Problem Statement
Introduction
This dissertation critically illustrates the perceptions and attitudes of earning management and factors touching their motivation and exploration within the modern organisation where the corporate fraud of Kelong and WorldCom have been passed. The dissertation has been organised and contained the five major episodes designed below
- Problem Statement: This episode of the dissertation has organised with a study in wide-ranging among the selected organisations, endow with the underlying problems of the earning management, hypothetical principles of corporate governance and agendas for the research; raise the research questions and affirms the limitations and scope of the study used within this present dissertation.
- Literature Review: This part of the dissertation launches with a chronological indication of earning management and its motivation theories; then, recites too more up to date literature integrating modern corporate governance measures and accounting standards with the aim to theoretically answering and arguing to the research questions; and expression on accomplishment of conceptual framework of regularity authority in China and USA to ensure suitable stock market situation and sustaining investors confidence;
- Research Methodology: This episode of this dissertation furnishes the explanation and way out on how the research would be conducted, describes position and population selection, data assembly and treatment, develops a qualitative analysis of the data, gives explanation of the process and states limitations of this study;
- Findings & Discussion: This segment of the dissertation specifies the collected data, denotes unexpected results by concreting on the findings as well as hypothetical uses for the information delivered from the earning management practice of Kelong and WorldCom and proposes idea generation for the research from secondary data; enlightens the results in reflecting the outcomes of the research and discuss on validation of findings;
- Conclusions: This final episode of the dissertation summaries the process, advises sensible outcomes that constructs the key recommendations; and promotes conclusions as well as implications of this study.
Background of the problem
Hirshleifer (2008) has explored his brave opinion saying that from the very ancient age cheating and fraudulent operation is a common phenomenon of economic history and there are rising depicts that the businesspersons are thieves as well as murderers, thinkers like thinkers as Aristotle and Confucius had also supported such views. Francis et al (2003) added that the fraudulent reporting of certain results of capital market by inadequacy, has endow with a attractive company base for capital allocation integrating with corporate governance as well as corporate social responsibility
Richardson et al (2002) concentrated more on the performance of earnings management and urged the academia to paying keen attention to sustaining the stock market from massive fraud. Lee et al (2007) added that the most common feature of earnings management is to produce an income smoothing which is an old debate in the accounting arena while the other features comply with the objectives, process, and implication of manipulation with excellence. Laux (2003) pointed out that the modern accounting scandals those have produced analogous panic in the corporate world and urged for mass awareness upon the genuineness of the quality earnings as well as the earnings management practice while the accounting practitioners eager to pact with management to get undue advantage keeping aside GAAP 1 standard of accounting.
Moberg & Romar (2009) addressed that in 2002, the collapse of WorldCom confessed that through practice of earnings management it has rudely kept aside more than US$ 3.8 billion showing in the annual report as usual costs of capital expenditures but escaped this handsome amount in secret account. The officials, directors, and auditors of WorldCom escaped from the civil and criminal litigation by filing for bankruptcy without returning a single farthing to the investors and borrowers. At the background of such corporate fraud of WorldCom, Enron and other corporate houses, the US legislation introduced SOX2 to strength corporate governance and to ensuring transparency of accounting practice.
Reuters (2008) reported that the corporate fraud of Kelong is the prevalent stock market scandals of China, the previous chairperson of Kelong Mr. Gu Chujun was charged for his ill practice of earning management and sentenced for 10 years imprisonment with penalty of US$ 992,700 including the paying back of 165 million Yuan, which has stolen through earning management. Chairperson of Kelong Mr. Gu pleads an appeal, but the high court upholds his punishment.
In such a background problem of earning management, where the officials, directors, and auditors of WorldCom rescued just filing bankruptcy but Kelong Chairperson penalised, Hirshleifer (2008) raised question marks to the corporate governance and corporate social responsibility of the business community and argued for stronger driver of financial regulation as well as regulatory control.
Rationale for the research
Many scholars tried to find out the solution of the question how earning management in a certain company’s accounting practice could influence the investors in the capital market to raise share price of that company and how the corporate fraud occur breaking the stock market stability and investors confidence from last era. Most of the contemporary researchers have concentrated on the accounting standards, corporate governance and regulatory reform in the stock market, but no overarching research agenda has yet been proposed on whether the earning management is a conscious drive of corporate world for cheating or not. Gonedes and Schnellar (1984) pointed out that if the companies focus more on accounting statement manipulation with the tools of earning management then they will try to retain more investor’s confidence and the large companies began to utilise such tools as a way to retain more enhanced share value and investors. Rath and Sun (2008) added that earning management openly distresses the whole truthfulness of the financial statements as well as notably manipulate resource distribution in the economy while the academia, regulators, and investors are eager to prevent malpractice of earning management.
The rational of this research is to analysis the earning management experience by observing the real scenario of Kelong and WorldCom to evaluate to what extent earning management is effective to retain investors and increase share price and how they collapse. In addition, the fraud of Kelong and WorldCom has escalated the awareness of regulators to take control over the earning management tools and bring back the investor’s confidence; this dissertation will assist the academia, regulators, and investors with better understanding about the corporate frauds including its driving force such as non-holy alliance with the managers and non-executive directors. Through this investigation, the listed companies will get a potential investment environment in the stock market and get a better level of inventor’s confidence, which will provide the companies a practical advantage over their non-executive directors and managers.
