Abstract
Tesla Motors Inc. is one of the organizations striving to maintain an indisputable presence in America and other parts of the world. This submission provides an introduction that recognizes the current leadership of the company while highlighting the elements under discussion. The subsequent section deals with leadership skills evident in the company, with a particular emphasis on participative leadership. Apart from aligning the company objectives with the leadership styles, the paper also discusses the influence of a leader on the organizational culture. Further, the discussion focuses on a SWOT analysis before proceeding to the strengths and weaknesses of the primary leader of the organization who is Elon Musk. Before concluding, the paper provides three recommendations aligned to leadership, innovation, and marketing in order to improve the organizational position in a rival environment.
Introduction
Electric cars are unheard-of luxuries in most parts of the world. The truth is they are more eco-friendly in comparison to their gasoline counterparts. Tesla Motors Inc. decided to take the initiative in order to manufacture and market electric vehicles by customizing the machinery to consumer needs. Since its inception, the company has dealt with many challenges, including changes in leadership for the 10-year old company. The American firm has experts working in different departments, including car assembly, modification, design, and overall production. In most cases, the company acquires cars from car manufacturing firms in order to design them in a way that suits the needs of the target consumer population. Registered under NASDAQ, Tesla Motors has publicly advertised its stock exchange rates for interested parties to buy the shares since its first IPO (Tesla Motors, 2014). Besides acting as a point of analyzing the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of the company, such information is relevant in discussing the leadership style of the firm. Elon Musk is the company CEO who tirelessly works while liaising with Toyota and Daimler, among other car suppliers, to provide the companies with lithium-ion batteries (Heck, Rogers, & Carroll, 2014).
Organizational objectives
Commercialization of electric vehicles
Company objectives always change depending on the environment of operation. The stakeholders, including target consumers, the supervisors, and the managers, have a direct impact on the formulation, execution, and implementation of objectives in any firm. Tesla Motors Inc. was started by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, and in 2003 had to change the way it operated when Elon Musk joined them. In essence, the first two founders had ideas but lacked the requisite financial resources to stabilize Tesla, while Musk had a new idea and the fiscal resources to place the company in the rivaled motor environment in 2004 (Lussier, 2008). When Musk joined the board of directors at Tesla, the main objective was to make a commercial breakthrough in the electric car business, which was a completely new venture in the market.
Providing affordable solutions to car owners
Tesla’s board of directors had an objective of providing affordable motor vehicles to different consumers within and outside the US. The rationale was to create battery-powered vehicles meaning that the maintenance cost would be very low. In addition, lack of gasoline consumption would automatically rule out the possibility of buying fuel while cutting the cost of car management. People need sporty cars, but the cost of maintenance of high-speed vehicles naturally prevents them from purchasing SUVs (Daft, 2012). The main aim of innovation is always to improve the lives of people while having a similar effect on the cost of sales and production. Unlike high-speed sports utility cars, battery-powered cars use moderate speeding power to prevent car bumps and accidents caused by over-speeding. As such, the cost is also a contributing factor to safety maintenance for Tesla Motors Inc.
Supporting green businesses
The most obvious objective for the firm is to support green business. Avoiding gasoline use in cars reduces the release of car exhausts into the atmosphere. Environmental conservation is extremely important, especially with an increase in the cases of climate change and extreme weather. Carbon gases and other greenhouse gases always deplete the ozone layer. This enables penetration of direct sunlight, causing cases of skin cancer and genetic modification in the natural ecosystem.
Leadership practices of the primary leader of the organization
Characterized by participative leadership or democratic leadership, Musk remains one of the most renowned individuals who transformed the image and financial position of the company in a span of five years. Since its inception, the identified elements of leadership form part of the organization’s culture that uniquely identifies Tesla Motors in the rivaled electric car manufacture and design market. The leadership style displayed in the company has the elements discussed below.
