Business Overview
This plan aims at laying the factual strategies that will be involved in implementing a business to provide communication services and devices in Australia. The proposed name of the company will be Safaricom Limited. The company will offer such communication services as voice calls, short message services, internet subscriptions, and other media services including advertisements through mobile phones. Furthermore, Safcom limited will create efficient money transfer services throughout Australia as well as create shops for selling their electronic devices and products to facilitate communication.
Therefore, the plan has the mandate to show how the profit-making organization will be developed to maturity by making a presentation of target proceedings, competitive structures, risk assessments, point of developments, backup styles, possible challenges, and marketing strategies among others (Blackwell 2008). The establishment of Safcom Limited will include the development of a legal and ethical analysis of the venture it will undertake (Katz & Valiquet, 2012). These will not only include the step-to-step formation of a company, but also the appropriateness of each outcome in the target services in terms of whether they affect the public. Essentially, this will be supported by further recommendations to neutralize such negative outcomes from this venture.
Business Activity
The technical approach of developing Safcom Limited will be based on the sales name for its services and products identified by the word ‘Airtalk’. Airtalk will represent the various services during the establishment including the tokens for receiving the communication services from the company. The airtime tickets namely Airtalk will be cards with sealed codes to be used in entering credit for a mobile subscription. These cards will develop a system of prepaying services where customers can pay for the mobile subscriptions before using them (Ling & Donner, 2009). However, this will also include the establishment of a system the post-paying services where subscribers will make payments later.
Apart from the suppositions, the brand name will be applied in the sales of other goods such as mobile phones, computers, and accessories. The final establishment of this business plan will be to initiate service for making money transactions countrywide through mobile phones. The money transfer services will be referred to as EA Cash, which will be an acronym for Electronic Airtalk Cash. The agents of EA Cash services will subscribe as the beneficiary dealers with reputation dictated by having 5 registered businesses. Each dealer will employ 10 agents to operate the money transfer points and will own the money being circulated during the transfer. The dealer’s benefits will arise in form of profits from the charges being deducted during transfer which can be calculated and shared among the parties involved.
Vision and Objectives
Safcom limited will have the vision to become the most competitive communication company in Australia. The mission will be to develop a sustainable communication network in Australia. In a bid to attain the vision and mission, it will implement the following objectives.
- To develop a sub-brand name for the mobile subscriptions for communication services within and outside the country.
- To establish reliable shops for supplying their customers with communication devices
- To create efficient and reliable money transfer services through the use of mobile phones
The Competition
In a market where services are rendered without legal restrictions such as monopolization, businesses are able to establish competition strategies in order to attain the highest number of customers (Laffont & Tirole, 2000). Competition arises when two or more businesses offer similar or complimenting services or goods (Jenster & Hussey, 2001). Communication services have been established well in most parts of Australia, which depicts the need for a strategic plan to enter the market. The most recognized companies providing these services are discussed below.
iiNet Limited
iiNet was the second-largest internet providing firm in Australia by the year 2011, which was founded in 1993 within Western Australia (Lindsay, 2012). In this regard, the firm grew its customers from this region.
Total Peripheral Group (TPG)
This is the fourth most advanced communication company founded in 1992. Its headquarters are located in North Ryde, Australia. The company provides internet, mobile telephony, online television, and networking services.
National Broadband Network (NBN)
NBN is an Australian wholesale-only company that provides internet supplies to service providers all over the country. It offers fiber optic services to implement wireless networks to organizations and firms using data on large scale. This company had 109862 active subscribers by 2013.
How Safcom Limited is Better than the Competitors
The establishment of a developed and competitive system of communication in Australia has restricted new ventures. However, this company wishes to introduce a new strategy where various thin Sim cards can be availed to work in single Sim phones. This will allow the users to retain a previous Sim line and attach the new line from Safcom Limited as shown in figure 1. The initial Sim card will have an attached version for the Safcom Limited connections and storage.