Research Question and Objectives
This dissertation aimed to investigate, does earning management is a conscious drive of corporate world to cheating with the investors in stock market? To highly structure the aim, the dissertation has been designed to respond to the following research questions, the answer to this question would enable the legislators and regulating authority to organise the policy and towards a greater motivation for increased confidence of investors. Three research objectives are listed below:
- Does earning management inspire corporate fraud rather than maintaining Accounting Standards?
- How earning management turned corporate governance structure worthless?
- Is it possible for regulatory authority or listing rule to stop ill practice earning management?
All of these above issues will assess under certain considerations along with theoretical background and these tasks are significant since each of those issues are closely interrelated with scenario of the said companies Kelong and WorldCom and their performance of earning management.
Limitations of the project
The researcher of this research paper has suffered following problems to formulate this paper –
- Lack of reliable secondary data sources or unnecessary information was the main problem to organise the paper, for instance, relevant data on Kelong Electronics is not available in internet;
- In addition, the author gets very short time for planning and conducting research;
- It was not possible to collect data from the executives or employees of Kelong and WorldCom. As a result, the researcher would complete the paper based on secondary sources and primary data from the LSE investors to overcome this dilemma;
- Budget was not sufficient to purchase relevant reports or journal articles.
Scopes of the study
- The author has selected a unique topic, which gives the opportunity to research on various issues, for example, the effect of manipulation of accounting information, gap of corporate governance system and so on;
- One of the main objectives of this dissertation is to evaluate the impact of earning management on the multinational companies;
- The researcher has scope to find out the difference between Kelong and WorldCom case;
- As the issue of earning management interrelated with corporate fraud, the endeavour of the researcher to fill in the gap or loophole of the outcomes of previous research;
- On the other hand, many large companies have collapsed due to manipulation of accounts or ineffective earning management system. In this context, the researcher has scopes to give proper guidance to reduce corporate fraud.
Relevant Literature Review
Overview of the Topic
This literature review has integrated with the writings, researches, and scholarly opinion concerning the practice and evaluation of earning management, its aggression to the stock market and its influence on corporate governance connecting to corporate fraud. The design and motivations for this literature are associated to creating value and confidence for the investors and to overcoming the threats of corporate fraud raised due to aggressive practice of earning management and to guiding the regulators to bring healthy atmosphere in the stock market. It provides the background for desirable evaluation of does earning management is a conscious drive of corporate world to cheating with the investors in stock market, factors are most significantly persuade the concerned capital market.
The scrutiny and illumination of contemporary researchers concerning earning management and its motivation towards misrepresentation, acceptance, and effectiveness of corporate governance to preventing earning management are also discussed simultaneously. The chronological theories as well as modern approaches of accounting norms are also addressed form an unyielding foundation from which will enrich this research study bringing the changes in practice.
Scope and Limitations of this Review
This research work replicates the authors and researchers paying full attention in the description, dimension, evaluation of earning management as well as corporate governance implication within the concerned counties and its resultant effects in those stock exchanges. The report highlights on studies those converses on the implications of earning management and corporate governance practice, to the regularity authority’s service development, knowledge utilisation, and skills in change governance. The extraordinary emphasis has been adopted upon the regulation and the management excellence while both the remarkable and contemporary writings are reviewed with added concentration provided to those authors’ theories.
With massive width of literature concerning earning management, this evaluation has been limited to the mainly sustained theories as well as established principles while it has just a prototype of the mass of earning management literature. Similarly, the extensive assortment of beneficial writings related to success of corporate governance where regulations are effectively necessitated, this review has taken out from principally mainstream works of time-honoured authors. The underlying assumptions for applying these limiting selections are that the accounting professionals are implicated in unique, singular thoughts on earning management and managers motivations in this regards.
Organisation of the Literature Review
This literature review has organised with following heads
Paradigm of Earning Management
McKee (2005) engaged his efforts to defining the earning management as a manipulation of an organisation’s economic indicators in the earnings report by direct misrepresentation or by accounting magic game, earning management is also familiar named as reengineering of income statement and aggressive accounting.
Spohr (2005) added, though there are many standard norms of accounting, earning management practice bypass or ignore all of the accounting information and stands to occur manipulation in their reports, even without mantling GAAP, FIFO and LIFO to adopt in the inventory management to represent elevated financial ratios to the investors and stakeholders.
Cohen and Zarowin (2007) explored that the accounting has aimed to providing the dimension and interaction among the decision makers regarding economic information while such information users have classified into two segments and presented with external and internal accounting. The external accounting is very influential approach for the stakeholders as they would try to understand the real businesses prospect of the company and then they will make their decision to what extend they would continue relation with that company. Companies always eager to sustaining their stakeholders in both good and bad time but the investors and other outside stakeholders are much more aware to leave the company before occurring any massive lose to keep their investment risk free. In such conflicting situation to misguide the investors, the modern corporate world has driven to manipulate their external accounting statements and this type of corporate dishonesty has given birth of earning management also noted as accounting magic or income smoothing.
