Introduction
The following paper presents an analysis of the challenges facing Royal Caribbean Limited in relation to the effort to enhance the safety, health and environment management. The analysis provides the basis for devising the solutions the company can adopt. Various management models are used in the analysis. The analysis established that the company has already adopted measures to enhance the safety, environment and health concerns affecting the company. However, there are still challenges that relate to management of its human resource and internal operations. The report is presented to the Management of RCL to help in improvement of safety, health and environmental initiatives as the basis for gaining a competitive edge.
Background of the Case Study
It is the expectation of the cruise ship passengers that their health and safety are given the paramount importance. Baker (2013, p.12) notes, “passengers confidence in the structural and management systems associated with safety and security must be such that it does not prejudice their enjoyment of the cruise experience”. Bearing in mind these aspects of health, safety, and environmental considerations, I believe that the management of any cruise ship should put in place measures to uphold the wellbeing of the passengers. Cruise lines are subject to various regulations that are administered by the maritime law, international organizations and governments. For instance, “safe return to port” is an essential requirement. The cruise ships should be able to comply with the laid down international regulations on the environment and safety.
The requirements place responsibility on the management of the ships to ensure that they are designed with sufficient security and health requirements. Therefore, RCL should put in place strategic management practices to ensure that there are adequate safety systems and policies to promote health initiatives and environmental requirements. The systems should supplement the already existing strategies. In addition, the strategies should be in line with the modern technology and should embrace a platform of continuous review and improvement.
Problem Statement
RCL has implemented initiatives to ensure that safety of the guests and that of its ships are upheld. However, the cruise ship industry still faces challenges that relate to unforeseen disasters and thus the need for continuous measures to ensure that environmental sustainability practices are adopted (Mileski, Wang & Beacham 2014). It is worth noting that nautical disasters remain to be a reality in the 21st century; though the fatality rate has considerably reduced. The incidents of the Titanic ship and the luxury liner Costa Concordia are a depiction of the reality that we cannot overlook in the modern times. In fact, the cruise ships fires, the missing passengers, personal injuries, and robberies in past years show that there is still a need to put in place systems to overcome the avoidable incidents.
In order to overcome the challenges, this report focuses on international business, strategy management, marketing management, human resource management and organisational behaviour challenges.
Research Questions
The following research is guided by five questions that relate to the five fields identified as major points where the company needs to improve in order to achieve a strategic goal of safety, health and environmental sustainability.
- International business: What are the challenges that relate to the international cruise ship industry and how do they affect the overall operation of the RCL in relation to health, environment and safety requirements?
- Strategy management: What management issues influence the overall decision making and the performance of RCL in ensuring a favourable environment for the guests?
- Marketing management: How can RCL align its strategic management operations based on the opportunities and strengths that the company already enjoys?
- Human resource management: How is the human resource capital aligned to the RCL’s strategic goals?
- Organisational behaviour: Has RCL put in place strategies to enhance an organisational culture that is necessary in overcoming the current challenges?
Research Objectives
The main aim of conducting the analysis is to generate viable solutions that will improve performance of RCL. Therefore, the objectives include:
- To find out the international challenges that hinder the ability of the RCL to implement the strategic management goals of enhancing security, environment and health concerns.
- To establish management problems that the company has faced in the endeavour to enhance the satisfaction of its guests in areas of health and safety.
- To investigate the marketing strategies based on the business environment that can be adopted by RCL to increase its market share.
- To explore the human resource management practices and policies that can be used to align individual performance of employees with the strategic goals of RCL.
- To examine the overall organisational culture and its role in overcoming the challenges being faced by the company.
Significance of the Study
The cruise ship industry is the fastest growing in the in leisure travel market. The industry has experienced steady growth of approximately 7.2% per year (Baniela & Rios 2011). Each year, there are millions of people on vacation aboard cruise ships. In 2012, statistics showed that over 20 million passengers cruised. The highest percentage of the cruise passengers were from North America, which contributed 11.5 million guests (Baker 2013). Amidst the growth, Lu and Tseng (2012) noted that there is the challenge of safety and security of passengers which could ruin the prospects. Furthermore, environmental responsiveness has become a key requirement for cruise ship industry. Therefore, this study will be important in understanding the challenges RCL faces and will devise measures to ensure that it remains competitive.
Structure of the Study
Chapter One
The chapter introduces the study and provides a summary of the key areas covered in the study. The main sections covered include background study of the case, the problem statement, research questions, objectives and significance of the study.
Chapter two
Chapter two is a discussion of the current situation in the market and the overall overview of the cruise ship industry.
Chapter three
The chapter provides the problem statements and the management models that are used to analyse each problem. The chapter also covers the research methodology, the research philosophy, data collection and ethical issues that are likely to be encountered in the study.
Chapter four
This is the analysis of the probable challenges facing RCL.
Chapter five
The chapter provides the probable solutions based on the findings of chapter four. Recommendations and action plan are provided in the chapter. Other sections covered include the limitations of the study.
Royal Caribbean Case Brief
Company background
Royal Caribbean was established by three Norwegian shipping companies in 1968. The main aim was to provide cruise services to elite customers who wanted to sail around the world. The first cruise ship for RCI was launched in 1970. The RCI parent company was incorporated in the Republic of Liberia in 1985. In line with its goals to target the elite customers, the company acquired its celebrity cruise line in 1996 at a cost of $515 million. Since then the company has recorded a steady growth, and by 2013, it boasted of 41 ships, which held 98,500 berths across its different brands. The RCL’s brands include Royal Caribbean International, Celebrity Cruises, Pullmantur Cruises, Azamara Club Cruises, Croisierres de France and Tui Cruises. In the year 2013, RCL served over five million customers that visited over 460 ports. It is worth noting that guests from the United States of America accounted for 51% of the company’s revenue.
