Abstract
Multi product strategy is the private disclosure of the companies with differentiated product line’s attributes. The discriminated multi-product implies multiple attributes to gaining consumer’s satisfaction and achieving the market share. The consumers’ response for each discriminated product should lead the firm to initiate different strategies. Extra diverse strategy would bring the threat for profit maximization. Thus, the firms are eager to come in an equilibrium disclosure for differentiated product line and this is identified as a multi product strategy. This term paper would consider the multi product strategy formulation, strategic process multi-product plan, decision-making process, organizational structure and multi-product strategies implementation process reason to use multi-product strategy in global market environment, different level of diversification, and essential criteria of multi-product firm. It also enlightens on the organizational structure and strategy implementation, preferences for quality, Industry life-cycle, market segmentation of a multi-product firm in global environment. One of the most important issues for these types of firms is the organizational structure and in this paper it will discuss proper figure. The whole paper will evaluate the strategic management, strategy management process or transformation plan, strategic analysis and external and internal environmental issues. There are four approaches to analyze internal environment of a company such as the SWOT analysis approach, critical success factors approach, the value chain approach, the core processes and system approach will be assessed. Moreover, will discuss the monopoly strategy in multi-product firm, advantages to introducing new product and the multi-product strategy, factors to draw a global firm’s strategy, methods to increase the profitability in a global environment. Finally it illustrates the importance of policy and procedures in implementing strategy, pricing methods or strategy, strategy implementation, leading and execution process, relationship of strategy with ethics and social responsibility market segmentation of a multi-product global firm, and acquisition and restructuring of the strategies.
Introduction
Strategies are a set of tools or techniques to achieve desired goals. The term ‘strategy’ comes from the battle field concept. Now this time in the business sector it is used for the cold war not for the front war. This term is starting to use in early 1970s. Firm that operates their business in more than two countries is termed as global firm. A firm through their global operation incarcerates production, marketing, logistics, research and development (R & D), financial advantages etc. These characters are not making available for merely domestic competitors. A number of renowned multi-product global firms’ are- Unilever, Samsung, LG, Sony, McDonald etc.
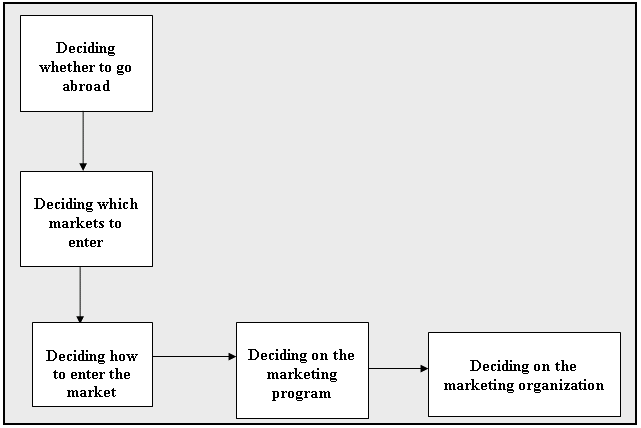
Global based firms plan, operate and coordinate their activities with a broader view on the worldwide market. To do so, the company does not need to be large enough. Practice of global nichemanship can make a small and medium sized firm as a global firm. Following figures shows major decision making process of a global multi-product firm:
The Importance of Multi-product Strategy
- Multi-product Strategy is an action-plan, which the firm develops in order to compete in varies product-markets.
- It progresses performance through applying the core competencies in order to pursue opportunities in the external-environment in over one product-market.
- This strategy smoothes out revenue & flows of earnings as well as it gives the opportunity to earn additional profits through developing the core competencies in further ways.
- The Multi-product Strategy provides the solution of the question- firstly, what goods will be offered and secondly, how will these goods be managed.
- There are many grounds to introduce Multi-product Strategies to Diversify, such as- to reach profitable growth is one of the causes.
- A firm always wants to minimize the risks; therefore, firms rely on Multi-product Strategies to decrease the hazard of being involved along with any single product-line.
- It also expands the economies of scope.
- This strategy aspires to broaden the firm’s brand into further product-areas.
- It offers the way how the firm can adopt core competencies in other value-creating ways.
Different level of Diversification (Low-level, Moderate-to-High and very high)
Low-Levels of Diversification
This level consists of single business or Dominant business, in former one over 95% of sales revenue generates from single product or a variety of the single-product and in dominant-business from 70% to 95% of revenue generates from single-product business. Here it is necessary to say that growth in one of its non-dominant product line is able to alter the nature of any firm’s diversification.
The Moderate to High-Levels of Diversification
Under this level of diversification, sales revenue of a firm’s is not depends on the single-product business, that means, it forms of Related-Diversification or related-constrained multi-product strategy, for example in case of related constrained and related linked less than 70% of revenue creates from dominant-business and in production process all businesses share materials, technology, marketing process and distribution channels. However, in related-linked business limited-links presents between businesses. Most of time, these types of multi-product firms apply the SBU (M-from) the multidivisional structure. On the other hand, when they follow unrelated-diversification Multi-product Strategy, it never shares their transport-resources, organisational behavior, and the core-competencies among its divisions. Operational Relatedness will be accomplished if the firms effectively share assets & actions to manufacture and sell their goods. However, corporate-relatedness will be reached while the core competencies are efficiently transferred.
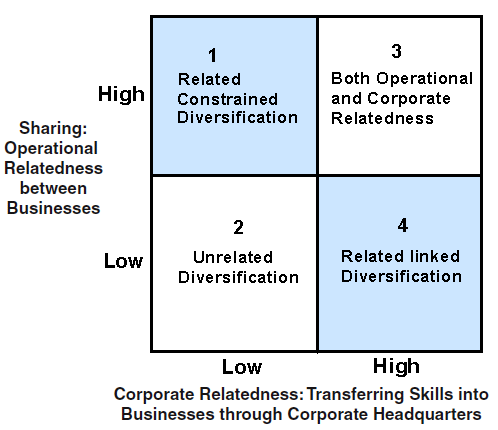
The Strategic advantage of operational-relatedness and the related-constrained Multi-product strategy is the firms can share functional activities and other resources but it has risk that it may reduce the production-capability. The Strategic advantage of corporate-related Multi-product Strategy is they have transferred the core competencies and they arrange managerial and leadership training programs to improve the production capacity and distribute it in international market.
The Very High-Levels of Diversification
In this level, most of the business of the multi-product firm will be completely unrelated and must be less than 50% of the sales revenue will be generates from dominant-business and there will be no connection presents among businesses. The Managerial motives to diversify is it decreases the risk of cutting their jobs and the main reason for higher-level executive is high diversification amplifies the firm’s overall size and there are close link between size and executive-compensation. As a result, managers, high level executives and other employees would like to have the very high-levels of diversification multi-product strategy.
Essential criteria of a multi-product global firm
Foreign languages, rules and regulation, political and legal suspicions, economic systems, foreign currencies, multidimensional customer tests and needs are the issues those a global firm has to need. In order to sketch a global field and also make the business easier and safe following factors are considerable:
- Better product quality or low price than firm’s domestic market is a feature of global firms.
- Compare to a domestic market foreign market is a source or opportunity of higher profit.
- Large scale of production in terms of economies of scale is a gate way of larger customer base.
- Multi-product firms have no dependency on any one market and it’s a factor of reducing risk.
- A portion of consumers require international service when they stay abroad.
Strategy and strategic management
Strategy is the game plan of a company’s management that evaluates market position, operation procedure, attract and keep potential and growing consumers, achieve organizational objectives and compete successfully. A company’s heart and soul is managing the tasks of strategy.
A managerial process in which a strategic vision development, setting objectives, strategy crafting, strategy implementation and execution and at last performance appraisal, new development supervise and took alternative strategy or correct the existing if requires are accomplished by a manager. Strategic management process is incomplete if these tasks are not properly carried out.
Significance of strategy
Following are the factors behind the significance of strategy from view point of multi-product global firm:
- Managers of a company needs strategy to identify the ways through a company’s business would be accomplished and proactively shape business of the company.
- Exert strategic leadership is the responsibility of management. This prescribe the organization whether and when it shifts it’s track.
- Strategy is the road map of doing any business and it builds the perception of managers.
- Strategy makes a firm conscious so that it please consumers and sketchy the way of competitive advantage.
- It is important for both mold the efforts and for decision making.
Types of strategy
Based on components or elements strategy are of two types. These categories of strategy draw the way to be a multi-product global firm.
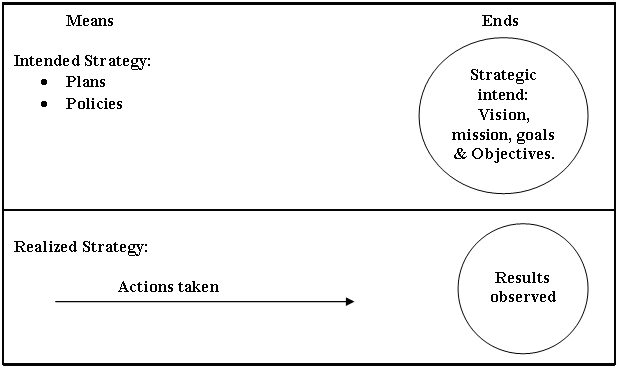
Intended strategy
Based on historical data or information a theoretical assumption is intended strategy. Intended strategy provides guidelines how to conduct or find out the ways of the work of the organization. Intended strategy is of two types:
- Plans: Plans of an organization describes the steps needs to take in conducting tasks of the firm. In another word, dealing with actions is plan.
- Policies: Policies generate rules and regulations of an organization. It also defines the constraints and the limitations of the firm. Policies make enable to understand the intended strategy of the organization.
Realized strategy
Realized strategy evaluates the ratio of development. It also measures the amount of tasks completed. Incomplete tasks are labeled as unrealized strategy.
Strategy management process or transformation plan
A multi-product firms needs to tag along with a set of sequential steps. These steps are defined as transformation plan. A short description of this plan is presented in bellow:
Strategic vision development
Strategic vision is for long term direction that defines the nature of the company and originated from the question-“Where are we going?” Developing a strategic vision manager of a firm has to identify the answer of following questions:
- Where are we wanted to go?
- What should we focus in future (product and services, consumer, technology)?
- What form of organization do we want to be?
- What do we want to achieve in long time (after five years)?
Answer of the above questions sketch the business plan; identify long-time business objectives and organizational identity. According to the query of this term paper, vision of a global firm is –capture different markets through their long product line.
Setting objectives
Objectives are the implementation of strategic vision developed by the managers and measure the difference between target performance or wants to achieve and results or outcomes. In short, implementation of vision and mission in practice. From view point of managers objectives are of two types:
- Financial objective: Management’s aspiration to achieve financial outcomes is the concept of financial objectives. Earnings or revenues, market value, cash inflows and out flows, growth rate, credit worthiness etc. are the areas of financial objectives.
- Non-financial objectives: Non-financial objectives are for stronger the market position, enlarge competitiveness, enter into new market, reduce costs, present innovative product and services, achieve customer loyalty, magnify market share, continuous improvement of technology, keep and grow competitive advantages, capture the opportunities to expand the existing business. These are the regions of non-financial objectives of a multi-product global firm.
