Introduction
The purpose of this report is to provide strategic consultancy to the South Korea-based Samsung Electronics Company (which is a wing of the giant conglomerate Samsung Group, established in 1969) by focusing on one of its business units in a particular industry. According to Samsung (2014), geographically the company has presence in many countries across the globe and it has divided all its diverse business operations in three main business units, which are IT and mobile communications unit, consumer electronics unit, and device solutions unit. This report focuses on conducting strategic analysis on Samsung’s information technology and mobile communications unit particularly in the European market. In order to do so, the paper analyses the competitiveness of the European industry, evaluates the strategic positioning of the company’s business unit, explores the potential strategies that the business unit might pursue, and arranges certain apposite recommendations in due course with some concluding remarks.
The Analysis of the Competitiveness of the Industry
In spite of the great level of competitiveness in the European industry, Samsung’s information technology and mobile communications unit is doing a great job there and according to a report of Reisinger (2013), in certain European Union member states, the use of some groundbreaking strategies aided Samsung to boost the market share of Smartphones by more than seventy percent. The World Bank (2012) suggested that even though the EU market is highly competitive and is affected by regulatory and policy barriers, the global giants are able to generate huge turnovers annually due to their economic efficiencies and the effective consumer demand. In fact, The World Bank (2012) stated that the business environment of the European market is quite attractive in terms of overall ranking, as shown in the figure below:
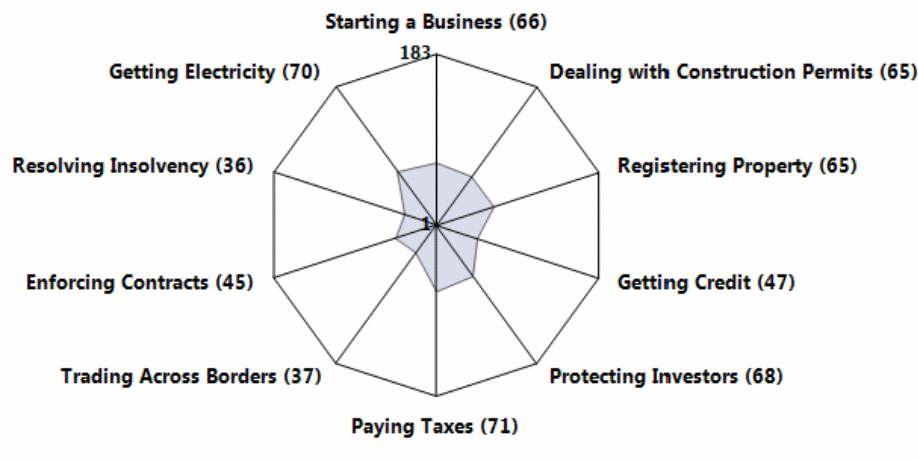
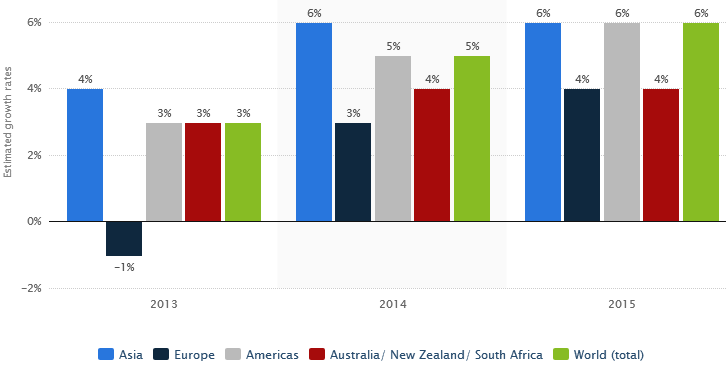
Nielsen (2015) noted that the consumer confidence of Europe is developing gradually as the impact of the global financial crisis is disappearing, and the business environment is advancing accordingly as well; moreover, according to Statista (2016), Europe’s industry has developed by four percent in 2015:
In order to comprehend the competitiveness of the European industry for Samsung’s IT and mobile communications unit profoundly, it is essential to scrutinise the following factors:
Threat of new entrants
As the figure above shows, starting a business in Europe has large number of barriers, and so this threat is very low; in fact, a new entrant would require huge funds to operate in this saturated market, and it would be unable to participate and sustain in competitive price wars (Brostoff 2014).