Unlike other competitors who rely upon developing twin Sim phones in Australia, Safcom has established a way of using single Single Sim phones as well as duo ones in reaching the customers. In this regard, the customer will not have to change their phones at the expense of choosing another communication service provider. Furthermore, these Sim cards will be provided at a small cost as they will be made at the expense of the company and supplied to the customers where needed. A comprehensive SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities & Threats) analysis, comparing Safcom Limited to its competitors can be found in Appendix 1.
Safcom Customers
The company not only targets to attract customers through issuing the standard Sim cards to those who do not have them at the moment of sale but also to provide alternatives for the customers subscribing to the rival companies through the use of a thin Sim card. All subscribers will be registered through their national identity cards, which implies that users below this age will register with the information of their parents.
In another perspective, the establishment will begin within such populated areas as cities where most customers can be reached. When the networks are well established within these regions, the company will start to establish the points through the areas when the network services of other companies are not properly efficient in a bid to gain access to those customers. However, the overall target of customers will be every person living or visiting Australia. This attribute implies that the company can become the best company in the market since it can share the customers of all companies using the Sim cards.
Moreover, it possesses the capacity to receive fresh customers as other companies do in Australia. This development will reveal a double edge sword to tackle the prevailing challenges that are making the market entry hard and unachievable. The market of their services is expected to be beyond reproach until the rival companies decide to use the thin Sim cards. Most customers will have subscribed to Safcom Limited and received its services, which can make them loyal and satisfied to choose its networks.
Suppliers
As presented in figure 2, Safcom will offer various services which call for an integrated evaluation of where each service will come to arise. These include the supply of electronic devices, hired firms, security services, data protecting, satellite services, and customer care management.
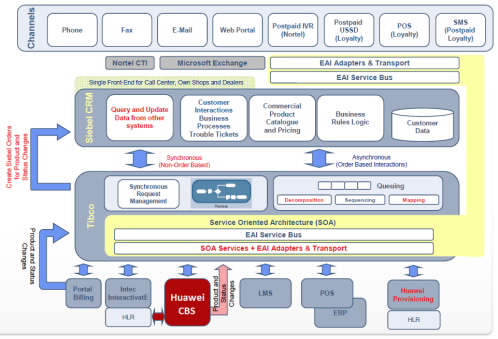
Siebel Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Siebel will be one of the suppliers to offer Safcom services and products of sale management using technical analysis of demand-supply. The company is owned by Oracle Corporation and its headquarters are located in San Mateo within California (Marshall, 2014). The company will market services, provide reliable devices for sale, and develop digital electronics for Safcom’s use.
TIBCO
TIBCO is a software service provider that develops and secures information for financial calculations, cloud computing, data management among other features to facilitate the efficient running of Safcom. The headquarters of the company are found in Palo Alto within California, but their services and offices are distributed throughout the globe. It is a key competitor of Oracle Corporation.
Marketing and Promotion of Safcom Limited
The prevailing advancements in information technology (IT) together with other forms of advertisement will facilitate the marketing of Safcom’s products and services. Some of the effective strategies of advertisements for the business will include the use of posters, signboards, brochures, and magazines (Pride & Ferrell, 2008). These strategies will target the people living within the cities because they could be reached quite easily. For instance, there will be a billboard or poster outside the business house to show the name and services offered. The name of the business will be visible at night because it will have light enhancements.
The public notice boards will be fed with the services and products being provided by Safcom. Therefore, people will get contacts of Safcom and become aware of the presence of the network. The clients will have contacts that could be used to request and inquire about the services and information on how the services are offered and the best way to receive them. In fact, since voice calls do not incur much cost or time, a service line will be established to handle the requirements of the target clients.
Internet marketing such as the use of social media is being applied by the Australians in platforms and pages on Facebook, Twitter, and Google plus to reach and serve the clients effectively (Pride & Ferrell 2008). Also, the management will establish a website where clients will find explicit information about the business. The information contained in these pages and platforms will include news and events, contacts, business identity, products and services, working hours, and a chatbox. Moreover, the internet will allow the collection of suggestions and comments from clients to enlighten the investor in making modifications that can fit the demands of clients. Other forms of advertisements will include mass media and networking.