Crafting a strategy
Ways of achieving target is a critical issue of management. In this procedure, strategy is the means or way and objectives are ends or outcomes. Be a global and multi-product firm strategies are the mixture of –necessary steps in practice reissue or make improvement whether have need of, evaluate market condition and threats of the competitors.
Strategy implementation and execution
Take necessary steps to ensure organizational capabilities and attain target objectives just in time are the tasks of strategy implementation and execution. Skilled managers are capable in doing the indispensable tasks, prove expertise and brought better outcomes. Strategy implementation is the concept that overlooks managerial exercise of chosen right strategy for right purpose. On the other hand, under strategy execution managerial task is to supervise the adopted strategy and took necessary steps develop that. Areas of strategy execution are- strong organizational foundation, company’s internal resources, policy and procedure that support strategy, took right strategy for the right place, motivate employees, established reward system, build organizational culture, continuously improve data base, information system, and operating system.
Performance appraisal, new development supervises and takes action for corrective adjustments
Measuring the growth of organizational performance along with both internal and external environment placed at the top. In strategy management process evaluating company’s current situation and then measure strengths and weaknesses and also conscientiously monitor threats and opportunities.
Factors to draw a global firm’s strategy
Crafting strategy for multi-product global firms need to pay attention a number of factors. Either directly or passively these factors influence on the strategy making and management process. These factors are also useful in inflexible situation. A short description of these factors are:
- Societal, political-legal and citizenship consideration: Every organization need to connect with large population of the society. Concerning this government determine what a firm can and can not do. All organizations are legally bound to follow this rules and regulations when conducting their business activities. Different country follows different rules and for this global firms should pay attention those diverse regulations when crafting strategy. These rules and regulations consider ethical values, standard of better community citizenship and perform social requirements.
- Overall factors of competition and industry attractiveness: Another strategy determining factor is considering factors of competition and ways of industry attraction. Price, product and service quality, warranties, performance standard are factors that play behind of strategy tailoring as competitive factors mix. Competitive weakness that could be presented as challenge. These rivals are most prospective opportunities for a strategic crafting.
- Opportunities and threats of the company: Opportunities and threats are another key influencing factor. Both are equally important for strategy in practice. Aim of a company’s strategy is to ensure sound growth of opportunities. On the other hand, threats faced a defense provide by strategy and this could influence company’s growth and future performance.
- Company resource strengths and ability to compete: Considering company’s internal resources is most pivotal factor of strategy shaping. This consideration would capable a firm to invest in a specific opportunity, fabricate the firm to attain competitive edge in market and become a significant part of the firm’s strategy.
- Manager’s personal ambition, beliefs of business and ethics: In strategy crafting procedure, manager’s emotion assesses and guides the strategic course. Managers own vision influence- competition way, positioning strategy, manufacturing image of the company, company’s future perception. Not only these but also manager’s individual ambition, ethical beliefs, values, risk taking tendency, business philosophies has a great influence on strategy.
- Impact on strategy by company culture and shared values: A firm’s culture is made of plans, policies, traditions, business philosophy and practice. A stronger strategic culture makes the way smooth for strategic action and movement and assists to draw strategy. On the other hand, shared values of a company pass on the employees benefit and values given by the firm in terms of their contribution.
The organizational structure and Implementation the Multi-product Strategies
Anderson, S., & de Palma, A, (1992) expressed that the organizational structure is one of the important factors to implement the Multi-product Strategies and it will be different from structure of a single product firm. Generally, the Multi-product firm using the Multidivisional (M-form) Structure which has also 3 variations and these are the Cooperative M-Form, the SBU M-Form and the Competitive M-Form and in the figure 2 this three variations has shown. First of all it should required to consider the reason why a Multi-product firm use this Multi-divisional structure which will considered as follows:
- This is an organizational-structure by which a firm is organized to form economies-of-scope or financial economies.
- The Multidivisional (M-form) Structure is used merely to execute multi-product strategies with moderate as well as eminent stages of diversification.
- This Structure is also develops as the firm out-grows its dominant business-strategy & implements the related-diversification strategy.
By altering policy, the firm has to modify its structure from the current organisational structure to the appropriate form of the multi-divisional structure and these process help to develop its profits level.
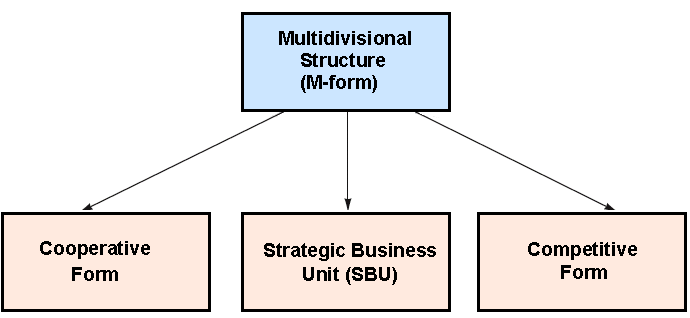
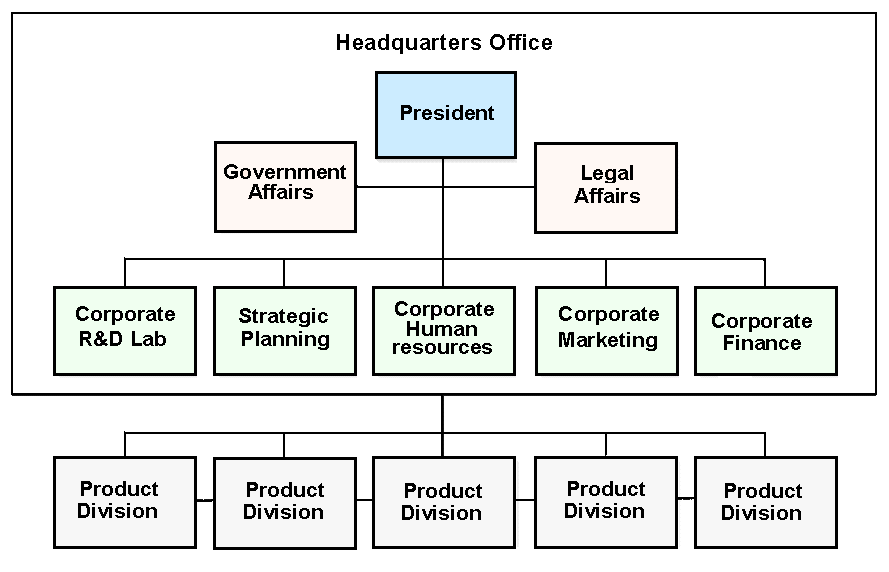
As the Multi-divisional Structure has three different variations, therefore, it should require discussing that these divisions separately and in order to do this, at first the Cooperative M-Form & the Related Constrained Multi-product Strategy will be considered, and it will be representing in figure- 4.
The Cooperative (M-form)
- It is an organisational structure where the horizontal integration is used so that resources as well as actions can be shared among product divisions.
- The President will lie at the central power and control of the venture, which will be composed by five sub departments.
- Five major departments of corporate R & D Lab, strategic planning, corporate HR, Corporate marketing and Corporate- Finance will be headed by them also.
The Horizontal-Integration
The product-divisions are processing information in relation to the resources & actions they intend to share, in addition to it decides how product-divisions intend to share them and production department will be responsible for controlling quality of the production.
Moreover, the temporary-teams or task forces are the 2nd horizontal integrating mechanism which has minimal control upon the multi-product firm.
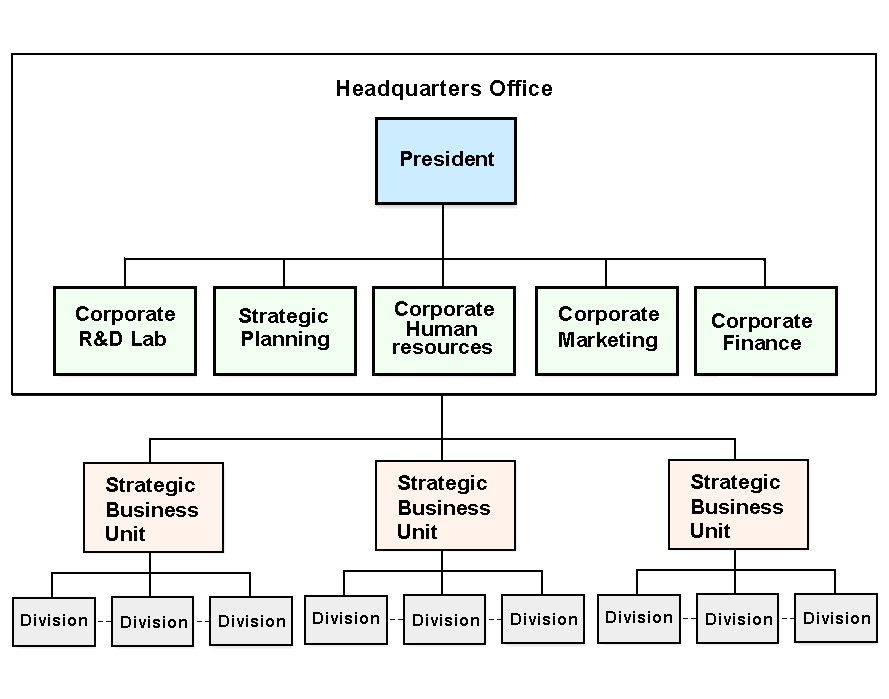
Secondly, it should consider the structure of the strategic business unit (M-Form) & the Related Linked Multi-product Strategy, which has been shown in the figure- 5.
The Strategic-Business Unit (M-form)
- This is an organizational structure where the divisions within each Strategic-Business Unit mainly focus on the transferring core-competencies rather than on sharing assets & actions, which indicates the opposite function of The Cooperative (M-form).
- Comparing to the Cooperative (M-form) structure it can be found that it has also five major departments such as corporate R & D Lab, strategic planning, corporate HR, Corporate marketing and Corporate- Finance.
- All strategic business units are a profit center, which is illustrated & controlled by corporate-headquarters as well as both strategic controls & financial-controls are exercised in order to assess each SBU.
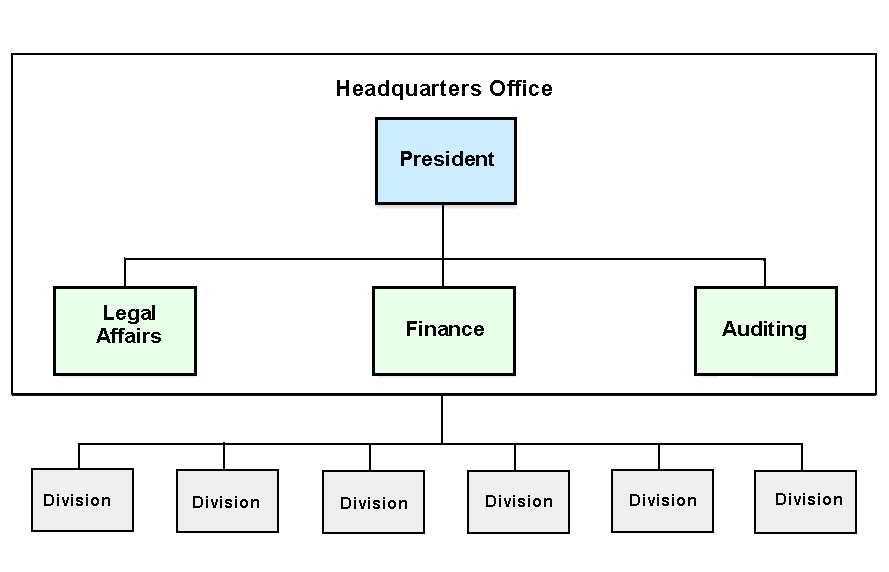
Finally, it should be discussed the Competitive (M-Form) structure and the Unrelated-Diversification the Multi-product Strategy and it has demonstrates in the figure- 7.