Royal Caribbean Current Condition
The incorporation of the parent company in 1985 led to the current Royal Caribbean Limited (RCL). Subsequently, the consolidation of the firm’s operations into a New Miami headquarters in 1990 revolutionized the management of the company and led to the acquisition of more cruise ships such as the Celebrity Cruise Line Inc, which targeted the elites. In 2013, RCL welcomed over five million guests. RCL‘s employees were over 62,000 across the globe. The revenue for the company was almost $8 billion. The numbers pointed to the steady growth that the company has been recoding. Concerning the safety, environment, and health initiatives, in 2005, RCL initiated an incident room which to date is used in case of any serious onboard emergency. The incident room is critical in engaging the affected vessel and helps in troubleshooting to determine the best way to address the problem.
Competitors
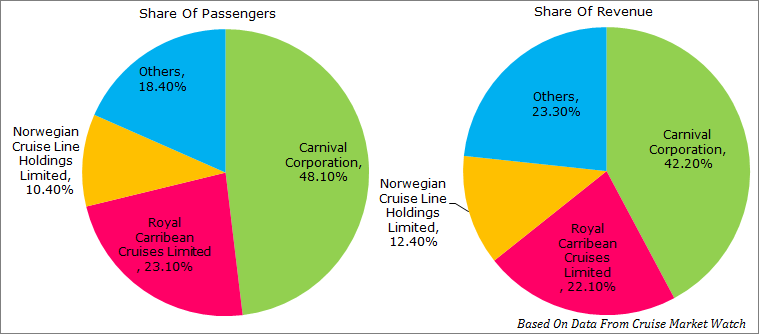
RCL has a considerable market share in the cruise ship industry. For instance, in 2013, RCL was ranked as one of the firms that contributed to over 93% of the passenger nights. As depicted in figure 1, the firm with the largest market share was Carnival Corporation Limited (CCL); the company had 12 leading cruise ship brands across the key markets of Europe, North America and Australia. In 2013, the revenue outlook for CCL was $15.5 billion compared to the $8 billion for RCL. Also, Carnival operated 100 ships that had the capacity for 200,000 passengers compared to the 98,000 for the RCL. The company projected to add extra nine ships to the fleet by 2016. The portfolio of CCL’s brands was based on price tiers and geographic areas of operations just as the case of RCL. RCL is the second largest cruise line with 41 fleets.
The second competitor is the Norwegian Cruise Line. The company was the third largest cruise line as by 2013. It was founded in 1966, and its revenue base reached $2.3 billion in 2012 with a projection of the revenue to increase by $2.6 billion in 2013 due to the cost cutting initiatives it had taken between 2008 and 2013. Its strategic market focus is European market.
The basis for competition in the industry has mainly been based on the price and regional tiers. For instance, CCL and RCL focus on the North America market while the Norwegian has mainly focused on the fast growing European markets. However, RCL has had a marketing strategy of differentiating its fleets to focus on the various markets and different class tiers. For example, there are fleets which target the elite and those that have normal prices, i.e. targeting the young families. In addition, it has focused on enhancing safety and health of its guests.
Safety, Environment and Security Requirements
RCL has undertaken great measures to upgrade the security of the cruise lines. However, there are still concerns whether the initiatives undertaken are sufficient to keep RCL in its current market niche and ensure the maintenance of the industry’s best practices. The key concern is whether RCL should adopt differentiation strategies to beat its competitors in terms of safety, environment and health initiatives. These concerns arise amidst the many international and government regulations. For example, the United States of America has enacted various laws to enhance the safety of the cruise ships. The Cruise Vessel Security and Safety Act signed into law in 2010 by President Barrack Obama stipulate that it is the duty of the ship owners to ensure that the vessels are fitted with the right technology to enhance the safety of the passengers. Some of the requirements as stipulated by the law include video surveillance, and overboard detectors (Carne 2012). Also, they should have medical personnel and equipment to assist passengers in case of sexual assault.
In the cruise ship industry, the success of business is based on the satisfaction of the customers. It is the value of the customer service that leads to repeat customers and referrals. In the RCL, the security and health of the customers play a paramount role. Thus, the company has the policy to ensure that it has put in place policies to enhance safety. RCL has instituted safety, environment and health committees which carry regular checkups and investigations. To promote the aspect of safety, health and environment, performance bonuses are awarded to the top-performing executives. Besides, the company has an incident room at the company headquarters.
The ships are also designed to meet the safety standards as per the US Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). RCL has augmented a video security on its fleet in order to enhance safety and health of the passengers. The main aim of augmenting the security with updated video management is to increase the capability to identify problematic situations in the ships and to help in the investigation.
Problem Statement and Plan of Analysis
The cruise ship industry is faced with many challenges that relate to the safety, environment and health concerns. As a result, there have been many regulations at the international, country and organisational levels to address the three problems. It is important to understand the challenges that RCL faces in order to design an in-depth analysis. However, it is worth noting the problems that the company faces are not in isolation; it is a major challenge affecting various cruise ship companies. This chapter outlines the major problems faced by RCL. Various management models to be used in the analysis of the problems are discussed in order to provide an in-depth understanding of the problems and possible remedy to enhance the performance of the RCL. The section also outlines the research methodology applied in the study. The plan of analysis explores various spheres of business operations and their implications on the customer satisfaction.