Succession plans
When Drori left Tesla in 2007, Musk assumed leadership, and he incorporated succession plans to avoid lay-off plans instituted by his predecessor. In organizational management, laying-off skilled workers normally create a breach in normal functioning because it forces the firm to acquire and train new employees. Besides being a costly exercise, the process is equally time-consuming, and it interferes with the resources that e firm would use in improving its position. With the core objective of innovation, green business, and provision of affordable vehicles, distraction was the last thing Musk required for the business when he became CEO in 2008 (Heck et al., 2014). Creating a succession plan at Tesla is a collective process, which ensures that the seniors train the juniors while they prepare to retire so that an in-house expert takes the position of his/her predecessor. This reduces the cost of training while increasing the value of the company in the US.
Liaison and teamwork
Musk transformed Tesla within a year of operation, making it possible for Daimler, the prestigious Mercedes Benz manufacturers, to consider designing the cars into electric pieces. Aabar Investments acquired 40% of the stake from Tesla by 2009, and the company had 50% shares under the management of the new leader (Tesla Motors, 2014). Besides liaising with suppliers and customers, Musk enabled the firm to acquire a company loan from the United States Department of Energy. This was a step towards building networks for the company in dire need of a growth opportunity within a rivaled market. Other innovative institutions began showing interest in Tesla immediately after Musk assumed leadership of the company. Nissan, Chrysler, General Motors, and Ford displayed interest in customizing vehicles at Tesla, meaning that teamwork played a significant role in consumer identification and acquisition of contracts.
Partnerships and communication
According to Melik (2007), open communication channels create enough room for maintaining two-way communications between supervisors and workers at Tesla Motors Inc. When the company advertised its first IPO in 2009, there were several board meetings in relation to enlisting the firm in the NASDAQ stock exchange program. Besides, the company’s profits of end of the year 2009 assisted in the improvement of innovative programs. As such, the company could patent the innovations of various employees who shared their ideas through daily company meetings (Heck et al., 2014). The team of workers in both the shipment and technical department has to communicate effectively to facilitate exchanges between the company and its customers. Tesla also communicates to customers when the company wins awards, as well as when it has new products it seeks to offer the target market.
The following illustration summarizes elements of leadership in the organization.
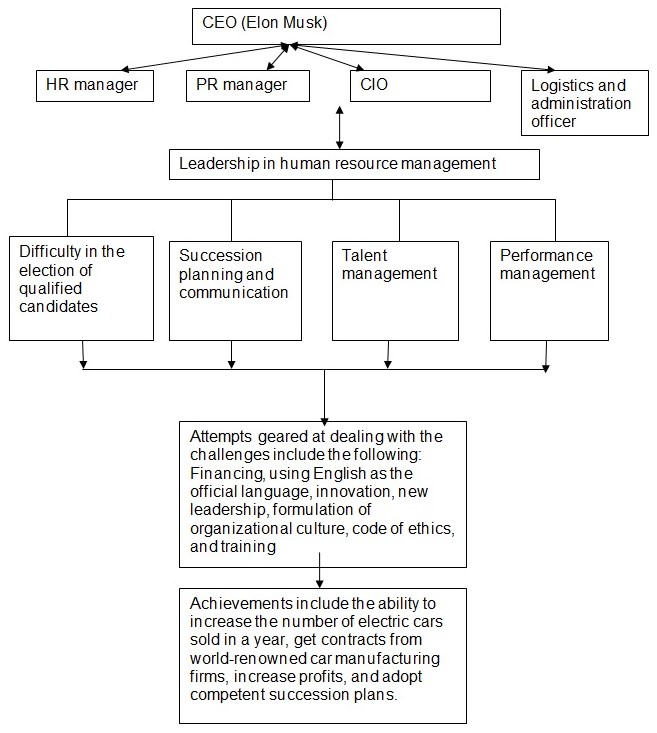
Impact of leadership on the organizational culture
When Drori was the CEO of Tesla Motors Inc., employee lay-offs exceeded measures geared towards damage control and restoration of the organizational image. Communication became a complex process because autocratic leadership provided limited room for popular participation in decision-making. The trait theory of leadership suggests that leaders are likely to use their personal qualities to influence decision-making within organizations. Leaders born with authoritarian attitudes often act out of impulse, making it difficult for the individual to control their emotions. This explains the position of the previous CEO of the company in 2007; his leadership style led to a collapse of the firm, almost denying Tesla the opportunity to trade in any stock exchange firm (Lussier, 2008). The reverse happens to leaders raised in an environment in which they could exercise independence. Musk understood that