Safaricom’s Pricing Strategy
The company has planned to counter the stiff competition by offering low prices to the customers. However, it is may reduce profit in the long run. Also, the financial statements show an increase in Safcom’s financial position hence the strategy is reliable (Grant, 2010). Therefore, it can help the company to address its weakness and develop its strengths. The price of the products and services will depend on the production, distribution, and marketing cost (Weinstein, 2004).
Once these costs have been calculated, the price of the products and services will be identified depending on their quantities and location. Furthermore, the imported products will have higher prices due to taxes and shipping costs. These prices will reduce if the sales rise successfully and a cost-effective system is attained. Conclusively, the company will follow its corporate strategies and match between them and business approaches to thrive the Safcom in the ever-expanding market with numerous companies growing globally.
Safaricom’s Location/Assets
Location
The headquarters of Safcom will be in Canberra. Since Canberra is the capital, customers will be able to access the services adequately. Where possible, most assets of the company will be hired whereas others will be constructed such as the network transmitters among others.
Plant and Equipment
The most vital concern equipment will be the computer of various forms to perform the companies’ chores. These will be bought when new to affirm their security and prevent inference with other organizations. All the tools of work required in the company will be bought while new.
The Founding Team
Charman
S/he will serve to manage the operation of the company and respond to the calls of the managers. The chairman will be the CEO of the company. The chairman must have a degree and seven years of experience as a manager in another company.
Vice-chairman
S/He will undertake the shores of the chairman when he directs.
Secretary
The secretary must also have a degree and three years of experience from another institution. His/Her duties will be to record issues discussed in a meeting
Treasurer
He/She will have a degree and 4 years of experience in finance management from a reputable firm. He or she will control funding and allocate funds to the branches of management accordingly.
Succession Planning
The succession of leadership will apply depending on the qualification and selection determined thorough vetting of the shareholders. Therefore, each of the selected individuals will have qualifications dictated before appearing in the vetting committee.
Limitations and Assumptions
The development of Safcom will mitigate many loops about new opportunities and techniques (Mangold & Faulds, 2009). This development is expected to integrate marketing through Facebook. It is targeted that a company/business will have signed customers. The development of Safcom is being tested and will be available after some time. There are several risk attributes that can affect the progress and establishment of Safcom. Risk factors for the business include poor management of resources, theft of resources, death of the investor, and lack of enough clients to maintain it. In other cases, the manager might leave the job causing a high impact on the progress of the business if other leading employees are unavailable.
A contingency plan has been implemented to cover some risk factors that are prevalent in most starting businesses. First, accidents will be covered by an insurance company so that the lost facilities are replaced in such incidents. Secondly, in case the employee vacates the office unexpectedly, the general manager will take charge of the emergency issues before another employee is hired. Also, this replacement will be effective for the firing of the manager in cases of mismanagement.