In 2012, the cruise ship industry experienced two major disasters that greatly affected its reputation. The first disaster was the sinking of the Costa Concordia after it collided with a reef. The fatalities included deaths of 32 passengers, and over 64 passengers were injured. Later in the year, Cost Allegra caught fire that left over 1000 people onboard without power. However, there were no fatalities reported. These incidents serve us as a reminder of the reality of accidents in the industry. As a result, various players have come up with measures to improve the safety requirements of their fleet. For example, CCL increased the safety requirements of its fleet after the fire incidents. RCL’s Grandeur of the Seas caught fire in May 2013. At the time it had over 3,000 passengers and crew. Luckily no one was injured, and the ship did not lose power due to the backup systems.
These incidents are an indication that the safety and health of passengers are always at stake. As such, there is the need to devise mechanisms to ensure that the lives of the passengers are safeguarded at all times.
Plan of Analysis
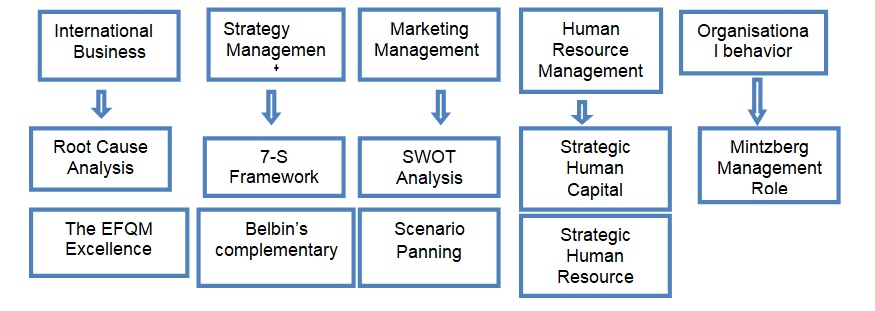
The design of the analysis is based on solving the identified business problems in the industry. Based on the inherent problems, different management models are proposed to analyse and provide possible solutions to the problems. The categorisations of the problems include international business, strategy management, marketing management, human resource management, and organisational behaviour. Figure 2 is a summary of the problems and the management models to be applied in the analysis.
International Business Problems
Pressure to comply with international regulations rather than the internal mechanism that create value and enhance safety
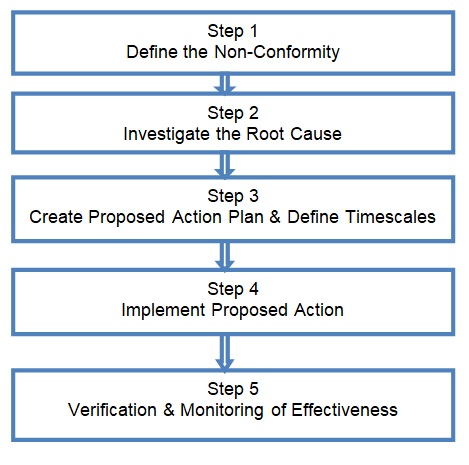
The Root Cause analysis is an operational model for identifying the causal factors. The model applies an approach that provides the basis for identifying a problem and the ways to solve it (Mahto & Kumar 2008). Figure 3 presents the steps used in the analysis process. According to Mahto and Kumar (2008), it is an analytical tool that assists in performing a comprehensive and critical review of incidents. Anderson and Fagerhaug (2010) noted that it includes the identification of the factors contributing to the problem, identification of the measures to reduce the risks, and to develop the action plan to solve the problem.
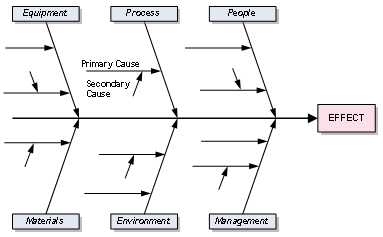
The Root Cause Analysis provides a thorough understanding of the issues that affect the industry and identifies the existing gaps (Duggett 2009). This is based on the cause and effect as illustrated in figure 4. Stringent regulations have been put in place to regulate the cruise ship industry. This has led to the shift of many companies to focus on ways to comply rather putting internal measures to enhance their productivity and safety of the patients. Even though the international regulations centre on the core issues of environment, safety and security they have not helped in the elimination of the issues. Thus, the root cause model provides an alternative to understand the issues facing the industry and how to address them.
Increased Competition
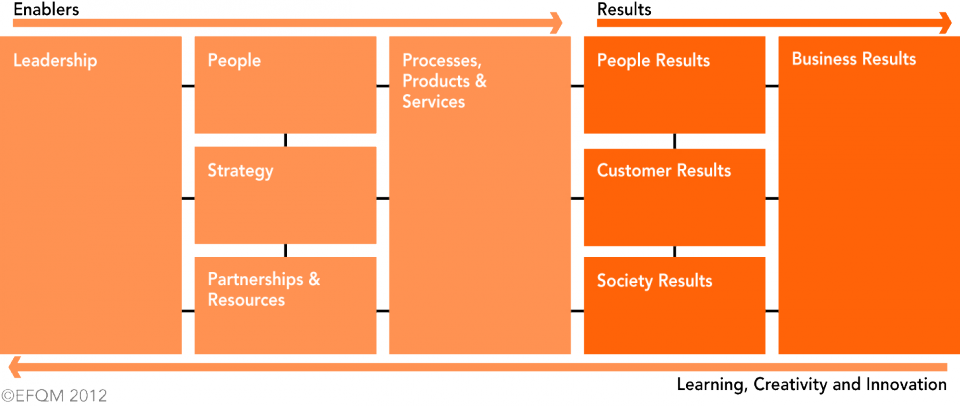
The international business environment is not at a standstill. It keeps on changing, thus for any company to remain competitive, it has to continually innovate and improve in the different areas of operations. According to Rompuy (2012), companies need to understand, balance, and manage effectively the needs of the stakeholders. The EFQM excellence model provides a framework that helps management to comprehend and manage the complexities that relate to the cruise ship environment. Rompuy (2012) noted that it ensures continuous improvement. For instance, the model is used in the establishment of the cause and effect relationship.