independence played a substantial role in promoting the careers of different employees at Tesla since it was the only avenue for exercising self-expression. Nature and nurture, as discussed by contingency theorists, always determine the type of leader an organization will have, as well as the type of leadership tactics he/she will display when working with the followers. During Drior’s era, it was impossible to ignore the vision and mission of the organization. However, people operated under fear and tension because they never knew when the executive would fire them. By the beginning of 2008, Musk had to employ about 72% of the entire employee population working at the firm because the laid-off workers had a significant impact on the organizational progress during his tenure in office (Tesla Motors, 2014). A good leader prioritizes, listens, and creates room for popular participation in decision-making (Phyper & MacLean, 2009). Creating a team in the organization enables brainstorming. As such, the qualities of a leader and the principles he/she propagates have direct impacts on the general organizational culture because the followers always depend on the leadership style of the CEO.
SWOT analysis
Strengths
Brand positioning
Tesla Motors Inc. creates unique brands that remain rivaled in most parts of the Americas and Europe. Many firms strive to create an organization dealing in such products, but rivalry from other gasoline vehicles normally acts as a setback to progress. Tesla Inc. has a competitive brand name that earns it the goodwill of competitors such as Toyota and Nissan that contract the firm to customize their vehicles into battery-powered vehicles. The competitive technology makes the company improve its products and services as the investment capital of each New Year keeps increasing. Strengths that place the firm at the top include an established brand name because Tesla provides affordable high-tech products to the target population. Contrarily, most electric car manufacturing firms prefer selling at extraordinarily high prices in order to meet the cost of production. By 2017, Tesla Motor Inc. will provide cars with high value and low costs. It will be easy to acquire a brand new Series X vehicle at less than $40,000 in the next three years. With the current leadership based on liaison, Musk will also ensure that other rival firms find the lithium-ion battery attractive, meaning that the company invests largely in quality marketing that constantly makes it visible to the public.
A competitive corporate strategy
One of the most difficult things is to launch an electric car company in an environment in which people mostly trust gasoline-operated vehicles. Tesla has a competitive corporate strategy that majors on the deployment of talented, passionate, and innovative employees who share a common vision with the firm. Technology runs most functions in the firm from communication, product design, and overall product development. Unlike companies that target the rich and sophisticated customers, Tesla decided to target the middle class in the new corporate strategy of 2009. When all employees and supervisors adhere to the policies of the corporate strategy, it becomes very difficult to fail. Musk also maintains objectivity when the company needs an annual capital, when it acquires a loan, and when it gets an award. In essence, it means that people develop trust in the leadership, which reinforces solidarity that remains very significant in defeating competitors. In addition, the entire organization settles on a product design and price before making the information public. For instance, Musk sought the popular views of the employees and managers before settling for US$57,400 as the price of the Model S (Heck et al., 2014). With subsequent model productions, the company aimed at reducing the prices of products in order to attract the middle class.