The Competitive (M-form)
It is most significant factor here that it is an organisational structure where there is absolute independence among the firm’s divisions and these divisions in fact compete against one-another for the firm’s resources.
- Thomson Business (2008), published that the multi-product firm, which seeks to generate financial-economies rather than improve the economies-of-scope by means of either the operational-elatedness or corporate-relatedness may use the SBU (M-From) structure.
- Normally, the center of attention of headquarters is on performance assessment, distribution of assets, and long run planning in order to make sure that financial-capital is being utilized to maximize economic success.
The Multi-product strategy & relative-preferences for quality
Ghazzai, Hend (2008) argued that the consumer choice may affect from the Multi-product strategy and it may have both positive and negative impact on customer, in addition, the customer choice always changing with respect to the other customers’ choice. Here it will be established that a multi-product strategy perhaps implemented by the monopoly if the customers’ social characteristic aspiration is strong enough. If a customer purchases a highest quality product, customer gets a positive-satisfaction from consuming the best-quality product, on the other hand, if customers fail to purchase quality product then the buyer loses satisfaction.
The Monopoly Strategy in multi-product firm
It is noteworthy that monopoly can exist only when there are strong barriers to the entry of rivals the monopolist can maintain his position as the sole producer or seller of a product only when certain circumstance keep the rivals away from his line of production. First, it should assume that the monopoly is offering a separating list of options to the customers. Then identify the essential situation for the monopoly in order to implement the multi-product strategy in multi-product firm. After that, it will compare the monopoly’s earnings when they present two-qualities to them and profit when they offer only one quality. The barriers or problem of the monopoly’s is appear when it offering a separating list of options has discussed as follows:
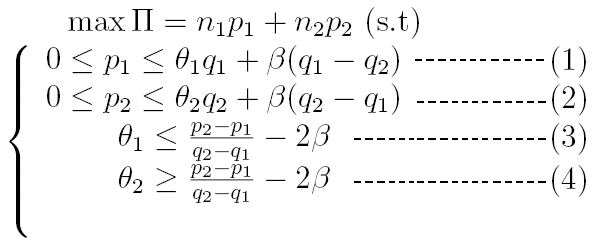
- Condition-1 involves that type -Ø1 customers like to buy the quality-q1 than making no purchase.
- Condition-2 means that type –Ø2 customers like to buy the quality-q2 than making no purchase.
- Condition-3 indicates that type –Ø3 customers favor q1 to q2.
- Condition-4 indicates that type –Ø4 customers favor q1 to q2.
From the above discussion, it can be ensured that the market is fully covered and that the monopoly is proffering a separating list of options. The quality-q1 is purchased by the type -Ø1 customers and the quality-q2 is buying by the type –Ø2 customers.
Ghazzai, Hend (2008) also discussed that Customers with low-intensity of preference for quality purchase the low quality product; on the other hand, customers with high-intensity of preference for quality purchase the product of high quality, therefore to solve the problem monopoly should emphasis on the quality products.
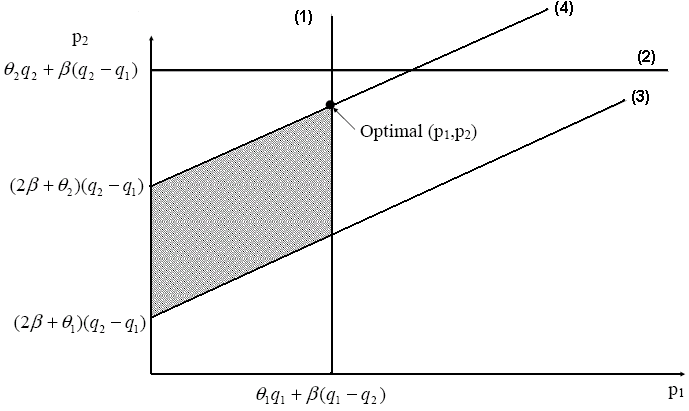
Introducing new product and the Multi-product strategy
Since introduce a new-product is a difficult issue in global competition, numerous manufacturing firms, research departments have studied how effective they can introduce new product effectively. It is easy for a multi-product firm to develop a new project because they have already establishment in global environment. Moreover, they are well organised because there are technologically developed inter-project linkages.
Nobeoka, Kentaro, & Michael A. Cusumano, (1994) stated that one of the main objectives of new-product improvements at the corporate-level is not simply to launch a new technology & design into the single-product line, but also to establish them into the set of product-lines targeting diverse market-segments as rapidly as possible. A multi-product firm may use existing technologies from present and past projects to produce multiple-produce line, in this way they can diversify their business. However, before introducing new product or reintroducing older designs, the firms should consider the existing competitors of the product in market and it should widely decide to follow the rapid design-transfer strategy.
Strategic analysis
Internal environment analysis
Evaluating the strengths that grounds the organization and the weaknesses need force to leave in formulating strategy is internal analysis. Finding the scope of resource allocation is the first step of internal analysis. This analysis occupied the way of the firm’s growth. Factors that have a significant influence on strategy are considered as strengths. Griffin, R. W. (2006), argued that internal analysis could be assigned by the planning department or by the outer consultancy firms. Most of the global multi-product firms appoint consultant for their internal analysis. Internal analysis capable a firm assesses its market position and inter-organizational structure, execute the growing methods of the firm, serve customer value, enjoy competitive advantages, and sketch resource base competing modes in terms of skills and capabilities. Internal analysis is also constructive for risk or threats minimizing, and incarcerate new opportunities.
Areas of internal environment analysis
Strengths and weaknesses evaluation requires considering several relevant factors. Firm’s long term survival and success manipulate by these factors. Common areas that are include in analyzing are as follow:
- Financial position: Cash flow statement, balance sheet, financial ratio analysis and income statement are tool or techniques of financial analysis. These methods are useful to compare and capable available financial resources to utilize, examine financial position and took necessary steps in decision making.
- Product and service position: Awareness of product and service position in market makes a business successful. For a multi-product firm it is an important managerial task to categorize market share according to the market segment.
- Product and service quality: Another key issue of internal analysis is evaluating product and service quality. Continue survive and growth of a product and service prove guarantee of its high quality at a reasonable price.
- Marketing capability: Marketing capability make sure to deliver right product or services at required price in the right place. Regarding this marketing is the task or societal process that includes-product, place, people, promotion, distribution channels, market demand, market positioning and segment, advertising and target market.
- Research and development (R & D) capability: For new product development today’s organization needs to adopt research and development (R & D) either formally or in an informal way. For global multi-product it is difficult to survive devoid of advance technological involvement and practice of research and development (R & D).
- Organizational structure: For product manufacture and get to in a market place there need to have an organizational structure. Corporate level, business level, functional level and operational level are the four essential layer of an organization. These layers are the gate way to assess internal strengths and weaknesses of the firm.
- Human resource management (HRM): Condition that ensures the competitiveness of the firm is providing proper facilities to the employees and proper utilization of the resources. Human resources are the employees who work for the organization. Where as human resource management place right people in the right place. HRM also involve in all management practice and decision making that directly affects the organization.
- Previous and on going objectives and strategies: Previous and on going objectives and strategies are instruction or principles for future objectives and strategies. That’s why, internal environment analysis would be ideal if the firm consider previous and on going objectives and strategies as the indicator of future.
Approaches or ways of internal analysis
There are four approaches to analyze internal environment of a company. A brief description of that are:
The SWOT analysis approach
The acronym of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of an organization is SWOT analysis. In another word, a company’s overall appraisal or consideration is SWOT analysis. With the aim of strengthen a firm’s market position SWOT analysis support the firm sizing up strengths, evaluate weaknesses, external opportunities and threats. In short, overview of a firm’s business position is SWOT analysis. Factors of SWOT analysis are presented in following table:
Critical success factors approach (CSFs)
Critical success factors are those capable an organization achieving triumphs and help to enjoy competitive advantage. Though they are small at numbers but their power of manipulate is high. A combination of environmental factors determined individual company’s critical success factors (CSFs). Factors that manipulate and increase competitive advantage such as-manufacturing costs, product quality, product image, after sales service etc. are considered as critical success factors. Common factors are:
- Industry characteristics: A firm’s critical success factors (CSFs) determine or present feature of the industry. For a global multi-product firm CSFs are-product mix, sales promotion, pricing method and inventory turnover.
- Competitive position: Based on competition or market position CSFs are varying in different firms. A firm of an industry may dominate if it is small in size.
- General environment: General environment are sometimes affect the CSFs and create unnecessary complexity.
- Organizational development: A short term issue that influence CSFs is organization’s internal development and also produces a new CSFs.
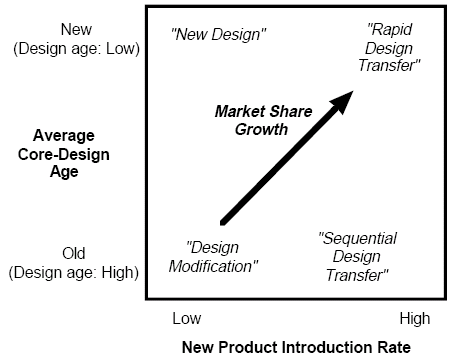
The value-chain approach
Value chain is a frame work that combines primary activities and supportive activities of an individual. Overall level of customer value and financial performance are also constituted here. A set of allied activities that assess strengths and weakness of the firm serve value to the consumer. Functions of a customer value are of three broad categories:
- Product differentiating factors.
- Costs reducing factors.
- Factors that capable to identify customer respond quickly.
Above are considered as key internal factors help a firm to gain competitive advantages. It is also mentionable that firm’s key internal factors are more cheap or better than its competitors. Aggregate performance of value activities support a firm’s product and service to design, manufacture or produce, distribute and marketing. There have nine fundamental activities those could be grouped into two broad categories as mentioned early on this concept and these are regard as strengths and weakness analysis tool.
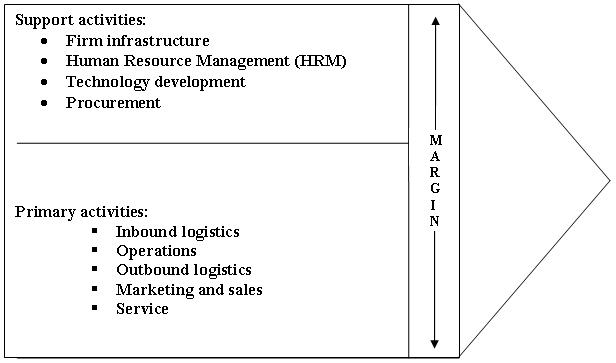
- Primary activities: Activities that work for the physical creation of products and services of the firm are primary activities. Primary activities include-inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales to the buyers or consumers and at last after sales service.