McKee (2005) criticised that due to the GAAP reporting rules are most likely contradictory and complex, it is not easy going for the investors and regulators to trace out the misrepresentation of accounting magic, has provided vast opportunity for the corporate world to pact with the accountants with the aim to lead aggressive earning management. As the real economy logged with GAAP motivated and encourage to maintain this principals, the unholy pact drives higher level of earning management while their group interest undermine to throw the investors in risk and such tendency lead the stock market towards massive fraud.
Nelson et al (2003) pointed out the secret accord among the unholy alliance to commence earning management as follows
- The auditors scrutinise that accounts of the companies and provider clean report findings on the quality of earnings of their clients as well as train how to commence earnings management, independence of auditors have a massive role to the corporate frauds;
- The regulating authorities trace out those are prevalent to occurring earning management and adopt regulatory measures and changes in that area
- The managers and audit committees look forward to the financial transactions which the investors would observe as a rule of doubtfully and emphasis to manipulate them ;
- From their own viewpoint CEOs or CFOs, and audit committees, as well as investors keep their keen attention to the areas of the financial reports at the point of their interest and feel most disbelieving;
- Academia teach students about earnings management and their adoption
- The researchers spotlight upon their studies in the areas of massive earnings management action and such action inspire further fraud;
Earning Management Model
The model for earning management estimation is a vital issue in the modern regulatory authorities to auditing the corporate accounting and financial reports and a few models has been organised with different features. There is long research with the earning management estimation, identification process and first of all Jones (1991) presented his model based on expected accruals measurement along with type-II & I error metrics that is mostly familiar as Cross Sectional Jones Model. Dechow et al (1995) investigated with the error type-I integrating discretionary accruals and several test results suggested to avoid such error to identifying earning management and they advocated for error type-II calculating with unexpected accruals for improved measurement of earnings management, which later named as Cross Sectional Jones Model. Rather than discretionary accruals, Zhang, H. (2002) presented his presented his earning management model with factors of the EPS3 round up issues while managers carry out this manipulate to confuse the investors in the stock market.
However, the practical evidence would spotlights on insights commencing the financial statement analysis moderately than incremental modification of models applied for making out unexpected accruals to detecting earning management while the practically well defined random samples have lacking power to detecting earnings management of credible standard of scale (Dechow et al 2003).
Bayley and Taylor (2007) have applied the binary logistic regression analysis to the degree of dissimilarity on financial statement features with observation next to two-sample groups such as earnings manipulation and control and presented the earnings management score as follows-
![]()
Here
EM = earnings management score (indicated with binary logistic score)
X = jth feature of independent variable (defined as red flagged financial ratios)
W = predicted coefficient to weight up the jth feature
Within the binary expression model, the dependant variable EM would be estimated equivalent of one while there is an evidence of earning manipulation; if there is no evidence of such manoeuvring then it tends to zero. Then applying the forecasted probabilities, which would be delivered from the above model, would expend with ![]() to weigh up finish values to settle on how far earning management practice has involved in the financial reporting.
to weigh up finish values to settle on how far earning management practice has involved in the financial reporting.
The costs without clarification include with error type-II & I where the type-I errors take place due to EM-score incorrectly engaged for manipulation and error type-II indicates the malfunction to identifying earning management occurred due to non-earnings manipulation, the costs allied with the both types of error are expected to differ significantly in practice while manipulation costs minimised with equation-
![]()
Here –
EC = Expected costs for earning management,
q1 = Estimated prospect of fraud occurred in the financial reporting,
q2 = estimated prospect of non-fraudulent financial reporting,
M12/N1 = Pragmatic error type-I connected with non-earnings manipulation,
M21/N2 = Pragmatic error type-II connected with earnings manipulation
C1 = cost associated with the errors type-I,
C2 = cost associated with the errors type-II (Bayley and Taylor 2007);
Zhang (2002) argued that the equation-2 is essential to identify for the preceding probabilities of false financial reporting and even for the standard accounting categorisation but it is quite complex to determine the intensity of earning management far from the GAAP tolerance.
Jones (1991) pointed out the that to evaluate and identify the comparative power of red flagged accounting report testing with extensively applied unexpected accrual tools, it is vital to relate the point of reference of EM-score metric aligned with expected accruals calculation that will contribute to generate unexpected accruals and modified cross sectional model of Jones stands as follows –
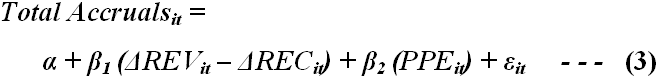
Dechow et al (1995) investigated with the expected accruals and argued to modifying Jones cross sectional model with an essential amendment connecting to the expected accruals to determining the earning management adopted in the real life practice for investors and regulators by ensuring validity and acceptance and the equation stands as-
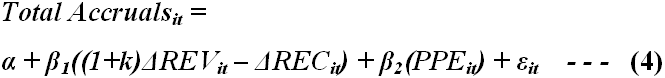
Bayley and Taylor (2007) explained the modified Jones models demonstrated in the equation-4 and deliberated on expected accruals estimation as follows-
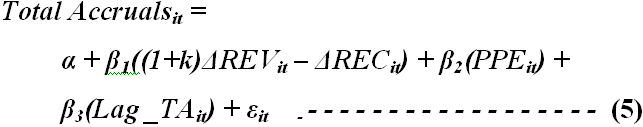
Zhang (2002) and Dechow et al (2003) argued that TA4 would be calculated while the differentiation involving the single episode hold-up with value of revenues earlier than extraordinary items and the operational cash hold-up value of total assets while accruals are not open understudying approach for investors like cash flows statement and the total accruals would progress the foretelling capabilities.