Weaknesses
Conflicts of interest in management
Between 2003 and 2007, Tesla had a leadership problem because Musk was a member of the board of directors even though he had the leadership qualities required of propelling the organizational position. When Musk became the CEO, Eberhard approached a court of law in California to petition against Musk and Tesla’s leadership. According to the first partner of the firm, Musk committed slander and libel, and this cratered a drift in the firm, making it reduce production in May 2009. The Roadster design for Magna International was the first to create a conflict between Tesla and a contractor (Tesla Motors, 2014). In the same year, 2008, Magna sued Tesla for non-payment of the cost of the design, and Fisker Automotive complained that Tesla took its design. This infringed on the copyright laws of the US while destroying the reputation of the company. Sharing confidential statements through public forums when there is a breach of contract naturally reduces trust among consumers in the products and the company.
The culture of a product recall
People are in the process of accepting that electric cars are safe and cost-effective. By 2009, Tesla Inc. suffered enough recalls guaranteeing organizational shutter. Roadsters had the greatest number of recalls in 2009, making the company cover for a loss of about 350 cars. Product recall is expensive because the costs of the product and consumer goodwill remain irreplaceable throughout the entire process. Such weaknesses in innovation affect the overall performance of Tesla because many people are less likely to require or purchase Roadsters (Tesla Motors, 2014). In 2010, about 440 Roadsters followed a similar trend. This created issues of low voltage and risks of accidents that most drivers exposed themselves to during driving. Weaknesses in product development are challenges because sometimes the head of design comes up with his/her principles of production that contradict consumer needs and proposals by other team members. The most difficult thing is to come up with fireproof vehicles that cannot produce heat during crashes. Notably, the company is still in the process of improving the same model (Phyper & MacLean, 2009).
Opportunities
Climate Change and Expansion
Society is in need of products and services that conserve the environment while preventing the depletion of the ozone layer. Tesla has an opportunity of maintaining sustainability because people believe in products and services that create a safe and healthy environment of stay for consumers and the rest of the world. Since the electric cars do not use gasoline, Tesla vehicles are eco-friendly, explaining why the firm gets global recognition from organizations that support green housing and green businesses. The activities of Tesla naturally promote sustainable and green business cultures, meaning that the company does not promote the principles of greenwashing (Phyper & MacLean, 2009). By maintaining the culture, the company will remain relevant forever. Tesla should take advantage of countries that opt for bicycles and a reduction of gasoline-powered cars in order to increase sales.
Technology
Technological advancements are evident in each competitive industry. Currently, Tesla creates electric powertrains to covert cars from Nissan and Toyota into electric vehicles. In most cases, the contracts involve low-priced vehicles from the target companies; however, the customization process is very complex. Unlike gasoline technology, Tesla offers a unique lithium-ion battery technology, which is cost-effective and environment-friendly. Technological advancement is the backbone of activities at Tesla; it forms the basis of competitiveness with other firms. Since technology keeps improving, the firm has to keep up with the changing processes since it currently has an online platform through which people can make orders before shipment occurs. Through the Tesla Motors Website, people can make all the business transactions requisite of car ownership from the company (Tesla Motors, 2014). The future of technology remains uncertain, but Tesla has no other choice but to embrace the changing trends in order to remain relevant.
Threats
Disputes within the external work environment
One upsetting factor of the operation at Tesla is the fact that the showrooms are different from the stores. In essence, people can either visit the company websites and the stores operated across different shopping complexes in the US, but they will see the cars later in the showrooms that are in distant states. It means that Tesla has to operate under the laws and principles of the mall owners in order to continue doing business in the designated areas. The company has to pay rent to the various store owners while operating under the restrictions of the mall owners. This contradicts operations of car dealers that have showrooms in which people can make business deals while viewing the available vehicle options. Besides adhering to the different principles of operation in the 48 states of investment, Tesla lacks joint ownership that other car dealers enjoy (Koller, Goedhart, & Wessels, 2010). As such, it has to sell cars directly, indicating that it spends a lot on marketing and promotional activities, and this threatens capital investment in other important areas of investment.