- Support activities: Allowing primary activities in order to make available infrastructure or effort for the placement of on going origin. Factors that foster the support activities are- firm infrastructure, human resource management (HRM) or placed right person in the right place, technological development and procurement or purchasing.
The core processes and system approach
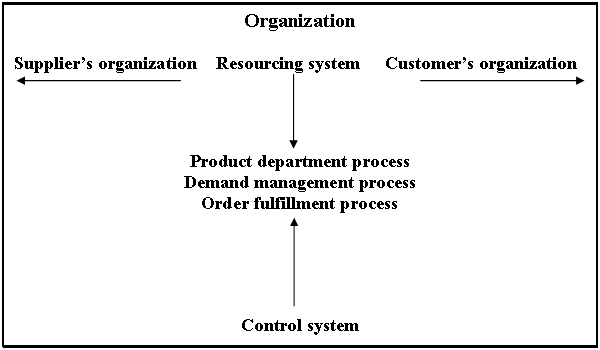
Core processes and system approach is a combination of activities performed by group. As value chain approach, core process and system approach combines two fundamental activities-primary activities and support activities. Creation of value for consumer is not possible by an individual that’s why contribution of group is required and this procedure is termed as the core processes and system approach. High level of customer value ensured through proper maintenance of value chain activities. The generic model of core process and system is explained as follow:
Primary process
Primary process includes product development, demand development and order fulfillment. Combination of these three steps is basic task of a business which also a consumer’s perspective should generate by managers. Steps of primary process are:
- Product development: Product development is ensured through continuous innovation and this also a helpful procedure for new product development. Global multi-product firm ought to ensure this for their business operation. A combination of available product selection and continuous product innovation is product development process.
- Demand management: Demand management is a large procedure that narrates different part of the business. Understand customers’ need and contaminate this understanding to the product development is the starting point of demand management. Demand management covered the areas of market research, packaging, advertising, promotion, sales and booking.
- Order fulfillment: Efficient and effective implementation of demand management is termed as order fulfillment. In other words, coordination of a set of complex activities is order fulfillment. For a global multi-product firm, activities of order fulfillment are-order to suppliers, production operating, finished products’ wearing, finished products’ installation, finished products’ shipment and at last installed product’s servicing.
- Support system: Management of resources passively serves the external customer and exists as coworker of the primary processes. In other way, resource management under primary process need support system to execute their tasks.
- Capital resourceing: Capital resourceing identifies the areas of investment. Sources of funding are-debt provided by the lenders, stockholders equity, obtained profits or retain earnings. Reasons of funding are-decrease liabilities, capable to pay dividend, maintenance expenses for current business operation.
- Human resourcing: Motto of this point is to place right person in the right place consistent with their efficiency and productivity. Maintenance the challenges of HRM, organizational performance along with internal and external environment, human resource planning, job analysis and work study including job description and specification, recruitment selection, career transition, skill training, performance appraisal, wage and salary administration, employee benefits, safety and security, rewarding, promoting individuals.
- Information resourceing: Information is basic requirement of operating any process. As a part of individual process information is treated as an essential part.
- Control system: Control system monitor the way of resource allocating providing by the support system across primary processes. In order to avoid implicit and loss and be explicit every organization has to adopt control system.
External environment analysis
Factors that are not under direct control of the organization as well its industry and consists of competitors and outsiders factors. Factors of external environment profoundly influence the industry and the organization. Under strategic management a critical component is environmental analysis that examines sufficient information for the future. Environment is also significant for environmental changing that capable the organization get benefited. For an organization environmental analysis is helpful for identifying threats, opportunities and competitive analysis.
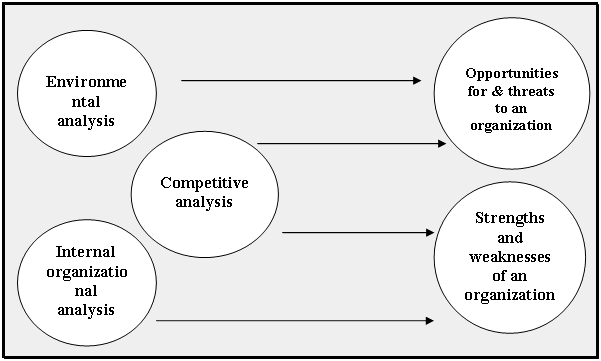
Features of external environment
For initiating external analysis of an organization it requires to understand a number of features that ground external environmental analysis. Narratives forms of these are:
- Type of external environment is not same for different organization but they are almost similar.
- For same product or services provider to the same segment of market face different competitive external condition.
- External environment analysis should focus or tailor for such organization those yet not formulate strategy.
- It is also considerable that relationship, conditions and events are not static though they build the organization’s unique environment.
- Small number of organizations faces same categories of factors for a long time at same importance magnitudes.
- Legal obligations, customers’ tests and change of restraints make an organization’s position different compare to its competitor.
- Political environment is an important factor that influences all level of business by means of special interest group.
- Less predictable factors are-consumers demographic feature, alteration of society that are closely relate to value and attitude alteration.
Steps of external environment analysis
External environment analysis is a future oriented process. This procedure does not require information extension; it needs to seek relevant information. Three major steps are involved in conducting external environment analysis.
- Definition of the external environment: General forces of an organization are-economic forces, technological forces, social forces and political-legal forces. Based on geography these forces are transformed. As for example-McDonald a renown fast-food restaurant that is more influenced by local than national fast-food restaurant chain. As a result, its international operation scope is exhibit through a wider range.
- Economic forces: Local, national and international economic vacillation constructs the base an organizational scope. GDP, income level, taxation, balance of payment, inflation are the indicator of production capability, product and service consumption level. International economy is split into four categories- 1) including Japan the western democracies, 2) the eastern block, 3) the developing nations and 4) the underdeveloped countries.
- Technological forces: Technology is the support system that makes tasks easier. Technology brought glamorous invention of product, gradual improvements in design, efficiency, new industry diffusion, application, tools, and supplement product and in materials.
- Social forces: Strategic decision could be alter with the changes of product and service demand and behind it social forces are act dynamically. Social forces include-demographic feature, values and attitudes.
- Political-legal forces: Strategic decision is also fluctuated by the political orientation. Political-legal forces sometimes influence positively though most of the time its acts are exhibit as restrictive.
Scanning and forecasting
Studying external environment forces is the concept of environmental scanning. Beyond a long time frame environmental scanning is engrossed. In this engrossment it combines two portion-environmental scanning and scenario planning. To do so; there need to answer two question:
- by whom it would be done?
- what would be the accessible mode of information?
On the other hand, forecasting is evaluated using following tools:
Qualitative method
Opinion and judgment are the source of qualitative method. Several qualitative methods are:
- Jury of executive: Here, several managers aggregately forecast and devise their pooled opinion.
- Sales force composite: Experienced sales peoples’ combination of sales prediction is forecasted here.
- Customer evaluation: This method accepts individual customer’s want in order to attain total forecast.
- Delphi method: Develop expert opinion consensus is the aim of Delphi method. Particular question is determined to study by a panel of expert. There is an important point that these panel members are not fall in a group. It is a complex but inexpensive tool.
- Surveys and opinion: Different medias like-telephone, mailed questionnaire, personal interview are the modes of this tool to forecast customer intention.
Quantitative method
Information analysis and statistical techniques used ensure quantitative method execution. Different quantitative method that are more sophisticated compare to qualitative are:
- Time-series analysis: Based on past information or data basic idea of time series is expressed through a trend line as following table: Time series analysis using lest square method, “Y = a + bx”. Where, Y = Total cost or price of a product, a = Fixed rate = Σ y / n, b = Variable rate = Σ xy / Σ x^2, x = Number of unit required to produce, y = Per unit cost of production or price of a product, n = Number of the period.
Regression modeling
A tool that forms into an equation and one or more variable one another is the basic concept of regression modeling. Individual and multiple regression equation is as:
Equation for individual regression analysis or linear regression: Based on least square method a linear regression equation is-,“Y’ = a + bX”. Where, Y’ = Y prime = for selected X value it predicts the Y variables value, a = Value of Y when X is zero and Y intercept, b = for independent X variable b is the slope of the equation, X = Value of selected independent variable
Multiple regression analysis: Multiple regression analysis is sometime denoted as the model of relationship. Equation of multiple regressions is as bellow:
“Y’ = α + β1X1 + β2X2 + …………….. + βnXn”
Where, α = The intercept the value of Y when all X’s are zero , β1= When other condition remain unchanged, the amount that changes Y for the particular increases of Xj. “j” is estimated through the value of independent variable.
Econometric modeling
It is more sophisticated model of forecasting is econometric model. Mathematical attempt to an entire economy is the general form of this model. It is complex and also expensive representation. Several regression equations that would capable to express relationship between economic sectors are incorporate in this modeling. As it is an expensive procedure, a small number of organizations have the ability to adopt by own. For a multi-product global firm it is essential practice for their business operation. They either owned it or appoint consultant to specialize. General econometric model of a multi-product global firm are described as bellow:
Evaluate parameter of the production
Parameter of the production is evaluated based on the fixed cost of the product. Product cost and the fixed relationship is proportional and be express as follow:
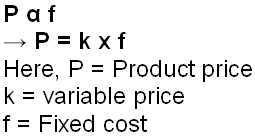
Demand for single product
Single product’s demand is calculated through following equation:
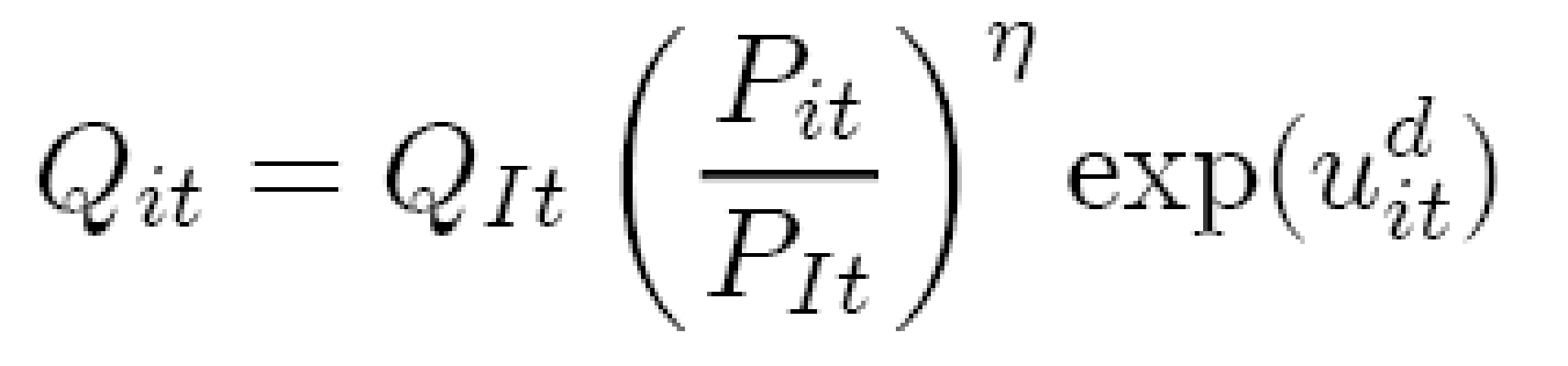
- Here, Qlt = In time t out put of an industry
- Pit / Plt = ith firm’s relative price
Demand for multiple product
According to the Loecker, Jan De (2007), demand for multi-product firm use following equation in estimating demand:
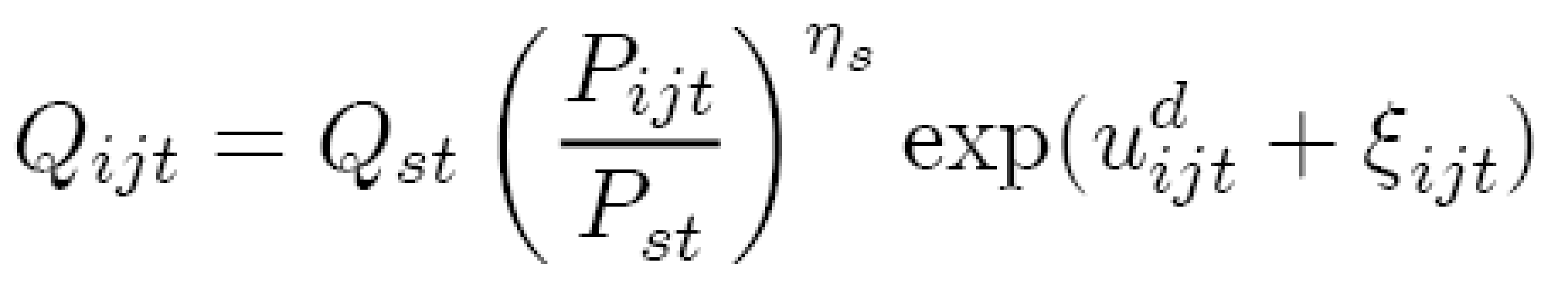
Here, i and j refer the product type.