Accounting Standards & Earning Management
Goncharov and Zimmermann (2008) pointed out that every accounting standard has its own approach integrating with different accounting choice with their unique costs and the accounting magic would apply those tools for earnings management where GAAP is the most popular approach. Bayley and Taylor (2007) has identified six categories of GAAP violation through earning management, these are as follows-
- Operating accrual magnitude (ACC): It is the assessment of functional accruals depressed by entire assets within the time of GAAP abuse and deliberated as net income before extraordinary items together with deprecation and amortization costs deducted from cash flow aimed to upwards earnings management (Zhouet al 2008)
- Sales index (SLSI):SLSI This type of violation evidenced with the ratio of net revenue comparative to the hypothetical estimate of net revenue without manipulation and to do so the process of time series analysis would be applied for further calculation of earnings management;
- Accruals index (ACCI): The difference among the earning and cash flow would be identified as a major sign of earnings management while this type of violation has measured as a summation of current value with one, while the operating accruals let down through the average of current and total during GAAP violation and eager to detain with time series analysis;
- Inventory index (INVI): The corporate management has substantial diplomacy regarding the timing of inventory write-offs and production decisions to blow up inventory levels and reducing connected charges for goods sold and they emphasis to manipulate them through inventory accounting techniques;
- Reserve index (RESI): The corporate management has significant subjectivity to the estimation of expense where audit partner pacts to producing manipulated report its most well liked process integrated with the ratio of the current bad debts for earning management;
- Asset quality index (AQI): The boost of ostensible soft asset balances suggestive to insistent cost capitalisation including intangible assets where the corporate management may indicate greater than before cost postponement and consequential upwards earnings management (Parfet 2000)
Earning Management leads to Fraud
Jones (1991) identified the evidence that the corporate houses drive to manage earnings downstairs while consider to have import duty relief due to lower import price where tariff protection is unavailable, thus they engage with fraud by means of earning management.
Gombola (2008) pointed out that earnings lean to be managed downhill proceeding to management buyout offers mostly drive to a down in the dumps stock price on condition of oppressed by managers captivating over the company, it may result the evidence of noteworthy ascending earnings management during the stock offerings. More evidence of frauds is available at initial public offerings; companies may not forget to adopt earning management during seasoned equity offering, and earlier to reverse LBOs including typical level of abnormal accruals before IPOs.
Cohen et al (2007) explored that due to the occurrence of frauds has been evidenced under the operation of excellent corporate governance approach and elevated practices resulting to escalating independent directors out side from the companies are getting entry in the board and for the most part on the audit as well as compensation committees. There type of outside directors has different intention and different values to engender with fraud, so it is quite difficult what would be the ultimate policy respond though well-defined corporate governance practices argue to escort lesser degrees of earnings management in the contemporary operations. Dechow et al (2003) demonstrated that the accelerating number of outside directors and further economically sound members at the audit committee might decrease the company’s involvement with earnings management but what is dependable that the companies may not corrupts the regulatory personalities.
Corporate Governance Conflicting Earning Management
Wang et al (2010) mentioned that the essence of corporate governance and the corporate motivation to commencing earning management is very conflicting with each other, when the corporate governance uphold the ethic of transparency to preventing frauds, earning management or accounting magic always look for ambiguity and trick to occur massive fraud from investors or public money.
Cornett et al (2006) pointed out that the introduction of corporate governance has implemented with the view to reduce earning management while it has directed about the board of director characteristics, ratio of non-executive directors in board, institutional ownership, duration of the CEO and chairperson including board size and age limit of CEO or CFO.
Ahmed et al (2008) added that both the accountants and financial consultants have constant and extensive awareness to observe the impact of governance structures as well as compensation schemes based on corporate behaviours and by this time, some of the accounting research has demonstrated that this approaches have an extensive impact on earnings management.
A number of literature mentioned that if the corporate governance has influence on earnings management then the noticeable impact of such arrangements would split on financial performance with structure and direction of corporate governance for encouragement base compensation persuade companies performance while deliberated performance will be adjusted to assess the impact of earnings management in those companies.
Regulation Dynamics for Aggressive Earning Management
Munter (1999) mentioned that to preventing corporate fraud, the regulatory drives are long been modifying with the acceleration of aggressive earning management where Securities and Exchange Commission5 has introduced a comprehensive plan to deal with the dilemmas of stock market to reinstate confidence of the investors. Zhou et al (2008) argued that the role of SEC is merely confusing in some instance while there is history of huge massive corporate frauds in the financial market, there has not yet any complete regulation to preventing frauds for long run, but after every fraudulent collapse, they bring regulatory reformation or new legislation.
Being the regulatory authority SEC needed to formulate advanced the accounting framework with enhanced exterior auditing in the financial reporting procedure and underpinning the audit committee process for controlling aggressive earning management to interact with the members who has lack knowledge with the essential principles of financial reporting including mandate to enquire the penetrating questions.