The fundamental concepts of EFQM Excellence Model are based on sustainability and creating an organisational culture. For example, enhancing the culture of safety, health, and environmental excellence is important for all the cruise lines. The eight fundamental concepts of the model are illustrated in figure 5. In addition, Pyke et al. (2007) noted that EFQM excellence model is based on the enablers and the results. For instance, for organisations to have clear strategic direction there is the need to invest in measures that improve their human resource and enhance partnerships which are important in creating a strategic direction for the business.
Strategy Management Problems
Failure to identify internal management issues that derail performance
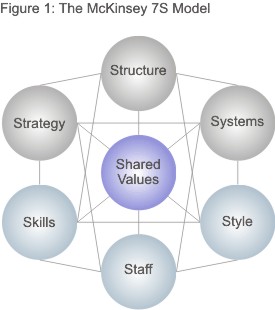
High levels of performance can be enhanced by a clear understanding of the competitive position of a company. The 7-S Framework identifies seven factors that are needed to ensure effective execution of strategy (Tracey & Blood 2012). The model is based on the inter-relationship of the seven factors. The factors must be aligned in order to improve the performance of the organisations. Kathuria, Joshi and Porth (2007) argued that the 7-S framework provides a robust approach in examining the organisational alignment. However, Woods and Wall (2007) noted that no evidence supports the veracity of the framework. In addition, Woods and Wall (2007) noted that the model does not specify the importance of the seven factors. In support of the model, Tracey and Blood (2012) pointed out that all firms experience different environmental challenges. As a result, there is the need to put in place strategies that enhance competition and sustainability. As such, the 7-S framework acts as the basis for an excellent start point in the identification of what the company requires to succeed.
Inability to understand the strengths of the employees and their capability
According to Gündüz (2008), Belbin’s Complementary Roles is an operational model designed to help each member in the team to enhance self-awareness. The main aim of the model is to help the members of team leverage on strengths of each other. According to Kumar (2013), Belbin’s complementary roles are used to create self-awareness. Thus, the model is based on the capability of an organisation to have a clear knowledge of strengths and weaknesses of its employees in order to forge productive working relationships in an organisation. It is through the model that an organisation can build mutual trust, understanding and help in the creation of productive human resource capital. The model describes roles based on six factors which include mental abilities, values, motivation, role learning, experiences and restrictions. Gündüz (2008) argued that the six factors form the basis of creating the self-awareness.
However, Chong (2007) argues that he Belbin’s model fails to demonstrate how the role-play can be applied to bring about organisational change. The proposal of the model is that teams that are high performing require balanced distribution of all the roles.
Marketing Management Problems
Inability to identify the organisational niche in the target market
An organisation needs to carve a niche that is sustainable in the market of operation. According to Ayub (2013), SWOT analysis helps organisations uncover opportunities that a business can exploit. It is based on understanding the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of an organisation. Ayub (2013) stated that with a clear understanding of the four concepts, the management can help eliminate the weaknesses and exploit the available opportunities. Chang and Huang (2006) argued that actions taken by organisations result in some internal and external changes. Coman and Ronen (2009) pointed that the model provides marketing intelligence for internal and external processes. However, Finnegan (2010) pointed that many managers have not embraced the model. Agarwal, Grassl and Pahl (2012) argue that the model is based on subjective perception; it does not embrace quantification and has less prognostic performance.
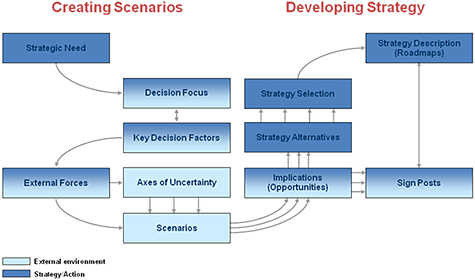
Focusing on the current performance and failure to prepare for the future
According to Wulf, Meissner and Stubner (2010), scenario panning entails developing different possible situations that are likely to happen in the future and thinking through their consequences in the organisations. The model prepares managers to initiate programmes that address possible future occurrences. According to Wulf, Meissner and Stubner (2010), this forms the basis for forecasting what could affect the future market prospects and hence planning in advance to ensure that the organisation is prepared with ready solutions for any eventuality. However, Bradfield (2008) pointed out that the model does not provide the strategic tools required to lead to the superior performance. Bishop, Hines and Collins (2007) stated that the application of open and creative strategic thinking leads to innovative strategies that are required for improved performance. Figure 7 is diagrammatic presentation of scenario planning model. According to Bishop, Hines and Collins (2007), the model fosters the implementation of strategic thinking in businesses. The critics of the model argue that it is complex and results in high investment of resources.
Human Resource Management Problems
Lack of clear policy on how to implement the strategic decisions that are supposed to enhance the safety and security of the guests due to poor planning
The strategic human capital planning model provides a policy framework on how a company can enhance its performance by supporting the human resources. According to Budhwar and Aryee (2008), it is important for an organisation to assess how the activities of the human resource capital align with the overall strategic goals. Bratton (2007) pointed out that the model places an organisation in a position to understand whether its people and management are working towards achieving the company’s strategy. As a result, the assessment of the available human capital and the capability prepares an organisation to seize the internal opportunities based on its workforce. For example, the organisation can improve performance by training or employing the most competent staff.