Single product’s and multiple product’s productivity and strategy estimation
Equation used for both single and multiple product is as:
![]()
Pricing for specific product
Specific product pricing need to consider a set of equilibrium and fixed costs.
Pricing along with different brands
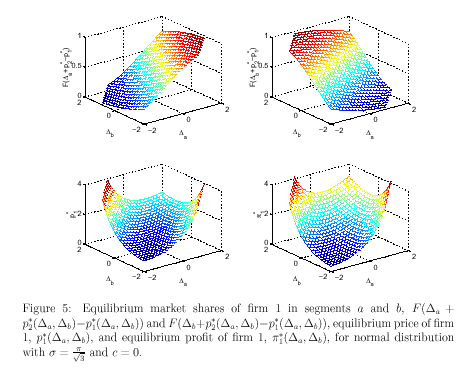
Doraszelski, Ulrich, and Michaela Draganska (2006), argued that the demand preference is of two types- normal distribution and multiple distribution. Equation used in both of two cases are:
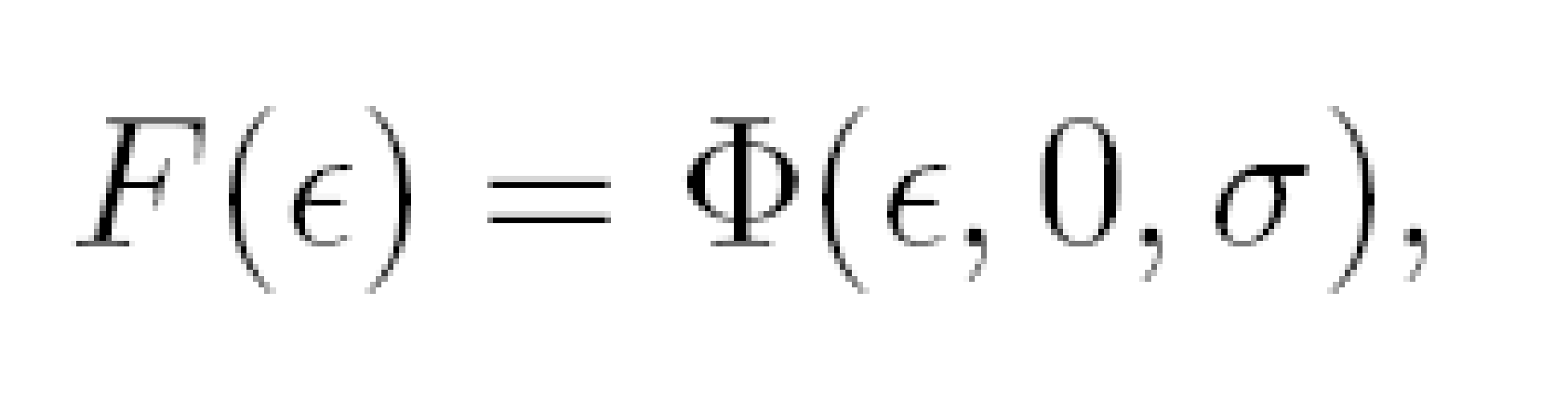
![]()
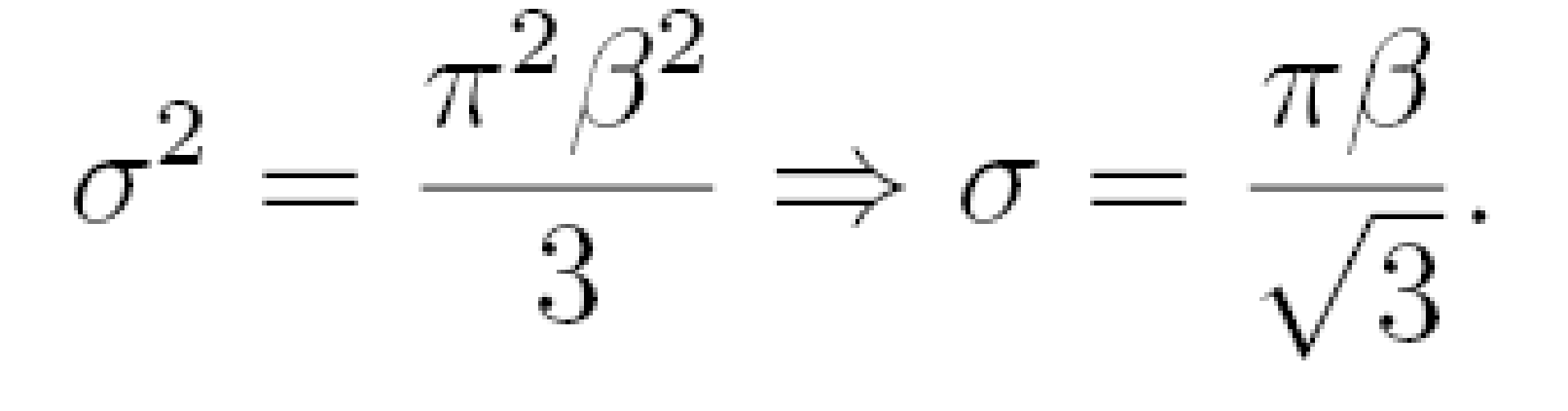
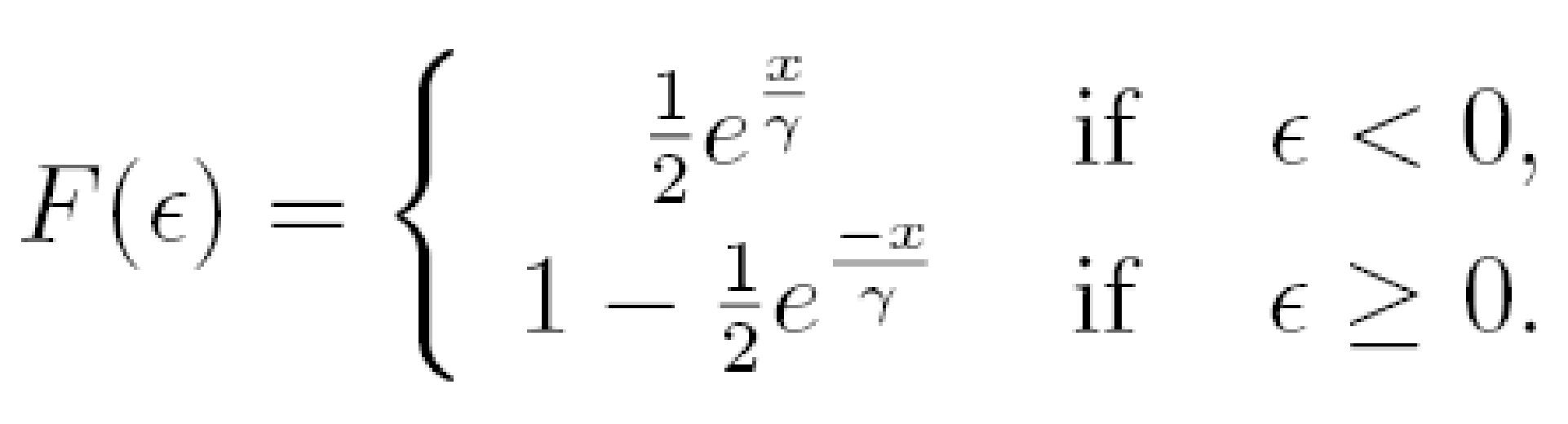
![]()
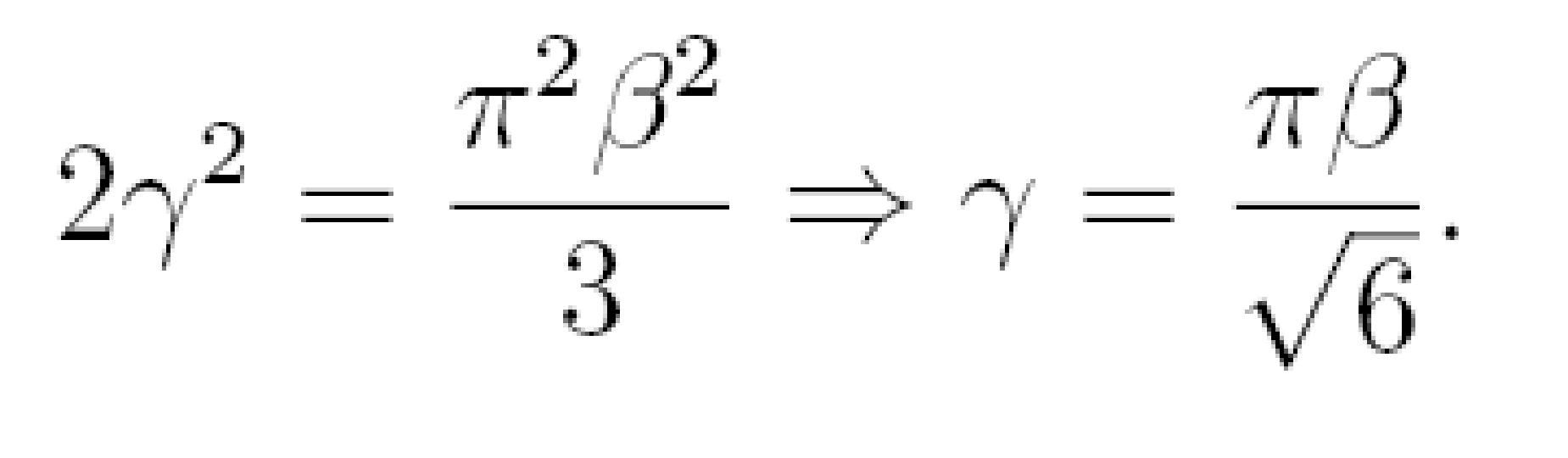
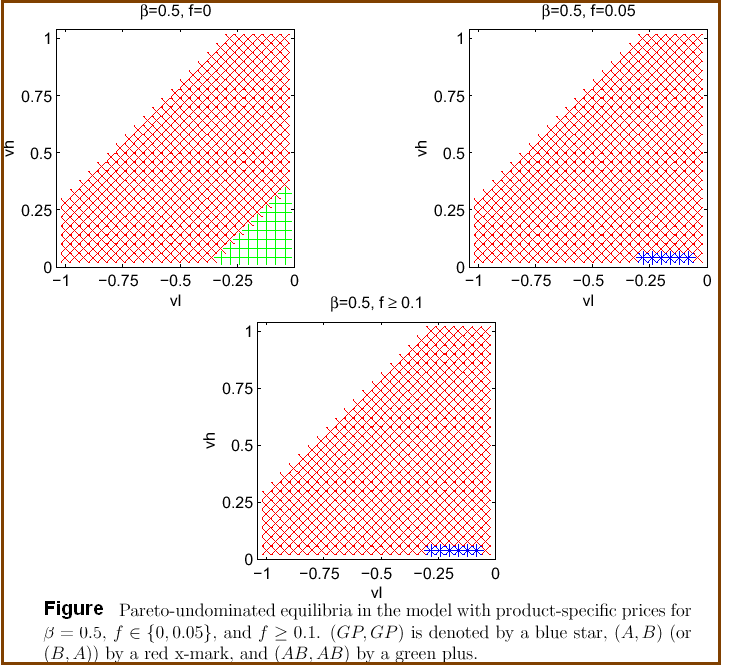
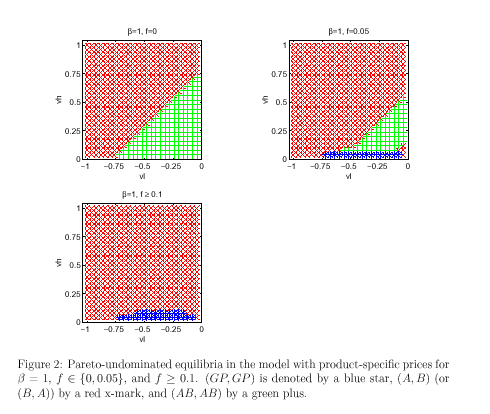
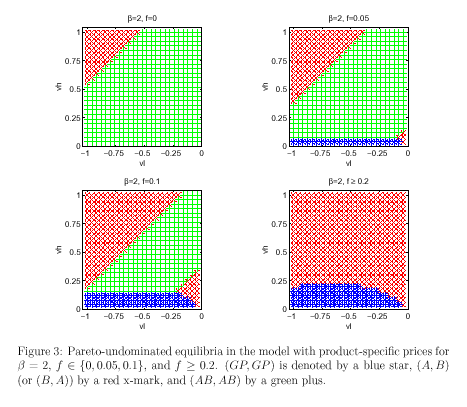
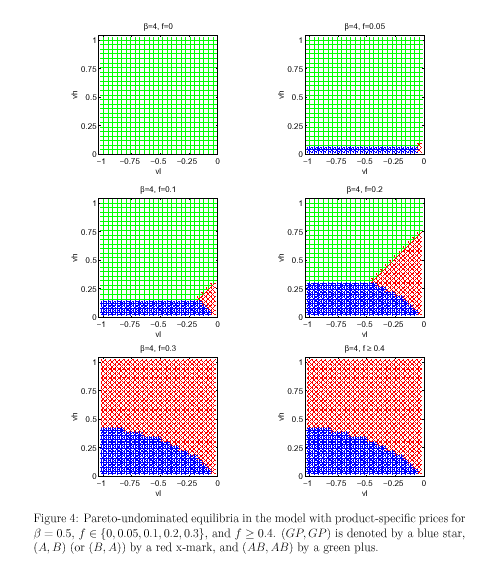
For more clarification, appendix has attached six figures with a sort description.
Along with forecasting tools special precautions
Special caution is required by the use of forecast. Quantitative forecasting is the future projection not prediction. Formulating strategy and strategic decision making is difficult when historical trend is only source.
- Interpreting environmental information: A source of raw material in projection and the forecast. This raw material is for future development and organizational decision making.
- Ranking threats and opportunities: Ranking procedure fall into two consequences of an organization. Opportunities are termed as positive consequences because of their advantageous impact. On the other hand, threats are denoted as negative consequences for their demerit influence.
- Dual ranking: Actual occurrence and organization’s potential impact is plotted in two dimensions under dual ranking system.
Industry and competitive analysis
Industry and competitive analysis is for achieving a greater appreciation. Now a day, it is a crucial task for global multi-product firms. Through this system examining industry boundary, structure, competitive factors and also key success factors (KSFs) are easily understood by an organization’s executives. This procedure requires to answering the following factors:
- Identify the company’s current and potential competitors.
- Evaluate the firm’s vision, mission, goals, objectives, aspirations and capabilities.
- Define the company’s strategic intend and describe strategies.
- Identify how and where the firm will compete.
Industry analysis is complemented by the competitive analysis. As for this managers’ easily focus the key rivals, strengths, weaknesses of the firm. Following factors are also defined by competitive analysis:
- A distinctive competence: Compare to the rival a firm’s position is superior is the activity of this term.
- Competitive advantage: To achieve higher profitability could be ensured the firm’s superior position than its competitor. To do this, first the firm need to develop distinctive competencies and make use of it as for creative compete.
Objectives of industry and competitive analysis
Understanding industry and competitor dynamic market highly and brought sensation. Recently, industry and competitive analysis is a supportive tool for the manager to gain purposes throughout data or information collect, analyze and interpret of the industry and the competitor as follow:
- Industry and served markets definition help focus and select competitive arena of the company.
- Define prospective business opportunities.
- In order to maintain a slam competition adopts benchmarking.