Financials
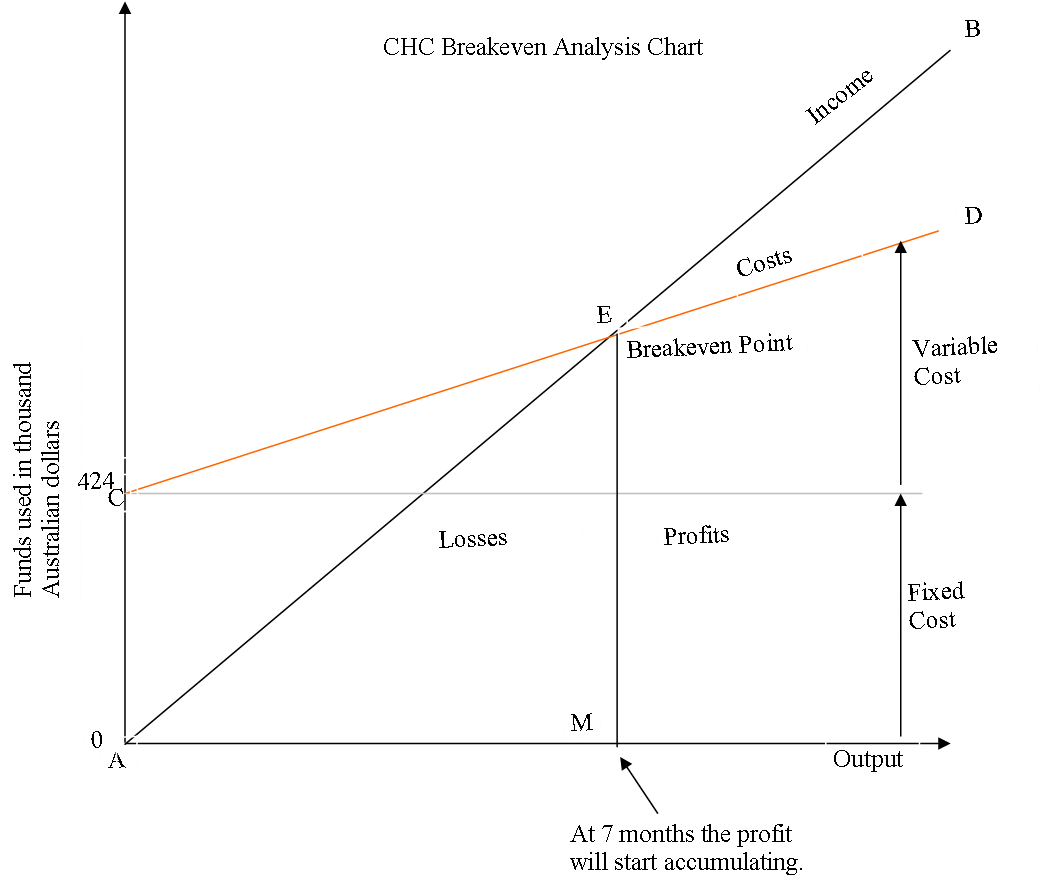
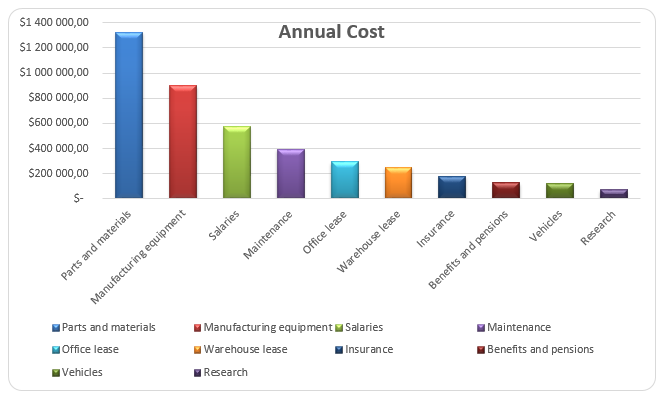
Appendices 2, 3, and 4 contain the projected cash flow, break-even analysis, and the Pareto chart respectively. The statement for financial performance for the business will only be available after the first year of operation (Li & Zhang, 2011). Safcom will run with a funding of $4250500.
Risk and Risk Management
Other companies can take over the strategy initiated by Safcom and start using the thin Sim card for rendering services to its customers. This adoption can lead to an immature establishment of the company and failure. This risk among others can be categorized as follows;
Personal
There is a possible loss of shareholding funds in case the business fails to make profits or is declared bankrupt.
Financial
The company has managed to get enough funding to fund its growth holistically at the establishment point. This aspect makes the identified business opportunity vulnerable to imitation, which can arrest the smooth functioning of its functioning. The total starting funds of the company will be $4250500, which wholly be used to establish the company for the first financial year (12months).
Legal
There may be a legal requirement where the court can allow the attachment of the thin-Sim on the standard Sims. However, a security audit on information confidentiality will be conducted by Oracle corporation to verify that information cannot be shared between the subject rival companies.