Management practices that do not take into consideration the individual capabilities of the human resource based on their qualifications and diversity
The Strategic human resource management model is based on understanding that people are the common element in all social organisations. According to Ericksen and Dyer (2010), people are tasked with the creation of goals, innovations and execution of the various activities which result in effective organisational performance. Thus, people are resources that are not inanimate. It is through the people that organisations exist. Based on the understanding of the aspect of the people in an organisation, the Strategic HRM Approach is based on a framework that puts into perspective the diverse talents people have and hence devising strategies to use them to support the goals of the organisation. However, Katou and Budhwar (2006) noted the people cannot achieve the set goals without proper internal and external framework for operation.
Organisational Behaviour problems
Poor coordination of the various management roles
Mintzberg classified managerial work into ten roles. The roles are further categorized into three broad categories of decision roles, interpersonal roles and informational roles. Shapira and Dunbar (2012) noted that the ten roles as outlined by Mintzberg operate in an integrated manner which depicts the competence of the managers. The roles are integrated and cannot be isolated based on the three classifications. All the roles are critical in enhancing effective management and organisational performance. Therefore, management should not rank the roles by importance or priority. Failure to consider one role results to ineffective management.
Research Methodology Adapted to analyse the Case Study
According to Denk (2010), study methodology is systematic planning of actions that are applied to the collection and the subsequent analysis of data in a logical manner. Research methodology helps in the realisation of the research purpose. It entails the use of different research designs such descriptive, cross-sectional, experimental, case studies and explorative researches. Therefore, the following section covers the research philosophy, the research design and research approaches and the ethical considerations to be observed in the case study brief.
Research Philosophy
Research philosophies are important assumptions used by the researcher to discover meaning or reason for existence of a phenomenon. The purpose of a scientific study is to discover answers to the research questions. According to Kothari (2005), it entails the use of scientific procedures to find the truth which has not been discovered. Neumann (2007) noted that the objective of a research is to gain familiarity with the issue being studied or to gain insights into a particular phenomenon. In social and business studies, the main philosophy paradigms are the positivism and the interpretivism.
Positivism entails application of methods of natural sciences in which quantitative methods are used to measure constructs. On the other hand, the paradigm of interpretivism is based on idealism. Interpretivists argue that examination of meaning and reasons can be used to understand a social phenomenon. In essence, it discounts the positivist view of the natural objectivity. According to Weber (2010), it applies social constructionism and hermeneutics. Therefore, issues that relate to human construct are better studied by qualitative approaches that use the interpretivism paradigm.
The Philosophical Approach
The aim of the research is to provide a platform for the discovery of the phenomena being studied. In the current study, the main phenomenon under investigation relates to RCL’s health, environmental and security strategies. The main constructs under investigation are with how the three aspects affect RCL’s prospect in the international business, marketing, human resource management and organisational behaviour. There are many theories used to get a clear understanding of the challenges. Therefore, a paradigm of interpretivism which is based on a qualitative understanding of human activities is best suited for the study, unlike the positivism which is more aligned to natural sciences.
Research Strategy
The research strategy to be employed in the study entails the use of secondary data. Secondary data comprises of the information that has been gathered and is readily available. The secondary data is critical in providing a basis for understanding the cruise ship industry and the past performance of the RCL. However, the secondary data may be out-dated and thus the inability to reflect the current business environment (Denk 2010). The basic research types applied in research include the qualitative and the quantitative. The quantitative method involves gathering of empirical data that can be subjected to numerical manipulation. On the other hand, the qualitative approach entails the type of studies that apply assessment of perceptions, opinions and behaviours (Denk 2010). The approaches can be combined based on the nature of the study. In the current study, qualitative methods which provide descriptive analysis will be used.
Research Design
Study methodology entails the use of different research designs to inform the process of the data collection (Denk 2010). Examples of the study designs include descriptive, cross-sectional, experimental, and explorative researches. In the current study, descriptive study design is used.
Research Approach
There are two approaches to research which include the deductive and inductive. The deductive approach focuses on causality. The inductive approach looks at an already researched phenomenon by applying a different perspective. The inductive approaches are mainly related to qualitative research while the deductive approaches relate to the quantitative studies. However, some qualitative researches may apply deductive approach. Therefore, this study adopted an inductive approach.
Sources of Data
There are varied data collection methods. According to Kothari (2005), the choice of the method to be applied in the data collection is determined by the strategy, type of variable being measured and the point of data collection. The main types of data collection methods to be used in the study will include secondary sources of data collection. The secondary data used for the study is from journals, published articles and web sources.
Ethical issues
In accessing the data, there are ethical issues that should be considered such as using data without proper authorisation and sharing of confidential information. The current study relies on secondary data sources which are readily accessible.
Analysis and findings
Increased need for safety within the cruise ship industry has led to the introduction of a lot of measures to ensure that passengers on board are safe at all times. The focus of this analysis was in the case of Royal Caribbean Cruise Ltd, which has experienced numerous problems in the past. This chapter is based on the problems identified in the previous chapter as far as the case of RCL’s safety, health and environmental operations are concerned. Thus, this analysis aims at offering in-depth analysis concerning the security and business problems that the company faces in its attempt to provide services to customers.
The analysis employed various models and approaches such as the company’s SWOT analysis, the root cause analysis approach, the EFQM excellence model, the 7-S framework model, the Belbin’s complementary roles model, the scenario planning model, the strategic human resource management model, and the Mintzberg management role model to analyse the different scenarios within the company. From the analysis of the safety, health and environmental issues at RCL, the study identified the following findings:
Findings
- The company suffers from international business problems that tend to interfere with its smooth operations.
- Strategy management and related issues affect the performance of the company.
- RCL does not have effective marketing management strategies.