- Build a precise time frame or response time of the firm associate to the competitors’ movement.
- Draw the way to restrict competitors’ movement.
- Develop communication system in order to develop organizational motivation.
- Enjoys superior competitive advantages rather than rivals this analysis provides necessary information to the executives of the firm.
- Promote, expose and continue competitive learning in order to counter the ideas and actions of the rivals.
Industry and competitive analysis procedure
Industry and competitive analysis is a complex procedure described as bellow:
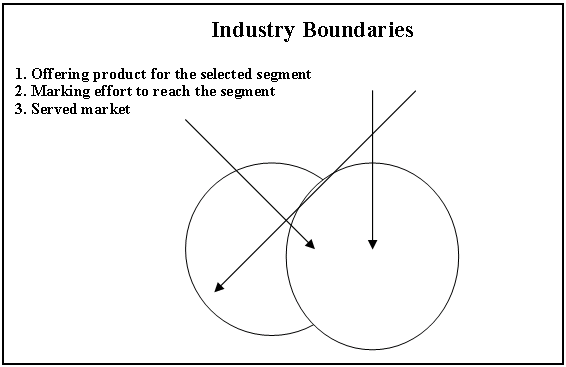
Define industry boundary and select served market
Sketch the boundaries of the industry is the first step of the competitive analysis. After that, based on customers’ needs it requires to segmenting the market for desired product and services. For more clarification, a graphical presented is given in bellow:
Understand the industry life-cycle
External factors turned an industry into an existing form and this form is continuously changed with change of time. Managers have to understand these changes throughout the sequential phase or stages of the industry life-cycle as follow:
- Introduction or emergence: In this stage, technology of the firm is not well developed and offer products for a large market.
- Growth: In an industry life-cycle this is an exciting phase and from this stage a firm start fighting to survive, gain profitability, market share acquiring and build brand name.
- Shakeout: A large range of change has manipulated here. Factors of shakeout are- industry saturation, evaluate industry growth rate and radical change forced by competitive factors.
- Maturity: In this stage firm breed to consider new factors. Aggregate marketing process determines success of the firm.
- Decline: A new phase of evaluation is entered termed as decline. It is a great challenge for an industry competes as declining industry.
Time →
Industry structure analysis
Analysis of industry structure is fostered by following factors:
- Barriers to entry and exit: First of all entry into a market is a great challenge for a new firm. This barrier is of two types- tangible and intangible. On the other hand, exit from a market is a managerial decision examined on the basis of market demand.
- Product differentiation level: Product differentiation is ensured through developing technology and aggregate marketing tasks.
- Concentration level: Increasing dominating sales portion of the industry is the concept of the concentration level.
- Scope of economics of scale: Economics of scale is a significant factor that patronizes large scale of production at a lower cost.
-
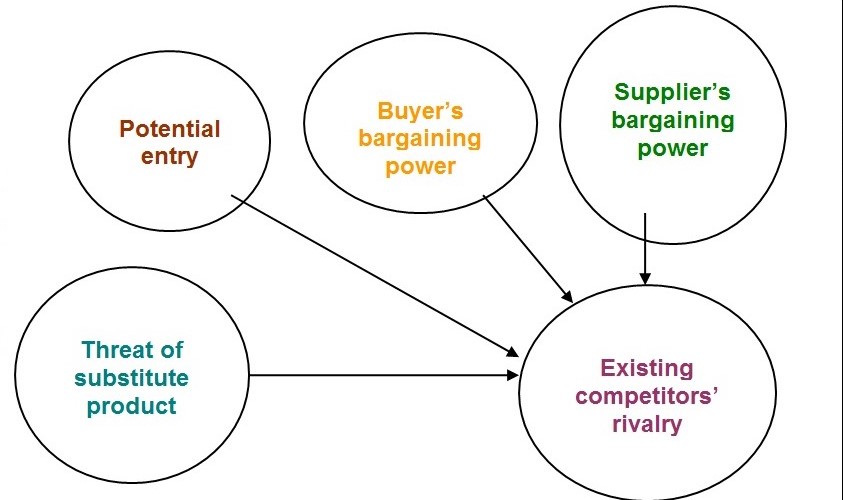
Identify the dynamics of the competition
In this phase competition dynamics is evaluated through five factors define by Michael Porter. Five factors are:
- Potential entry: Potential entry is controlled through a number of variables those act as threat of entry into industry and reduce potential entry. Such variables are-distribution channel, capital requirement, rules and regulation.
- Buyers bargaining power: Bargaining power capable a buyer influence the production capability of the industry.
- Suppliers bargaining power: Suppliers influence an industry when they are few at numbers, lacking of substitute product, product price system.
- Threat of substitute product: Products that has the ability to fulfill same purpose is termed as substitute product. Exist of substitute product affects competitive dynamics and rivalry intensity.