Corporate Governance Structure & EM
Typically, corporate governance in any country has characterised organisation’s behaviour towards their stakeholders particularly, shareholders in collaboration with public, private and the government. Currently, scandals of the reputed corporations have faced difficulties in business ethics issues as well as they have a great trend be a public listed company. In case of private organisations, few regulations of the corporate governance have infrequently practiced to boost capital structure, market growth as well as greater acquisition (Balasubramanian, 2010).

USA
The US corporate governance has concisely considered two aspects during formation of legislation boundary, regulatory structure, as well as market responses. Firstly, limitations of the existing corporate governance performance and second, how would be these limitations overcome? In recent times, the US corporate governance has greatly criticized due to an immense financial scandal of the WorldCom, Enron, Tyco, and several famous organisations. Consequently, the US legislative system has immediately taken an amendment through introducing Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 along with regulatory amendment proposed by the NYSE6 and NASDAQ. Before Enron and WorldCom scandal the US legislation has termed as “catalysts of lobbying” and hence incomparable twist occurred in 1990 the US legislation has alarmed to response promptly (Holmstrom & Kaplan, 2003).
Sarbanes-Oxley7 Act 2002
As said by the SOX, each one of the organisation’s audit committee has to be associated with the its board of directors as well as be autonomous, here the term autonomous has defined as it has prohibited that if a member of audit committee received direct or indirect compensation in terms of consultation until the board service wished to compensate. SOX Act has to execute during remuneration structure setting, nomination committee, auditing and formation of the NED8 and for all of these operation audit committee would be responsible. Additionally, it has to be disclosed that whether the company has appointed minimum one financial specialist to serve their executive committee though SOX has not yet define how the financial expert would be appointed. However, the SEC9 has proposed characterization for the appointment of the financial expert (Board Source, 2003).
UK Five Reports
Strategically, legislation system of the UK has diverse from US and has expressed through self-declaration approach in terms of “comply-or-explain”. After scandal and collapse of the Maxwell group during the end of 1980 corporate governance of UK has appeared in front. More specifically, whenever the Cadbury report has published during December 1992. Consequently, in order to fulfil corporate governance amendment claims another four report has published and sequentially they have named as Greenbury Report (July 1995), Hamel Report (June 1998), Turnbull Report or the Combined Code (September 1999) and the Higgs Report (January 2003). These five reports have proficient in dealing entire corporate governance issues and financial sectors specially the Stock market. Finally, the UK government has approved Companies Act 2006. In recent times, UK legislation system has started to follow US penalizing catalysts since private enterprises has now preferred UK to be listed in the stock market. As a result, in case of internal auditing UK legislation system has amended and included corresponding SOX provisions (Rayton & Cheng, 2004).
Cadbury Report 1992
Cadbury report has encouraged and affords support to the existing and potential private enterprises as a result they would be entailed entire feasible modes to effective discharge as well as enjoyed superior corporate governance as said by the current legislation system. Point noted that, for the first time comply-or-explain self-declaration approach has introduced and has retained. (UKSA, 1992)
Greenbury Report 1995
Followed by the recommendation of the Cadbury report, the Greenbury report (July 1995) has advocated about the remuneration package of the board of directors as well as more focus on internal controlling and auditing (FRC, 2006)
Hamel Report 1998
During June 1998 the Combined Code on Corporate Governance” has issued by the London stock exchange and termed as the Hamel report. The Hamel report has conceive throughout 17 principles and 48 provisions describing five major divisions of the board of directors, their remuneration package, transparent relation with the shareholders, investment policies, auditing and accountability. Cadbury, Greenbury, and the Hampel committees have consolidated outcomes of the Combined code (Rayton & Cheng, 2004).
Turnbull Report 1999
APB (2010) mentioned that the Turnbull report has provided the guideline for the board of directors implementing provisions of the internal controlling and auditing as said by the combined code. In short, Turnbull report has the most effective guideline for internal controlling moreover, more widely pursued guideline in UK (APB, 2010).
Higgs Report 2003
Higgs report has recommended about the role of NED to protect further review of the scandal and collapse cases as of the WorldCom and Enron (FRC, 2006).
Company Act 2006
Revised form of the Higgs report has strategically described in the provisions of the Companies Act 2006. Moreover, four chief regulatory objectives have also kept in this amendment and the intentions have included financial and stock market confidence, civic consciousness, stock punchers’ protection, and proportionate decline of the financial fraudulent. Among all of these forces, the Companies Act 2006 has drawn tackling both of the perceived and existent stock market collapse (Walker, 2009).
Corporate Governance In China
Wallison (2005) added that corporate governance in China has reformed thorough four chief sequential phases. In early 1970 first phase SOEs10 was formed, traditional model of corporate governance was developed in 1950 and afterwards in 1984 the transitional model of corporate governance was outlined. Finally, 1993, china has reformed the modern corporate governance model which has still practiced. Typically, corporate governance has greatly affected on Chinese firm’s valuation as well as illustrated the corporate governance policies. On behalf of business, analysis’s china has mostly practiced “control based corporate governance model” that has fairly oppose from the “market oriented model” widely practiced in both UK and US. In a survey report, it has evaluated that application of the market oriented model has able to achieve better performance as well as nursing shareholders interest compare to the control base model. Origin of the control base model has governed by the administrative governance strategies drawn by the regulatory authorities of China (Liu, 2005).