Competition
After General Motors contracted Tesla to design an electric version of the luxury sedan, GM sought out an innovative venture to manufacture the hybrid sedan in an attempt to imitate the renowned Roadster. Competition is a force to reckon with because the rivals are likely to take an original idea and improve it in order to suit consumer demands (Wong, 2013). Consequently, there are low gasoline-consuming cars and affordable Toyota versions that keep emerging to match the competition from electric cars. Additionally, Subaru and Mitsubishi have released high-speed vehicles at almost similar costs, and people are likely to purchase such cars. Speed is an issue that car manufactures cannot ignore because of reliability and convenience. Therefore, Tesla should equally make such considerations.
Strengths of the primary leadership
Visionary leadership
Before Musk became the CEO of Tesla Motors Inc., the previous chief executive laid off almost all senior supervisors. Ze’ev Drori, the 2007 CEO, had an issue with the performance of the workers. Musk, as a member of the board of directors, financially contributed towards the creation of an innovative workforce from the second to seventh rounds of capital investment in the company. By 2008, it was clear that Musk was a visionary leader in comparison to Drori, and he succeeded the previous CEO by the seventh round of capital investment in the firm (Tesla Motors, 2014). The company recorded profits in 2009 for the first time because Musk created an enabling environment through which different stakeholders could actively participate in improving the position of the firm through innovation. With a net profit of US$187 million and distribution of about 150 cars between January 2008 and January 2009, it was evident that the company had a bright future under the leadership of Elon Musk. Visionary leadership is an element of transformational leadership, which recognizes the significance of accepting change when necessary. Musk recognizes that technological advancement is the only way to remain relevant while enabling the firm to defeat the competition and meet growing consumer demands (Wong, 2013).
Liaison officer
Democratic leaders display liaison skills because they act as links between members of the team, suppliers, and other relevant stakeholders. It was the first year the company went public with its IPO, enabling Daimler to purchase shares from the company. Musk is a transactional leader who understands that understanding each department and its communication capabilities places the organization on a highly competitive platform. Emerging from contingency theories of the leadership of the mid-1980s, transactional leadership is very important for a fast-changing organization such as Tesla, whose leadership largely depends on the traits of Elon Musk (Phyper & MacLean, 2009).
Charisma
Musk is a pacesetter as supported by most democratic leadership theories. Charismatic leaders approach both managers and workers in a friendly manner while creating a good working environment for the employees and the target population. Contingency theories mention that leadership concerns behavior and not the personality of the leader. Besides the ability to quantify behavior, leaders should display high levels of accountability, which remains difficult to quantify through personality (Lussier, 2008). However, when the personality effectively contributes towards organizational progress, then it requires support from other team members. Musk is a leader who shares the organizational vision with team members while delegating duties to employees. Charisma also helps leaders acquire contracts and loans from credible institutions in order to facilitate the fiscal flow of resources in their companies.
Weaknesses of the primary leader
Need for perfection
Almost all trait leaders often pursue perfection, and Musk is not any different. Trait theorists always suggest that leaders have the ability to influence organizational decisions with their personalities. Musk always seeks to align all activities in the vision and mission of the company. Perfection is difficult to achieve, but visionary leaders always attempt to break the glass (McKnight, 2012).
Excess visibility
Musk enjoys excess visibility that mostly links to authoritarian leadership. It remains very difficult to know innovators in the company who strive to improve the company’s position in the rivaled environment. Other board of directors, including Brad Buss and Kimbal Musk, fail to make a prominent presence in discussions involving the company and its progress (Griffin & Gregory, 2010).
Motivation
Recognition of employees and supervisors provides an environment of growth. Succession plans are the most evident form of non-monetary motivation in the firm. People need pay increases, leaves, vacations, team-building platforms, and other forms of motivation in order to increase performance levels without duress. Both monetary and non-monetary techniques of motivation have an impact on the performance of different people in organizations, implying that workers of Tesla should enjoy the benefits of democratic leadership instead of giving all credit to the organizational leader (Lussier, 2008).
