knowledge? Why Now? Perspectives on Business Innovation, Centre for Business Innovation, Ernst and Young I.1
Sheppard, J. P. (1995). A Resource Dependence Approach to Organizational Failure. Social Science Research, 24(1), pp. 28-62.
Singh, A. (2011). Knowledge management antecedents and its impact on employee satisfaction. A study on Indian telecommunication industries, 18(2), pp. 115-130.
Slater, S & Narver, J. (1994). Does competitive environment moderate the market orientation performance relationship. Journal of Marketing, 58, pp. 46-55.
Storey, J. & Barnett, E. (2000). Knowledge management initiatives: learning from failure. Journal of Knowledge Management, 4(2), pp. 145-156.
Tsai, M. & Lee, K. (2006). A study of knowledge internalization: from the perspective of learning cycle theory. Journal of Knowledge Management, 10(3), pp. 57-71.
Tsui, E. (Ed.). (2005). Technology on knowledge management. Journal of Knowledge Management, 9(1).
Turner, M. E., and Pratkanis, A.R. (1998). A social identity model of groupthink. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 73, pp. 210–235.
Wang, T. & Chang, T. (2007). Forecasting the probability of successful knowledge management by consistent fuzzy relations. Expert System with Application, 32. pp. 801-813.
Appendix
Mapping
- i This table shows the duration that each activity will take. It is classified in months of a year. The shaded boxes represent the duration.