Threat of substitute products
Threats of substitutes are extremely high in the IT and mobile communications industry as the same items are also offered by companies like Lenovo, Mitsubishi, Acer, Apple, BlackBerry, Dell, Google, Toshiba, Motorola, and Sony; however, almost fifty percent of all Smartphones purchased by European customers are from Samsung’s brands (Reisinger 2013).
Bargaining power of customers
This is extremely high as well because buyers switch to other items easily due to the array of similar offerings by many other corporations at reasonable prices (Brostoff 2014).
Suppliers’ bargaining power
It has been suggested that due to the existence of numerous efficient suppliers in the localities and their low priced offerings, this threat is moderately low for Samsung in Europe.
Competitive rivalry
According to Amini (2014), this threat is very high for the company, as there are many multinational and local giants operating in Europe, for example, Sony, LG, Panasonic, Microsoft, Apple, Nokia, and so on.
Political factors
Most of the nations within the EU possess stable political condition, which is very important for Samsung’s operations; therefore, the business is rarely hampered due to political clashes.
Economic factors
The economy of Europe has revived from the global economic downturn and now it is flourishing in terms of better consumer demand, more per capita income, and more income stability; consequently, the economic conditions are very much business friendly.
Social factors
Europe’s society is increasing becoming more dependent on the use of technologies because people cannot think a day without sharing social networking messages through their androids; moreover, Samsung’s brands image is much admired there.
Technological factors
Operating in Europe is very much advantageous because all kinds of technical supports are easily available everywhere, and the suppliers, dealers, and retailers possess much technological knowledge to facilitate Samsung’s activities.
Legal factors
Operating as a multinational has many legal obstructions in Europe, and all companies are regulated with strict tax laws, labour laws, environment and consumer protection laws, and other commercial laws.
The Analysis of the Strategic Positioning of the Company
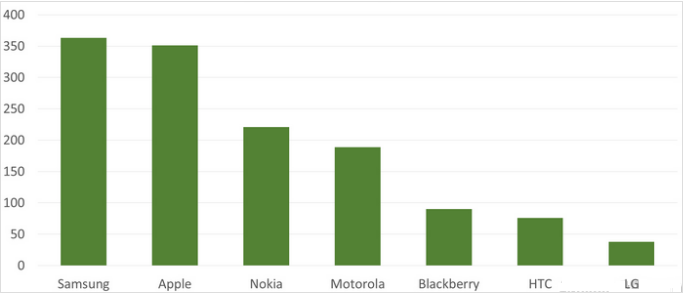
Samsung is constantly developing the strategic positioning of its IT and mobile communications unit in the European market; for example, PR Newswire (2016) has reported that the company is releasing stimulating and innovative commodities as part of its recent strategy in Europe; moreover, the new Samsung President in Europe has declared to advance the strategies and portfolios of commodities further. PR Newswire (2016) also noted that the company is shifting its strategic position in handling fiscal instabilities through reinforcement of connections with customers and dealers, and proffering items such as notebooks and computers in the significantly prospective markets; besides, Cheng (2016) argued that worldwide Samsung is undertaking a strategy of incorporating the latest technologies in androids and reducing their prices. Dudovskiy (2015) suggested that the company is successful because its strategic position is to enhance its brand image through huge expenditure in all forms of marketing and advertising tools – the chart below shows that it has more advertising expenditure than that of its rivals:
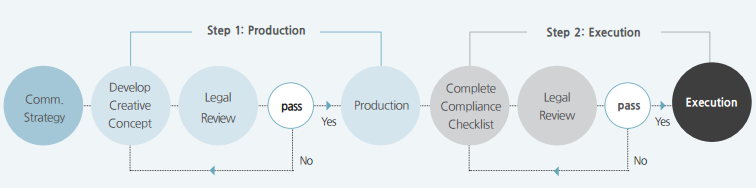
Dudovskiy (2015) argued that another reason behind the success in the marketing strategy is that the company focuses on analysing the legal effects of the advertisements through strict procedures before displaying them, and this prevents harm to its brand name:
International Data Corporation (2016) noted that Samsung was the market leader in the android industry in 2015 with more than twenty-one percent share, and this was possible because of its strategy to launch admired items like S6; moreover, Novet (2015) stated that this strategic stance has also helped Samsung to get back the leading position from Apple in the market. Nisen (2013) suggested that the strategies of Samsung and Apple are completely different, and under pragmatic circumstances, Samsung’s strategies seem to be more sensible and fruitful; for example, Samsung is able to learn things quickly from its rivals and adopt good things from their strategies; moreover, if Samsung has money in hand, it tries to utilise it in productive ways. Apple keeps its excess money in hand while Samsung expends it to maximise sales; for example, Samsung expended more than five percent of its turnover in R&D whilst Apple expended about two percent (Nisen 2013); consequently, Samsung is able to augment its sales annually and according to projections, in December 2016 Samsung’s sales will reach 203,240 million (Reuters 2016).
Analysis of the Potential Strategies That the Business Unit Might Pursue
In the European market, a number of potential strategies are pragmatically available to Samsung’s IT and mobile communications unit in the future, and these require certain modifications in the current strategic positioning, and consolidation of some new strategies in the current positioning. Fernandes (2015) noted that Samsung wants to focus on the idea of Internet-of-Things (IoT), and it dreams that through this program, people will be able to control and supervise household gadgets (washing machines, refrigerators, and televisions) through their Smartphones when they are away from home; moreover, the company hopes to finish integrating the household gadgets with IoT features by 2020.
Zeeman (2016) stated that to avoid diminishing sales figures in the future; Samsung is prepared to undertake some quick strategic repositioning so that it is able to boost the figures continuously; for example, in case of any demand downturns in the IT and mobile communications market, Samsung will diversify the product portfolios and enhance the software with some innovative ideas. According to Sepherteladze (2015), Samsung knows that people’s preferences change continuously and so it should improve and revitalize the current offerings; in fact, due to this understanding, the company was able to attain success in the past, and it expects that in the future it can perform well by expanding the crucial technologies and making people’s lives easier and comfortable. Last year, Apple’s corporate strategies hampered Samsung’s market shares in areas like China, Korea, and Japan (Sims 2015); however, in order to avoid such occurrences in the European market in the future, Samsung can pursue growth strategies in the Smartphone industry by launching new versions of its flagship products, just as it did in case of Galaxy S7 (Tanner 2016).
Samsung (2014) identified that every year, as the company’s sales and productions increase, the amounts of greenhouse gases released increase accordingly; this has been illustrated in the chart below:
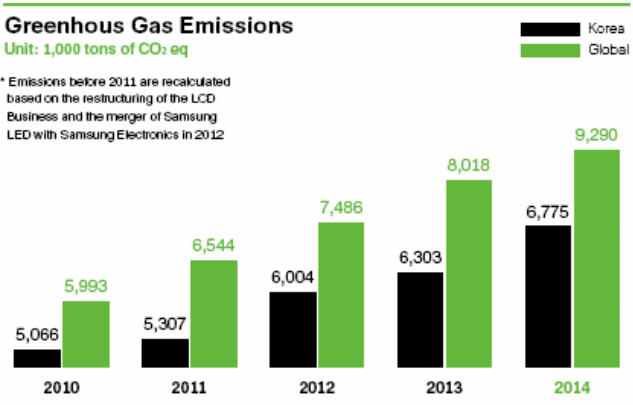
To reduce the impact, the company wants to pursue certain strategies by 2020; for example, it wants to instigate eco-friendly activities like collecting two hundred and fifty million tons of toxic gases, lowering emanations by seventy percent, creating eco-friendly workplaces, reducing water wastages, boosting recycled items, collaborating with eco-friendly suppliers, creating energy-efficient products, and so on (Sustainability Report 2015).