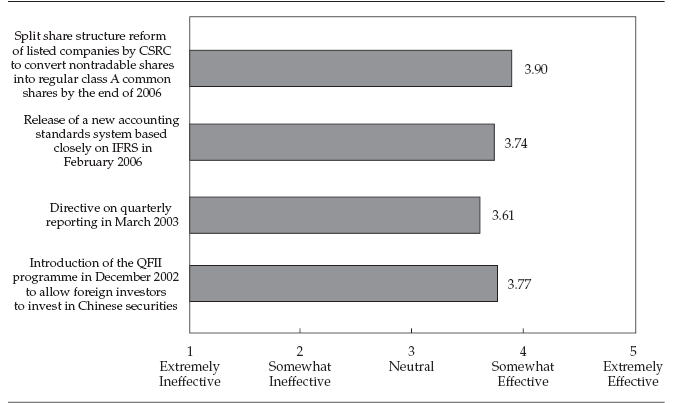
A brief draft of the first three phases of Chinese corporate governance model has demonstrated below.
First, the SOEs (1970–1950): since beginning of the 1970 Chinas has started to reform their SOEs segment where accounting standards, reporting attributes and reorganisation model has taken place. Alternatively, financial market has significantly driven by the SOEs reform. Moreover, SOEs has played a vital role to efficient business operation as well as economic progress. (Leung et al 2002)
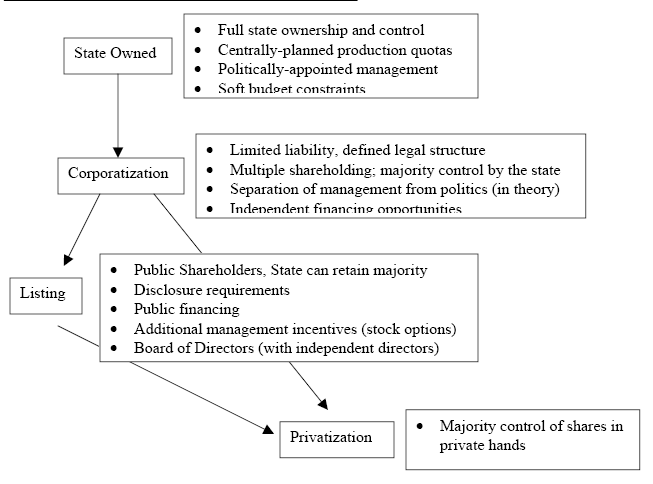
Second, the traditional corporate governance model (1950–1984): usually, the traditional corporate governance model has act as a legal defend to protect state properties and state ownership of the properties has played as key spine of the model (Richet et al, 2000).
Third, the transitional corporate governance model (1984–1993): during this period Chinese banking sector has immensely reformed and developed. The central bank of China has departed from ICBC11 and has started to operate industrial organisation, FDI12 firms, and the peasants has operated as well as dominated diversely. Moreover, the commercial banking sector has specialized under supervision of the monetary reform and segmented through four sectors (Leung et al, 2002).
Research Methodology
Introduction
The prime objectives of this chapter is to demonstrating the process how the preferred research methodology will go with the foremost goal of the present dissertational inquiry and how it will complete through out this concurrent study. The author of this dissertation will conduct the research in accordance with six major steps for research approach defined by Malhotra (2009) rather than the case study approach of Yin (2002). It should point out that the researcher had the opportunity to adopt case study approach as Stake (1995) and Yin (2002) guided that this approach is not applicable when the concerned research questions starts with “what” or “how”. The research questions supported Yin’s approach but it would be easier for the researcher to go with approach of Malhotra (2009), as the researcher has to research on overall the effects of earnings management practice at Kelong and WorldCom.
To organising this paper, the researcher would design a questionnaire taking into account of the topic and a research problem, collect primary data from the target interviewees, get rid of all mistakes from survey reports, and demonstrate the results with conclusion and recommendation.
Research Approach
Malhotra (2009) and Saunders et al (2006) have demonstrated same point of view that there are mainly two research approaches, for instance, qualitative and quantitative, in order to formulate this paper, this researcher will adopt both approaches to find out the problems but the researcher will deliberate more on qualitative approach. In addition, quantitative approaches have equal significance to determining the effect of earnings management from the corporate fraud of Kelong and WorldCom. Sekaran (2006) mostly categorised research design as exploratory as well as conclusive, and differentiated them arguing that the main purpose of exploratory research is to explore the impending and understanding of the dilemmas face up to the researcher whereas the conclusive research is more formal, structured, and categorised into descriptive and casual, this paper has utilised both the two approaches. However, the researcher designs the questionnaire by applying several techniques to gather primary data for perspective of investor’s attitude to the practice of earnings management at London Stock exchange.