- Existing competitors’ rivalry: Several equal balance company, competition diversity, slow growth rate, high fixed costs etc. are the forces that control Existing competitors’ rivalry.
Understand key success factor of the industry
Key success factors (KSFs) is understood by customer analysis and competition analysis. These analyses include market segment, consumers want and strategy formulating way.
Strategic group performance analysis
Group analysis is executed by set of key success factors, competition dynamics and industry structure.
Competitive intelligence (CI) conducting
Gather information of the rivals and analyze that is the task of competitive intelligence in order to infer plan and strategy of the competitors.
Competition profile and evaluation
Another way of identifying rival of the industry is evaluate and profile in a rank based on the CI’s gathered information analysis.
Competitive signal interpreting
Reduce costs, warn competitors, examine competitors’ assumption etc. are the ways of Competitive signal interpreting.
Define opportunities and threats
Define opportunities and threats are useful in scanning environment. External environment is benefited through opportunities and threats are hostile for the industry as well as competition.
Strategy formulation
Lynch, Richard L., (2000), argued that not only senior executives formulate strategies for multi-product global firm, strategic decisions took and executed through an organizational level- top level to the root level. Strategy formulation is for sizing up the internal and external forces.
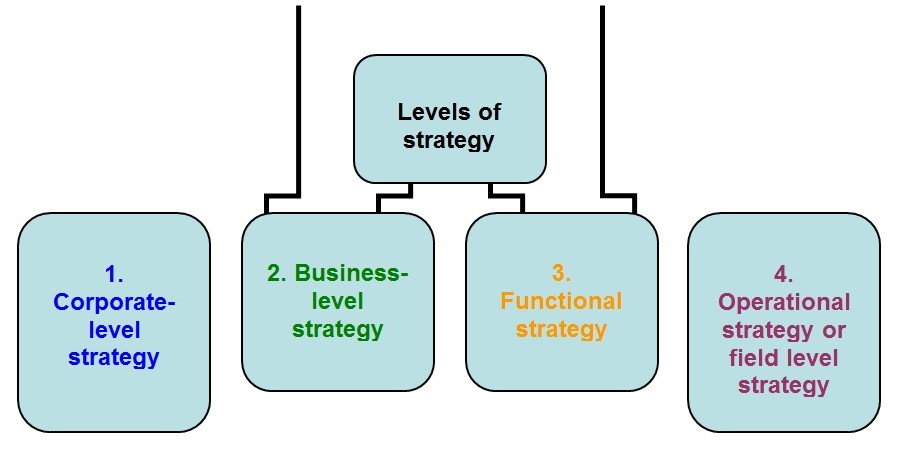
Levels of strategies
Strategy of an organization is conducted through four levels. They are:
Corporate level strategy
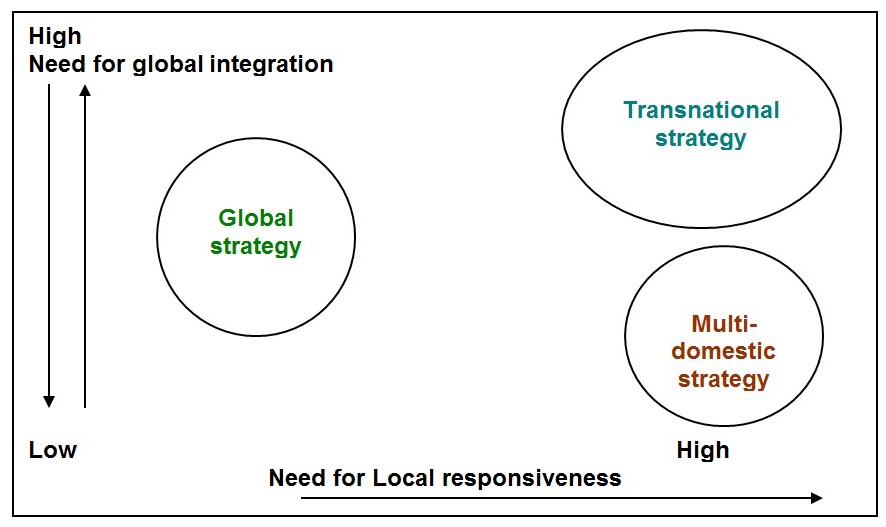
For all categories of business integrated form of strategy in the concept of corporate level strategy. Corporate level strategy is responsible for this type of strategy. This category of strategy is running for group of industries or conglomerate. It’s also a managerial game plan. For a global firm international corporate-level strategies are of three types:
- Multi-domestic strategy: Multi-domestic strategy is conducted through decentralization procedure in more than two counties in abroad. Competition in each country is focused separately here. Based on local consumers’ requirement strategy for product development is accomplished under this type of strategy.
- Global strategy: Home office of the global firm controlled strategic decision through a standard centralized procedure. Countries under global firm are interdependent in conducting their operation on the home office. Economics of scale, utilize innovative opportunities are focused by the global strategy of a firm’s corporate level.
- Transnational strategy: Aim of transnational strategy is to gain both global efficiency and response of local. Though their aim-global coordination is too difficult but shared vision flexible their way of tasks.
Business level strategy
Each categories of business of a multi-product firm needs diversified strategy for their business operation. Responsibility of business strategy is under general managers.
Functional strategy
Different function of a business-manufacture, production, financing, marketing etc. are under functional strategy. Head of each category function are supervised this task.
Operational strategy
This also termed as field level strategy and operated by the supervisor. Strategies of type are in narrower form and plant, sales regions are under the fundamental operating unit.
These levels of strategies are executed as following figure:
Relationship of strategy with ethics and social responsibility
In short, relationship of strategy with ethics is defined as-“what should do and what should not do”. Hitt, A., (2001) mentioned that strategy has to be ethical so that it would move in a right way not in a wrong way. In another word, conformation of legality is a measure of link of strategy with ethics. It is also termed as the moral security test. Human duty is concerned through ethics. For all type of business constitution following five are the essential constituencies for those they have ethical duty. Each of them is influence the firm and also influenced individually through it. Each of them is termed as stakeholders of the firm.
- Owners or shareholders: Shareholders or owners expect a sound return of their investment. Regarding this, business executives and the firm has moral duty to accomplish profitable management practice for proper return of the owners.
- Employees: Duty to employees is reflected through-compensation, job security, job satisfaction, career opportunities, working condition and overall compliance provided by the firm. Proper maintaining of these forces make an employee devoted to his duties, responsibility, skills, respect for his tasks and overall contribution that the firm wants from him.
- Customers: Consumers are the heart and soul of a firm. Appropriate accomplishment of consumers demand would attract them to purchase goods and services. Duty to consumers is to protect them from all of iniquitous and make available products that liable to laws through their agencies who could act as host.
- Suppliers: Suppliers the bridge to communicate between consumers and the company. In another word, relationship with the potential market goes through suppliers. Ethical duty of a firm maintains this affiliation so that both the firm and the supplier ensure standard quality product. It is an important point to mention that suppliers are partner and adversaries of the firm at a time. Kotler, Philip (2006), argued that supply quality affects the products quality and communicating of the business that’s why suppliers are the partner of the firm. On the other hand, suppliers treat as adversaries for two reasons-consumers want standard eligible product and services at a lower price where as suppliers thirst is getting high profit.
- At large the community: A firm ought to attentive in their ethical duty to the people of the society. Society is an institution where people are the member. Society expects business activities which should responsible in-fair tax payment, concern at environmental pollution, police protection, roads and high ways, health and hygiene, waste removal etc. Encouraging employees responsible and get awareness to mentioned factors and also involve in community activities. Thus an organization could exhibit ethical standard and involve in commotion as the requirement of the community.
Strategy implementation, leading and execution process
Turned a strategic plan into a practical form is the concept of strategy implementation, leading and execution. This procedure is more art than science. Individual company situation is the ground and feature of strategy implementation. Customized strategy implementation is a mixture of- work environment, policies, employee benefits, organizational culture and the industry type.
Tasks of strategy implementing principals
Some time organizational criteria have no impact on tailoring certain steps by managers. Such features are:
- Carry out strategy would be successful if the organization is built up according to the resource capability and competition.
- Strategic success depends on the critical value chain activities and budgets that ample resources.
- User friendly policies and procedures.
- Practices of value chain approaches and its continuous development.
- Continuous development of data base management, e-commerce, communication and operating system.
- To motivate employees establish reward system.
- Nurture a friendly corporate culture and work environment.
- Go forward is the task of internal leadership that advance strategy execution.
Importance of policy and procedures in implementing strategy
Three factors foster strategy implementation procedure. They are- competent personnel, sufficient resource capability and friendly internal environment. A short description of implementing procedure is presented bellow:
- Staffing the organization: All management practices that directly or indirectly affects the decision making process is under this step. Such practices are-planning, selection, recruiting, training and development.
- Construct strong competitive capability: Strengthen the internal resource capability with the change of external environment changes could strengthen the competitive capability of an organization.
- Construct friendly work environment: Strategy execution would successful through the proper maintenance of decision making and value chain activities.
Strategy control
Strategic control is a process that combines a set of steps and used as an effective tool of strategic management process. Vision, mission, goals, objectives, resource allocation, continuous development, prospective operation and work environment etc. are the out comes of strategic control. For strategy implementation and execution, strategy control is also an effective tool.
Objectives of strategic control
- Accurate determination of the assumption which would be used in strategy formulation.
- Determine the efficiency of strategy before implementation considering time and resource capability.
- Based on plans and expectation evaluate company performance and ensure a continuous movement.
- Make available information or data in order to decision making and performance execution.
Tools or component of strategic control
Strategic control brought outcomes to an organization through the effective implementation of strategy. Following are the tools of strategic control:
- Strategic surveillance: Evaluate the environmental changes by gathering and analyzing sufficient data in order to counter the changed occurred and for decision making is the concept of strategic surveillance.
- Special alert control: Special alert control is a signal of potential crisis. Sometimes crisis identification is tricky for a manager and accordingly in decision making.
- Premise control: Validity of the evaluation determines the success of premise control and based on this an organization’s strategy would craft.
- Implementation control: Supervise the action that undertaken in crafting strategy within the industry boundary and also evaluate the outcomes according to the plan.
Structure of effective strategic control
Effective control system could evaluated through following forces:
- Future oriented: Strategic control should along with the firm’s planning process and future oriented from every view point of the firm.
- Associate with strategy evaluation: This stage covers the area of consistency, advantage, consonance and feasibility.
- Focus on process issue and content at a time: Both activities and functions are closely interrelated of strategic control.
- Balance the demand involving in long time and short time: As this is future oriented process it recognizes demand for different time frame.
- Ignore bureaucracy and established formality: Strategic control established accountability through a logical and viable form in order that it minimizes the ratio of bureaucracy.
- Motivate learning: It appreciates experienced reflection that brought success for the organization.
- Sketch an integrated strategic control: Aggregate formation of strategic control minimize the system failure.
Limitation of strategic control
- Motivate formalization by put off risk-taking and initiative of management.
- Practice of over bureaucracy.
- Poor evaluation and negative expectation of management make slower organizational growth.