Recommendations and Conclusions
Recommendations
The company should create stronger alliances with component and chip manufacturers in Europe in order to enhance and improve the supply chain, as this would help the company to become more production efficient, timely, and competent in the future. In addition, the company should try to adopt lean production techniques in its IT and mobile communications factories in Europe, so that it is able to lower production costs and improve the quality management systems significantly, as well as helping the delivery of manufactured items ‘just in time’.
It is important to note that these mechanisms can assist the company to attain economies of scale, and this in turn can give the company significant competitive advantage over the key players in Europe, like Apple Inc. In addition, it has been discussed earlier that the production facilities of Samsung is not impressively energy efficient, and the company is liable for large amounts of pollution. The company should understand that the European consumers, in present days, are very much conscious about environmental sustainability, and this kind of activities can leave a negative image about the company in their mind. As a result, rather than waiting to integrate the environmentally friendly facilities by 2020, the company should take immediate strategic steps to lower the emission levels in order to protect the company’s brand image.
Conclusions
It can be argued that Samsung is a highly experienced multinational corporation, and it is very much aware of the costs and benefits of the strategic steps it undertakes in the European market. With the strategic knowledge it acquired from its long experience, it has been able to gain the market leadership in the European android market. In addition, it is notable that it has gained significant amounts of competitive advantage over the players in the IT and mobile communications market. However, as the European market is highly competitive and saturated with similar products from the rivals, Samsung needs to update its strategic positioning constantly. Moreover, there are many areas where the company should modify and enhance its strategies in order to preserve the success in the European industry.
Reference List
Amini, M 2014, Samsung’s Risks of Operating in Europe, Web.
Brostoff, B 2014, Samsung Client Report, Web.
Cheng, J 2016, Samsung Makes Aggressive Play for Emerging Markets, Web.
Dudovskiy, J 2015, Samsung Marketing Strategy, Web.
Fernandes, L 2015, Samsung Means Business: A Strategy Shaped by the Internet of Things, Web.
International Data Corporation 2016, Smartphone Vendor Market Share 2015 Q2, Web.
Nielsen 2015, Consumer Confidence, Web.
Nisen, M 2013, Samsung Has A Totally Different Strategy from Apple, and It’s Working Great, Web.
Novet, J 2015, Samsung Takes Back Global Smartphone Sales Crown from Apple in Q1 2015, Web.
PR Newswire 2016, Samsung Unveils European Marketing Strategy, New Products and Directions, Web.
Reisinger, D 2013, Nearly Half of Smartphones Sold in Europe Hail from Samsung, Web.
Reuters 2016, Samsung Electronics Co Ltd (005930.KS), Web.
Samsung 2014, 2014 Samsung Electronics Annual Report, Web.
Sepherteladze, S 2015, Samsung Marketing Strategy: the Master Brand, Web.
Sims, G 2015, Samsung Loses Market Share to Apple in Its Home Stomping Grounds, Web.
Statista 2016, Estimated Growth Rates for the Global Electronics Industry from 2013 to 2015 by Region, Web.
Sustainability Report 2015, Global Harmony with People, Society & Environment, Web.
Tanner, P 2016, What Is Samsung’s Growth Strategy in the Smartphone Market, Web.
The World Bank 2012, Doing Business, Web.
Zeeman, E 2016, Samsung Smartphone Strategy: Diversify Offerings, Improve Software, Web.