Primary research
Sekaran (2006) and Malhotra (2009) presented his views on primary data and asked to generate for the definite reason or resolve the research problems; as a result, the author of this dissertation would consider this type of data. To observe the authentic effect of earnings management to the LSE13 investors and to suggest desired preventing measures to protecting aggressive earnings management practice is the main motivation of primary data. With these objectives, the researcher would consider one hundred investors at LSE for data collection where both national and international small and large investors were available for interview. However, the following chart demonstrates more information about the primary research –
Table 1: – Selected Respondents for interview. Source: Self generated
Selection of Interview process
According to the view of Zikmund (2006) and Yin (2002), the most familiar manner of primary data collection process is confronting each other interviews; as a result, the author of this research paper managed sufficient time to gather primary data by adopting the technique of face-to-face interview. It has already mentioned that the researcher selected 100 individuals for interview; among them 50 are direct investors and other 50 are broker or investors representatives taken their appointment for interviewing about earning management. However, the researcher has chosen London based investors to avoiding harassment of visit different place. On the other hand, the researcher used some other instantaneous methods to conduct primary research, for instance, traditional telephone, and e-mail played vital role while the executives were unreachable for direct interview or reluctant to giving personal appointment.
Data Analysis process
At this phase, the researcher of this study would recheck all the data to remove the incompatible and fabricated information about the effects of earnings management practice at the stock market. Here, it is important to state that the researcher would refine primary data by considering secondary data related with the implications of earnings management practice on investors attitude. However, the researcher would compare and contrast the primary and secondary data regarding the impact of earnings management practice at LSE investors by presenting graphical charts and using other explanatory techniques.
Secondary data
There is enormous information accessible in the issue of earnings management practice and its impact on the stock market environment as well as investors, the researcher of this dissertation would organise the literature review and discussion chapters by using secondary data sources. Saunders et al (2006) pointed out that the assortment of secondary sources are the published research works of renowned authors, for instance, magazines, books, journals and previously execute research and media news. Malhotra (2003) and Yin (2002) recognised that the use of secondary sources has numerous advantages, as the information of these sources is more authentic and based on noteworthy research. At the same time, all these are processed data for serving the present function provided by the concerned institutes. Furthermore, the investor’s attitude in the stock market is one of the most sensitive matters in global economic downturns, so it would be easy for the author to collect such information from secondary sources.
Questionnaire Design
Malhotra (2003) and Stake (1995) explained that the questionnaire is one of the most imperative parts of the dissertation and it is an art not at all science, so the researcher of this thesis involved this highest effort to designing the questionnaire. Saunders et al (2006) further added that broad discussion with target interviewees might bring unjust outcomes with different observation and opinion whereas specific questions would lend a hand to the respondents to discuss with a particular issue. Here, it is significant to state that the researcher emphasised more on questionnaire because key recommendations, conclusion, and the findings of the research would developed from the feedback of the interviewees. In order to design the questionnaire, the author would like to put simple questions with uncomplicated contents in the questionnaire.
Limitation of Data Collection Procedure
The fraud case of Kelong Electronics Co is one of the most recent issues in terms of effectiveness of corporate governance. However, there are no available data for the companies, unreliable resources, unavailability of annual reports, and irrelevant information were the main troubles to collect secondary data for the paper. However to avoid contradictory data, the researcher conducted a survey and interviews only 100 investors in LSE, due to short time limit it just encountered with a small number of sample.
Data Analysis and Results
The most cardinal part of the dissertation, this chapter has deliberated to analysing data and discussing the results of the real survey to estimate and evaluate the effect of earning management evidenced from Kelong and WorldCom
The simple data analysis from the questionnaire results individual responses regarding the perception of the respondents towards earnings management can be varied from each respondents and it is accounted that group wise responds are not same that different from each other in the same group. However, the researcher categorised the responds according the closed end questions belongs to the attributes of earnings management.
The respondents comment to any question while provided ‘Yes’ or ‘agree’ to any attributes of earnings management, would be easily categorised to the available extract variables classes and recorded with proper number and percentage by giving indication to the respondent’s views what they argued to say. While the respondents answer to any question marked as ‘No’ or ‘disagree’, still it brings some sense to the point of earnings management that turns to the new standard earnings management and these data may not conflict with the previous but enrich the process of decision making towards those attributes.
This researcher has classified the questionnaire data and transformed coding into Microsoft Excel and analysed the data to convert the outcomes as per questionnaire data represented by relevant numbers and values indicated by the respondents and presented with graphs and pie chart. Here the data analysis and results –
Section A: About Respondents
Question (A) to (E) are the introductory question about the investor to get general perception about the interviewees.
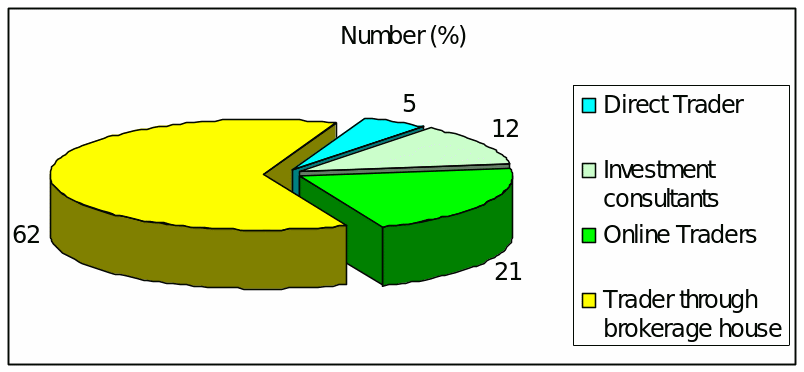
Question (A) : Integration with the Stock Exchange
Answer to this question demonstrates that among the respondents, the number of Direct Trader were 5, Broker /Investment consultants were 12, Online Traders were 21 and Trader through brokerage house were 62 and presented as –
Question (B ) : Gender grouping
Respond to this question demonstrates among the interviewees 32 were female and 68 were male
Question (C) : Grouping with Age
Answer to this question shows that there were 7 respondents of age group 18 – 27 Years, 48 respondents of age group 28 – 37, 22 respondents were 38 – 47 group, 14 respondents were of 48 – 57, and 9 were 58 and up group, represented as-
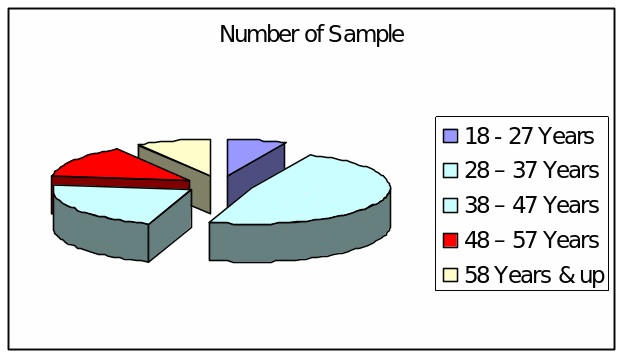
Result: Young people after finishing their Universities are most likely going to the stock market while the older are less interested in stock business.