- The company’s human resource is not effective in terms its policy and strategy issues.
- Organisational behaviour problems.
The following sections provide an analysis of each of the five findings as identified using various models of management in chapter three.
Problem 1: International Business Problems
- The study found out that RCL has been experiencing a lot of pressure due to the need for the company to adhere to regulations set up by international bodies as far as the operations of cruise ships are concerned.
- Based on the root cause analysis approach, the company does not have the necessary internal mechanisms that are very effective in creating and enhancing value. Coupled with the need to comply with international regulations, it becomes difficult for the company to operate smoothly.
- Following the several incidents that have since affected the reputation of the industry such as the collision of Costa Concordia, the fire incident of Costa Allegra, it is evident that the major problem facing the industry and RCL’s operations is the lack of effective measures to prevent and deal with security issues.
- The mechanism should supplement the international operations.
- It was evident that there is an increase in the level of competition within the industry, considering that there is growth in the cruise ship industry.
- Royal Caribbean Cruises faces a threat from increased competition because parties in the industry are working towards maintaining their organisational culture and to ensure that their customers and other stakeholders are adequately satisfied with their services.
Finding and Analysis
International Business Problems
Pressure to comply with international regulations rather than the internal mechanism that create value and enhance safety.
The Root Cause analysis.
- Increased Competition
- The company does not have measures that ensure improved human resources within the company and developing an effective partnership with key stakeholders.
EFQM Excellence Model.
Strategy and Management related Problem
- The company has problems identifying some of the internal management issues affecting the performance of the company.
- The company does not interrelate all important strategy and management factors, which resulted in internal management issues that continue to derail performance at the various departments in the company.
- The company was unable to understand the strengths of the employees and their capability, which is a major drawback as far as organisational success is concerned.
- To a large extent, strategy management problems are caused by the failure by a company to understand its position in the industry where it operates.
- The company has not fully exploited its capabilities.
- RCL failed to identify internal management issues that derail its performance.
The 7-S Framework Model.
- Inability to understand the strengths of the employees and their capability
Belbin’s Complementary Roles model.
Marketing Management Problems
- Inability to identify the organisational niche in the target market
- The organization lacked a good knowledge of the requirements of the market and the state of the organization in the market
- The company’s future is not secured both businesswise and in terms of safety, environmental practices and health.
SWOT analysis.
- Focusing on the current performance and failure to prepare for the future
- The company lacks clear policies to enhance safety within the company’s due to poor planning in the company.
- RCL lacks effective policies to assess how the activities of the human resource capital align with the overall strategic goals of the company.
Scenario Planning Model.
Human Resource Management Problems
- Lack of clear policy on how to implement the strategic decisions that are supposed to enhance the safety and security of the guests due to poor planning.
The Strategic Human Capital Planning Model.
Management practices that do not take into consideration the individual capabilities of the human resource based on their qualifications and diversity
The Strategic human resource management model.
Organisational Behaviour problems
- Poor coordination of the various management roles
- Lack of effective understanding of organisational behaviour concept at RCL has always led to poor coordination of the various management roles
Mintzberg’s management Model.
Conclusion
From the above discussion and analysis, it was evident that the Royal Caribbean Cruises Ltd Company experiences several problems that affect its performance, as well as threaten the security of the company’s operations. The analysis identified a lot of pressure due to the need for the company to adhere to regulations set up by international bodies. Such a scenario led to the lack of concentration on setting up the necessary internal mechanisms within the company that could boost its operations and security. In addition, increased level of competition within the industry, failure to identify some of the internal management issues affecting the performance of the company, the inability to understand the strengths of the employees and their capability, and failure to augment its niche in the target market were the major problems observed during the analysis.
Thus, from the analysis, it is evident that the company’s future is not secured. This is in relation to competitiveness, attracting and maintaining highly qualified employees. It is worth noting that these aspects have direct effect on the ability of the company to have good health, safety and environmental initiatives.
Proposed Solution, Recommendation and Action Plan
Solutions to International Business Problems
RCL should adopt strategic management practices that focus on enhancing the internal business environment as well as incorporate measures to deal with the external business environment. It should create a management team that will ensure synergy. This will guarantee RCL effective management of internal operations to enhance safety, security and environmental sustainability practices. For example, RCL should set a management team to create a programme for environmental sustainability practices such as the use of recyclable materials and ways to deal with non-biodegradable wastes in the company. It should also invest more in technology and create a business design that incorporates all the pertinent health issues and security measures.
In the cruise ship industry, health and security are key determinants of the guests’ satisfaction. The factors have a great implication on the competitiveness of any cruise ship company. RCL should use technology to come up with an application in which each passenger can voice health and safety concern by an alert system. The same system should also include components of security. Therefore, in the case of an incident affecting a single passenger, the system should alert the people in charge. This will supplement the incident room which currently deals only with major incidents. This will also boost the satisfaction of the customers and act as a means to gain competitive edge for RCL.
Recommendation
RCL should invest in research and development of the technological application that will enhance efficiency in the company. It should also empower the top management in order to be motivated in creating a culture that promotes safety and environmental sustainability. In additions, the internal design of the ships should put into consideration factors that enhance the health, security and environmental status.
Action plan
RCL’s top management is supposed to initiate restructuring programme of the organisation in order to create fully fledged departments to deal with the key aspects of health, security and environment. Furthermore, RCL should come up with a management strategy that creates synergy in all key departments and ensures free flow of information. The system should be automated in order to enhance general performance of the organisation.