Recommendations
Targeting countries that seek alternatives to gasoline use
Countries like Netherlands and Egypt opted for bicycles in order to reduce the process of environmental degradation caused by global warming. Even though the two countries are not part of the plan that the American strategy intends to establish in the business, it will be difficult to ignore the fact that several countries embrace the bicycle culture to avoid the release of vehicle wastes that have many effects. China and parts of the US are experiencing smog, which interferes with visibility while exposing children to asthma. The third and fourth series in which Musk actively played the financial role transformed the business into a fully empowered technological institution that immensely supported green businesses across the US. The round three-capital investment by the three partners earned Tesla Motors Inc. US$7.5 million. As a result, the company obtained the Global Green award for its quality product development in 2006. This makes the future of Tesla good in countries that believe in green businesses.
Improving technology through future car generations and maximizing marketing
While offering a range of sporty electric cars, Tesla operates in a rivaled market. This explains the significance of quality leadership in the overall management of human resources. Common vehicles designed by the company include the luxury sedan, model S, and Model X. Tesla is in the process of creating future car models with a mileage of about 650km, high battery power made from lithium-ion. Tesla has limited time to prove to the rest of the world that it is worth the attention received by gasoline-driven cars by improving on the vehicle technology (Vreede & Briggs, 2000).
Reduced dependence on loans
Both Advanced Technology Vehicles Manufacturing Loan Program and the previous loan earned Tesla US$8.465 billion in one year, enabling Musk to continue with the eighth and ninth capital investment plan of the company. The company began earning interest and acquiring contracts by 2005. In 2009, it was evident that collective opinions from different workers and supervisors earned the company the goodwill of suppliers. Additionally, Musk became the greatest shareholder of the company; he makes most decisions on loan acquisition – a trend that should stop completely. Other avenues of financial acquisition exist, and Tesla should seek financial and legal advice concerning organizational management (Daft, 2012). Reduced loan acquisition will enable the company to have its own malls that can make couples up as showrooms and galleries for contact centers (Phyper & MacLean, 2009).
Conclusion
In sum, Tesla Motors Inc. is in a financial position that most companies would seek to match, but there are elements of the organization, including the inability to share a similar vision in 2009, that almost disrupted its normalcy. The company should focus on minimizing the weaknesses while maximizing its strengths through an annual appraisal of leadership. Leaders should not be managers that make financial decisions while deploying people based on individual intuition. Instead, they should provide an enabling environment for combating the challenges.
References
Daft, R. L. (2012). Management. Mason, Ohio: South-Western Cengage Learning.
Griffin, R.W., & Gregory, M. (2010) Organizational Behavior: Managing People and Organizations. Brisbane, Australia: South-Western/Cengage Learning.
Heck, S., Rogers, M., & Carroll, P. (2014). Resource revolution: How to capture the biggest business opportunity in a century. New York: Brilliance Audio.
Koller, T., Goedhart, M. H., & Wessels, D. (2010). Valuation: Measuring and managing the value of companies. Hoboken, N.J: John Wiley & Sons.
Lussier, R. N. (2008) Management Fundamentals: Concepts, Applications, Skill Development. Mason, OH: South-Western/Cengage Learning.
McKnight, R. (2012). Steve Jobs and Leadership Theory: Reconciliation Needed? Web.
Melik, R. (2007). The rise of the project workforce: Managing people and projects in a flat world. Hoboken, N.J: John Wiley & Sons.
Phyper, J, D., & MacLean, P. (2009). Good to Green: Managing Business Risks and Opportunities in the Age of Environmental Awareness. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
Tesla Motors. (2014). Web.
Vreede, G.J. de, & Briggs, R.O. (2000). Collaboration Engineering: Designing Repeatable Processes for High-Value Collaborative Tasks. IEEE Computer Society, 1(6), 17-21.
Wong, W. E. (2013). Emerging technologies for information systems, computing, and management. New York, NY: Springer.