Competition
As mentioned earlier, other companies may adopt the new thin Sim strategy and make the strategy uncompetitive. However, Safcom will establish a patent to secure the use and ownership of this idea in order to regulate its application.
Knowledge and Experience
The qualification of the team that founded Safcom does not comply with all the requirements dictated. However, this team will retire and a new member with the specified qualifications will be selected or appointed.
Change Recognition
Social
If this idea reaches the target customers adequately, there is possible abrupt attainment of customers. This can be facilitated by the efficiency and attitude that people take in regard to the business. A positive attitude will lead to the development of an acceptable company offering competitive services.
Legal
When the court verifies the use of the thin Sim cards, there will be changes made throughout the country in terms of strong markets where Safcom can enter the market.
Economic
The company should have an annual target of establishing its business services in at least three countries outside Europe. The company should work to increase its business partners and the number of employees.
Political
Safcom will allow the government to create a strong market where there will be competitors to motivate the development of efficient and reliable services to the public.
Technological
Technology is the strategy being used in this business plan through the development of the thin Sim. It can be achieved through disciplined use of the business capital and annual SWOT analysis. The company should also increase the number of its digital transmitters and incorporate modern devices into its operations. This increment can be achieved by partnering continuously with modern technology companies such as Oracle Corporation.
Likely Business Success
Safcom has the chance of becoming successful in the market. This success can be initiated from continuous analysis of its performances. The customers’ interests should be addressed to provide a competitive advantage over the emerging low-cost carriers. The robust operations in terms of adhering to the low cost that the company aims should concurrently be affected by the alternative marketing strategies. However, it will ensure the maintenance of cost advantage even though it will be in a long term (Grewal & Levy, 2010). Assuming that other companies will not adopt the application of the thin sim card, there is a significant probability that the business will flourish.
Appendix 1: SWOT Analysis
Appendix 2: Cash flow
Appendix 3: Break-even Analysis
Appendix 4: Pareto Chart
References
Alkhafaji, A. & Aslin, R. (2013). Strategic management: Formulation, Implementation, and Control in a dynamic environment. New York: The Haworth Press.
Blackwell, E. (2008). How to prepare a business plan (5th ed.). London: Kogan Page.
Grant, R. M. (2010). Contemporary strategy analysis (7th ed.). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
Grewal, D., & Levy, M. (2010). Marketing (2nd ed.). Boston: McGraw-Hill Irwin.
Jenster, P. V., & Hussey, D. E. (2001). Company analysis: determining strategic capability. Chichester: Wiley.
Katz, R., & Valiquet, D. (2012). Telecommunications and lawful access the legislative situation in the United States, the United Kingdom, and Australia. Ottawa: Library of Parliament.
Laffont, J., & Tirole, J. (2000). Competition in telecommunications. Cambridge, Mass.: MIT Press.
Li, Y., & Zhang, Q. (2011). The Application of Principal Component Analysis on Financial Analysis in Real Estate Listed Company. Procedia Engineering, 15, 4499-4503.
Lindsay, D. (2012). ISP liability for end-user copyright infringements: the High Court decision in Roadshow Films v iiNet. Telecommunications Journal of Australia, 62(4), 56-76.
Ling, R. S., & Donner, J. (2009). Mobile communication. Cambridge, UK: Polity.
Mangold, W. G., & Faulds, D. J. (2009). Social media: The new hybrid element of the promotion mix. Business Horizons, 52(4), 357-365.
Marshall, P. (2014). An interview with Ian White Western Australia Location Manager Oracle Corporation Australia Pty Limited Perth, Australia. Journal of Global Information Technology Management, 3(1), 49-52.
Pride, W. M., & Ferrell, O. C. (2008). Marketing (14th ed.). Boston: Houghton Mifflin Co.
Prinz, F. (2011). Competition architecture. Salenstein, Switzerland: Braun.
Weinstein, A. (2004). Handbook of Market Segmentation Strategic Targeting for Business and Technology Firms, Third Edition. Binghamton: Haworth Press.