Solutions to Strategy Management Problem
RCL should outsource external consultancy services that will help in building management system where each department understands its mandates and responsibility in enhancing safety, health and environmental management. In addition, RCL should eliminate work duplication that contributes to ineffective role play. Finally, all the staffs should be re-evaluated to understand their strength and weakness. Hence, assign duties based on a work system where teams are constituted based on the capabilities of individuals. Hence, they can leverage on each other in the implementation of the company’s policies.
Recommendation
Bearing in mind that the satisfaction of the employees contributes to the overall performance of a business, RCL should enact policies that entice the employees to work towards achieving the overall company’s goal of safety, health and sustainable environmental practices. The company should build teams which have clear goals to accomplish. The goals should resonate with the health, security and environmental needs. The main teams will include a health team, security team, environment management team and a management team to oversee the operations of the other teams.
Action plan
In order to achieve the laid down strategies, RCL is required to set up a human resource department with the right personnel to develop the working teams and take care of individual needs of the employees. In addition, the company should invest in team building activities in order to create cohesive teams that understand their mandates and that of the company.
Solutions to Marketing Management Problem
To use the strong marketing position to enhance its position in the industry and create a niche characterised by safety standards, health and sustainable environmental practices. RCL should also capitalise on the available management capabilities to design a new business model in order to revolutionalise service delivery in the cruise ship industry
Recommendations
RCL should use the SWOT analysis strategy to understand the opportunities in the market and to minimise the weaknesses within the internal business environment. Bearing in mind that corporate social responsibility plays a great role in enhancing the competitiveness of businesses, RCL should invest more in technologies and practices that are friendly to the environment. This will make it a pace setter in the industry in relation to the environmental management practices.
Action plan
The first action plan is to design a corporate social responsibility program that is aimed at preserving the waterways. Secondly, to adopt management procedures that create value for RCL and at the same time remain socially responsive. RCL should also initiate health care and safety programmes to take care of the guests during the cruise period. The action should be anchored on a secured technology that integrates the processes to all the concerned departments.
Solutions to Human Resource Management Challenges
To amend the human resource policies and adopt practices which promote employee satisfaction. This should be through a work program that cherishes the diversity of the workforce and their areas of competence. To train its staff on the value of the guests and measures to create value for them thorough an organisational culture that emphasizes on the wellbeing of the customers.
Recommendations
RCL should design its HR activities in line with the overall goals. This should be made possible by setting systematic solutions that bring onboard all employees. In addition, the company should create a reward system to motivate employees who display good performance in security, safety and environment initiatives. Finally, a leadership style that enhances a work environment of creativity and innovation should be encouraged at all levels of management.
Action Plan
To create a human resource work system that recognizes the capabilities of the employees and awards them points based on their performance in selected fields and the execution of the company’s strategies. The system should include the aspects of empowering the human resource through a training programme that prepares them for the work requirements and service to the guests.
Solutions to Organisational Behaviour Issues
Streamline role-play in the organisation in order to avoid possible blame games. All the staffs in the organisation need to adopt the desired organisational culture that accentuates the wellbeing of the guests. This should be supplemented by the management’s investment in the security features in all the ships.
Recommendations
The investment in security features and purchase of safety and security equipment cannot translate to ultimate safety. The input of the people is very critical. Therefore, it is recommendable to invest in team building strategies that create a culture of care in all the cruise lines. Also, sensitise the employees on the goals of the company; the security and safety measures goals and lobby them to particpate in the implementation of the goals.
Action Plan
RCL should invest in the development of a preceptorship programme for all employees. The programme is to include activities that enhance the company’s corporate culture of excellence in all fields of operations. Also, it will entail a teaching and retraining programme on the company’s mission, goals and visions. This should be clearly articulated and emphasised for all the employees to adopt a work behaviour that resonates with the key requirements.
Implications for the Various Stakeholders
The solutions presented in the following paper are aimed at enhancing organisational performance by initiating simple strategies and strengthening the already laid down strategies. It is supposed to result in positive change to all stakeholders.
Guests
The solutions directly affect the guests. For instance, the safety and security measures are supposed to enhance the wellbeing of the passengers. Therefore, the customers will be satisfied with the excellent services; hence, the company will achieve repeat customers and referrals.
Management Team
The solutions insist on setting systems instead of solving problems as single isolated happenings. Therefore, the management team will be tasked with implementation. The systems will also make it easy for the managers to execute their roles. For instance, if all employees adopt the desired organisational culture, the managers will be guaranteed that the safety, security and environmental practices are in line with the company’s policy at all times. The requirements place responsibility on the management of the ships to ensure that they are designed with sufficient security and safety requirements. For example, the ships are supposed to have backup power systems to ensure that they can return to port in case of any incident such as fire.
Shareholders
The shareholders will need to invest in more resources to the various proposed initiatives. This will in result in streamlined operations and increase in market share and hence more returns for the shareholders.
Society
Society is a stakeholder that will greatly benefit from improved environmental practices. Even though the practices may not have a direct impact on them, it has long term implications. Besides, the proposed corporate social responsibility programme will lead to a better environment for all.
Resource Availability and Constraints
In order to achieve the set proposals, RCL will need to commit more financial resources to the various initiatives. The financial resources should be from the company’s revenues. The constraints the company is likely to encounter include lack of qualified management team to implement the tasks and time factors. The current team may be overwhelmed. However, the company can outsource the best skills.
Limitations
The solutions provided are feasible for RCL; in fact, the company has already started implementing some of the initiatives. Therefore, the current remedies will be to supplement the efforts that have already been put in place. However, the company is likely to experience limitations in terms of unprepared employees, and complex work environment. Another limitation will relate to insufficient budgetary allocations. Furthermore, lack of a clear plan for executions of the initiatives may result in modification of deliverables to suit the allocated budget. This may lead to some crucial activities not being implemented as planned.