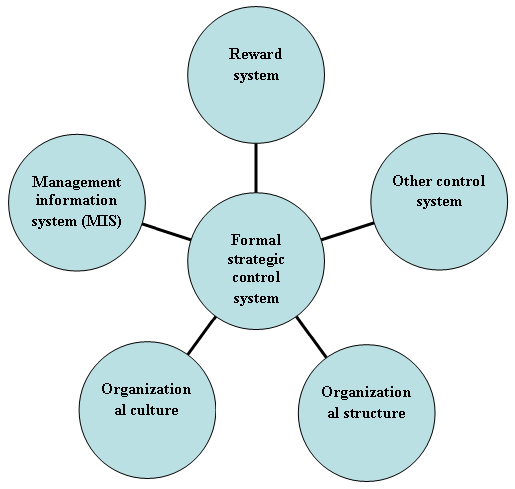
Relationship between strategic controls and with different organizational system
- Organizational culture: One of the significant ways of strategic control is organizational culture. Planning and operation and competent executive are the driver of organizational culture.
- Reward system: Reward system motivates personnel and they brought productive outcomes for the organization.
- Management information system (MIS): For successful decision making MIS is an effective operating system using advanced technology and electronic devices.
- Other part of control: Budget control, operational control and management control coordination ensure efficiency of the strategic control.
Methods to increase the profitability in a global Environment
For all categories of business organization to attract and keep or continue profitable customers marketing is a societal process or art. Marketing is also defined as “meeting needs profitably”. Most of the companies just identified and fulfill consumer satisfaction but they can not find out individual consumer profitability.
To increase the company profitability under a global environment customer profitability analysis is a productive method. This analysis is executed from “Activity-Based Costing” a tool of management accounting. Simpler form of this method is as:
Revenues from the consumer – All costs or expenses
In above method, costs not only include manufacturing and distributing costs of the product but also transportation costs to visit customers, costs for entertainment and gifts and costs for receiving phones from consumers. Resources of a company are for serving the growing and retain consumers. Each and every consumer under this procedure are categorized into following four profit tiers:
- Consumers who are most profitable termed as platinum customers.
- Another is known as gold customers and they are profitable for the company.
- Low profitable but satisfactory are the feature of iron consumers.
- Last categories of consumers are defined as lead customers and their criterion is that they are unprofitable and undesirable.
Task of a company is to shift gold customers into platinum exhaust, iron into gold and make profitable the lead customers either by reducing cost to serve them or by increase price of the product. Relationship between marketing investment and higher profit tires is proportional.
For more clarification, customer profitability analysis (CPA) is presented here in following table. In this table, products are plotted along the rows and customers are along with columns. There are three categories of customer-C1, C2 and C3. They are denoted as high-profit, mixed-bag and losing customer respectively. Here, products are of four types-highly-profitable, profitable, mixed-bag and losing. According to this table C1 buys all three profitable products-P1, P2 and P4.
Table: Customer-product profitability analysis under global environment:
A global firm would consider following steps as development procedure of profitability increase:
- TQM (Total Quality Management) – In an organization, responsibility of all people or personnel ensure quality using the concept of TQM (Total Quality Management). This procedure act as a tonic to improve business quality, product and service and operation procedure.
- Make the production process simple- Simpler process took less time in producing product. But under this procedure occurrence of error has a great chance. Using the concept of six sigma reduce the chance of human error as well as the whole process. In a specific measure, a set of methodology technique has identified to develop quality and reduce costs. Under this measurement, it is also estimated that within a million of product 3.4% are imperfect.
- Benchmarking- Benchmarking is a procedure that ensure the effectiveness in quality of a firm. This process need to take a sequential step as-provide standard product and services, perform activities in an efficient way and at last ensure standard of performance.
- Pay attention to the customer demand for product and service development- Another way of increasing profitability is to place at top consumer demand for product and services. It does not enlarge profitability but also improve the product quality and customer service.
- Reduce cycle-time- The term cycle-time refers time from the beginning to end to transfer a raw material into a finished goods. Though shorter cycle-time is a reason of error but it reduces costs of production and ensures profitability.
- Take action for improving product quality and design precision- Uses of technology especially use of software made a dramatically change in production quantity and quality. Uses of software also supportive in designing manual process, testing and produce higher quality product.
- Magnify the production in a precise way- For multi-product firms one of the key success factors behind quality production process is in a simple and precise way and develop durability and reliability of analysis practice.
Pricing methods or strategy
In strategy crafting, pricing method is another imperative tool. Price of a product is segmented as following categories:
- Ultimate,
- Gold standard,
- Luxury,
- Special needs,
- Middle,
- Convenience or flexible or ease,
- Me too but cheaper,
- Price alone.
Pricing policy is a set of sequential factors that follows a circular flow described in following figure:
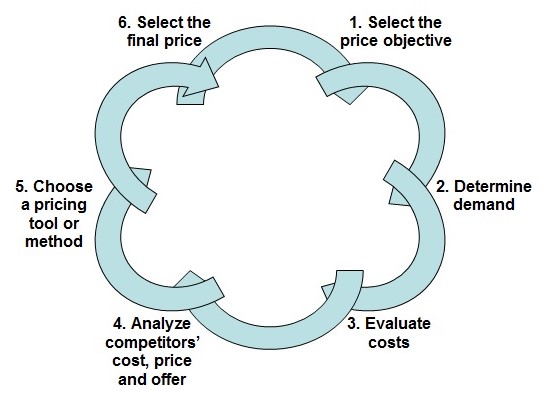
Areas of pricing policies is influenced by following forces:
- Psychological pricing: A number of consumers consider price as the indicator of product quality. Psychological pricing method is for them.
- Pricing for gain and risk sharing: This form of pricing concentrate on-marketing mix element, brand image, high promotional costs in determine their pricing policy.
- Geographical pricing: Cash offer, barter, offset, buyback arrangement, counter trade, compensation deal are the factors of geographical pricing method.
- Price discounts and allowances: Price discounts include-cash discount, functional discount, allowance, seasonal discount and quantity discount.
- Promotional pricing: Promotional pricing are for cash rebates, loss-leader, low-interest, special event, longer payment terms, psychological discounting and warranties and service contracts.
- Discriminatory pricing: customer segment, image pricing, product form pricing, location pricing and time pricing.
- Product mix pricing: Product mix pricing involve in-product line, captive product, by product, optional feature, two part pricing and product building.
Conclusion
This term paper presented features of global firm that produce multiple products. Strategy the game plan of a firm is shown here into a global form. Regarding this, here also adopt transformation plan, market analysis, market driven strategy, product plan along with market segment, pricing method, restructure and acquisition, environmental analysis both for internal and external. In this term paper also presented a set of models for weighing up the presentation of multi-product conveniences with global perspectives. It has presented the models toward a methodically categorized most advantageous mix up of enthusiastic facilities for multi-product firms under global aspect. The models endow with open lexis to achieving optimal level solution and the subsequent equilibrium situation can supply as a most valuable tools of advance approaching among the effectiveness of product mixture, process elasticity on multi-product plant facilities. The most advantageous quantity of multi-products of a firm in a global environment and the subsequent production flexibility is very much perceptive in relation to the system using schedule. Consequently the outcomes of product diversity on production performance are not repetitive. As soon as superior elasticity at a multi-product firm has escorted by boosting its capacity, the preliminary enlargement in product diversity would naturally get better performance. Hence it is for eternity significant to recognize the most advantageous quantity of multi-products as well as subsequent aptitude to distribute in a certain competence. If the product demands are analogous among the multi-product capacity it can liberally distributed within flexible facilities of the firm and a set of facilities of comparable dimension with the same elasticity would reach in an optimal position. At the same time if the quantities of facilities are fixed and the product distribution are elastic then the distribution of multi-product would drive to achieve its equilibrium position.
Bibliography
Anderson, S., & de Palma, A, Discrete Choice Theory of Product Differentiation, MIT Press, 1992.
Benjaafar, Saifallah and Diwakar Gupta, Scope versus Focus: Issues of Flexibility, Capacity, and Number of Production Facilities, 2009.
Begg David, Fischer Stanley, and Dornbusch Rudiger, Economics, 8th edition McGraw Hill, ISBN: 978-0077107758, 2005.
Doraszelski, Ulrich, and Michaela Draganska, Market Segmentation Strategies of Multiproduct Firms -Online Appendix- 2009. Web.
Doraszelski, Ulrich, and Michaela Draganska, Market Segmentation Strategies of Multiproduct Firms, The Journal Of Industrial Economics, Volume LIV, 2009. Web.
Douglas A. Lind, William G. Marchal and Samuel A. Wathen, Statistical techniques in business and economics, 12th edition, McGraw-Hill, NY, and ISBN: 0-07-111315-0, (2005).
Dewett, K. K. Modern Economic Theory, 22nd edition, New Delhi: S. Chand & Company Ltd., 2005, ISBN: 81-219-2463-4.
Ghazzai, Hend, Multi-product strategies and relative preferences for quality, 2009. Web.
Griffin, R. W. Management, 8th Edition, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston New York, ISBN: 0-618-35459x, (2006).
Hitt, A., Michael, R. Duane Ireland, & Robert E. Hokisson, Strategic Management, 4th Edition, South-Western Thomson Learning, Singapore, ISBN: 0-324-041891-2, (2001).
Hotz V. Joseph & Mo Xiao, Strategic Information Disclosure: The Case of Multi-Attribute Products with Heterogeneous Consumers, 2009. Web.
Jack R. Meredith and Samuel J. Mantel, Jr, Project management, 6th Ed., John Wiley & Sons (Asia), Inc., ISBN-13: 978-0-471-74277-7, (2008).
Kotler, Philip, Marketing Management, 11th edition, Prentice Hall, NJ, ISBN: 0-13-0336297, (2006).
Lynch, Richard L., Corporate Strategy, 4th edition, Pearson Education Limited: Harlow, Essex, ISBN: 0273701789, 2000.
Levin, J. Eric, Yue Ma, & Robert E. Wright, Profit Maximization in A Multi-Product Firm with Impatient Customers, 2009. Web.
Loecker, Jan De, Product Differentiation, Multi-Product Firms and the Impact of Trade Liberalization on Productivity in the Belgian Textile Industry, 2009. Web.
Loecker De Jan, Product Differentiation, Multi-Product Firms and Estimating the Impact of Trade Liberalization on Productivity, 2009. Web.
Nobeoka, Kentaro, & Michael A. Cusumano, Multi-Project Strategy and Market-Share Growth: The Benefits of Rapid Design Transfer in New Product Development, 2009. Web.
Saunders, Mark, Adrian Thornhill & Philip Lewis., Research Methods for Business Students, 4th edition, London: FT Prentice Hall. ISBN: 0273701487, 2003.
Stanlake George Frederick, Macro-economics: An Introduction, 2nd edition: 2, Longman, 1979, ISBN: 9780582352650.
Thomson Business & Professional Publishing, Multi-product Strategies, 2009. Web.
ZIGZAG Marketing, Inc., WHITE PAPER, POST-ACQUISITION INTEGRATION Transforming Product Companies into Solution Companies, A 5-Point Transformation Plan, 2009. Web.
Zikmund, William M., Business Research Methods, 7th Edition, Orlando: Harcourt Publishers, ISBN: 0030184320, 2006.
Appendix