References
Agarwal, R, Grassl, W & Pahl, J 2012, ‘Meta-SWOT: introducing a new strategic planning tool’, Journal of Business Strategy, vol. 33, no. 2, pp. 12-21.
Anderson, B & Fagerhaug, T 2010. Root cause analysis: Simplified tools and techniques, ASQ Quality Press, Milwaukee.
Ayub, A, Razzaq, A, Aslam, M & Iftekhar, H 2013, A conceptual framework on evaluating SWOT analysis as the mediator in strategic marketing planning through marketing intelligence. European Journal of Business and Social Sciences, vol. 2, no. 1, pp.91-98.
Baker, D 2013, ‘Cruise passengers’ perceptions of safety and security while cruising the Western Caribbean’, Rosa dos Ventos-Turismo e Hospitalidade, vol. 5, no.1, pp. 1-14.
Baniela, C & Rios, V 2011, ‘Maritime safety standards and the seriousness of shipping accidents’, Journal of Navigation, vol. 64, no. 1, pp. 495–520.
Bishop, P, Hines, A & Collins, T 2007, ‘The current state of scenario development: An overview of techniques’, Foresight, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 5-25.
Bradfield, R 2008, ‘Cognitive barriers in the scenario development process’, Advances in Developing Human Resources, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 198-215.
Bratton, J 2007, Strategic human resource management, Palgrave Macmillan, London.
Budhwar, P & Aryee, S 2008, ‘An introduction to strategic human resource management’, Strategic Human Resource Management: Building Research-based Practice, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 9-32.
Chang, H &Huang, W 2006, ‘Application of a quantification SWOT analytical method’, Mathematical and Computer Modeling, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 158-169.
Chong, E 2007, ‘Role balance and team development: A study of team role characteristics underlying high and low performing teams’, Journal of Behavioral and Applied Management, vol. 8, no 3, pp. 202-211.
Coman, A &Ronen, B 2009, ‘Focused SWOT: diagnosing critical strengths and weaknesses’, International Journal of Production Research, vol. 47, no. 20, 1-12.
Cruise Market Watch, 2014, Cruise ship industry market share, Web.
Denk, T 2010, ‘Comparative multilevel analysis: proposal for a methodology’, International Journal of Social Research Methodology, vol.13, no.1, pp. 29-39.
Duggett, A 2004, ‘A statistical comparison of three root cause tools’, Journal of Industrial Technology, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 1-9.
Ericksen, J & Dyer, L 2010, ‘Toward a strategic human resource management model of high reliability organisation performance’, The International Journal of Human Resource Management, vol.16, no. 6, pp.907-928.
Finnegan, M 2010, Evaluating SWOT’s value in creating actionable, strategic intelligence, Erie PA, Mercyhurst College.
Gündüz, H 2008. ‘An evaluation on Belbin’s Team Roles Theory’, World Applied Sciences Journal, vol. 4, no.3, pp.460-469.
Kathuria, R, Joshi, M & Porth, S, 2007, ‘Organisational alignment and performance: past, present, and future’’, Management Decision, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 503-517.
Katou, A & Budhwar, P 2006, ‘Human resource management systems and organisational performance: a test of a mediating model in the Greek manufacturing context’, The International Journal of Human Resource Management, vol.17, no. 7, pp.1223-1253.
Kothari, C 2005, ‘Contemporary methods of quantitative data collection and analysis in literacy research’, Reading Research Quarterly, vol. 39, no. 1, pp.94-112.
Kumar, R 2013, ‘Evaluation of Belbin’s team roles-a case study of Nizwa College of Technology, Sultanate of Oman’, Arabian Journal of Business and Management Review, vol. 3, no. 3, pp.1-4.
Lu, C &Tseng, P 2012, ‘Identifying crucial safety assessment criteria for passenger ferry services’, Safety Science, vol. 50, no. 7, pp.1462-1471.
Mahto, D & Kumar, A 2008, ‘Application of root cause analysis in improvement of product quality and productivity’, Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management, vol. 1 no. 2, pp.16-53.
Mileski, J, Wang, G & Beacham, L 2014, ‘Understanding the causes of recent cruise ship mishaps and disasters’, Research in Transportation Business & Management, vol.13, no. 1, pp.65-70.
Neumann, W. L 2007, Social Research Methods: Qualitative and quantitative approaches. Journal of Research, vol. 3, no. 2, pp.35-44.
Pyke, C, Gardner, D, Wilson, J, Hopkins, P & Jones, S 2007, ‘Achieving best value through the EFQM excellence model’, Journal of Finance and Management in Public Services, vol. no. 1, pp.29-40.
Rompuy, H, 2012, Overview of the EFQM Excellence Model, Web.
Shapira, Z & Dunbar, R 2012, ‘Testing Mintzberg’s managerial roles classification using an in-basket simulation’, Journal of Applied Psychology, vol. 65, no.1, pp.87-92.
Tracey, J & Blood, B 2012, ‘The Ithaca Beer Company: A case study of the application of the McKinsey 7-S framework’, Cornell Hospitality Report, vol. 12, no. 7, 6-13.
Weber, R 2010, ‘The Rhetoric of Positivism versus Interpretivism: A Personal View’, MIS Quarterly, vol. 28, No. 1, pp. 3-12.
Woods, S & Wall, T 2007, ‘Work enrichment and employee voice in human resource management-performance studies’, International Journal of Human Resource Management, vol. 18, no. 2, pp.1335-1372.
Wulf, T, Meissner, P & Stubner, S 2010, A Scenario-based approach to strategic planning–integrating planning and process perspective of strategy, Leipzig, New York.