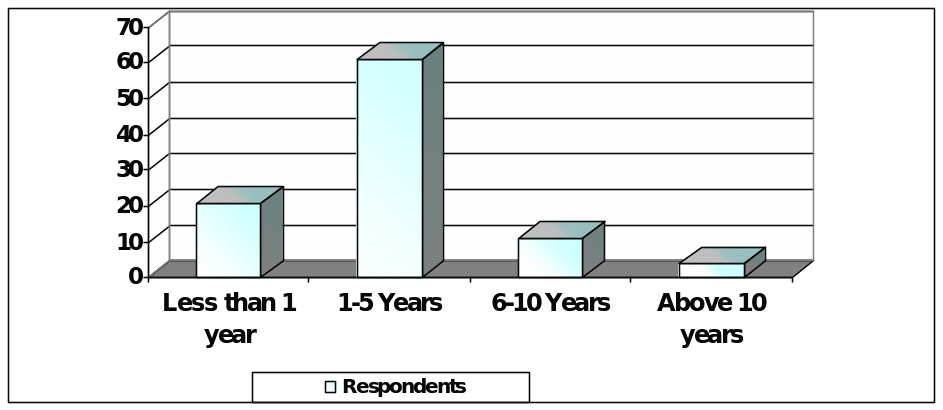
Question (D) : Experience in Stock Market
Results to this question indicates that 24 respondents were with less than 1 Years experience, 61 respondents had 1-5 years involvement, 11 respondents were with 6 – 10 years experience, and only 4 persons were above 10 years experience in the market.
Section 2: About Kelong and WorldCom
Question (E) : Knowledge about Kelong and WorldCom
Reply this question to this question that 73 of the respondents were familiar with the fraud of Kelong and WorldCom and 27 respondents were not well-known with the fact and findings of earnings management of Kelong and WorldCom
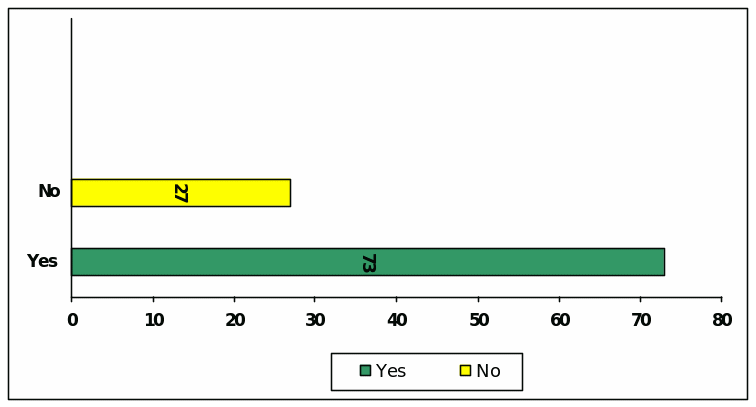
Section 3: Concern with Earnings Management
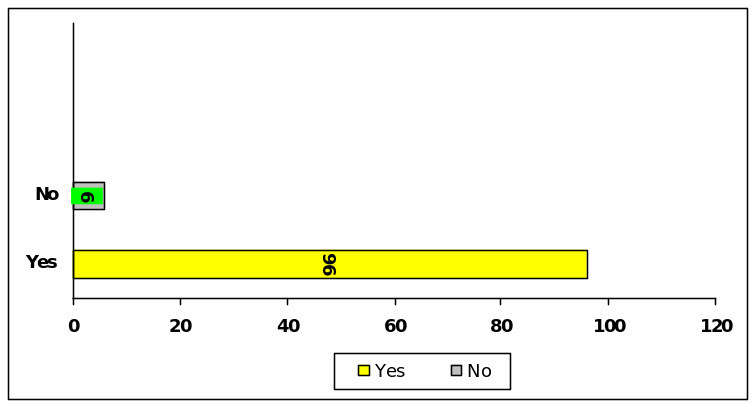
Question (F) : Knowledge about Earnings Management
This question implies that 96 respondents have overall understanding with accounting magic and six of then are not
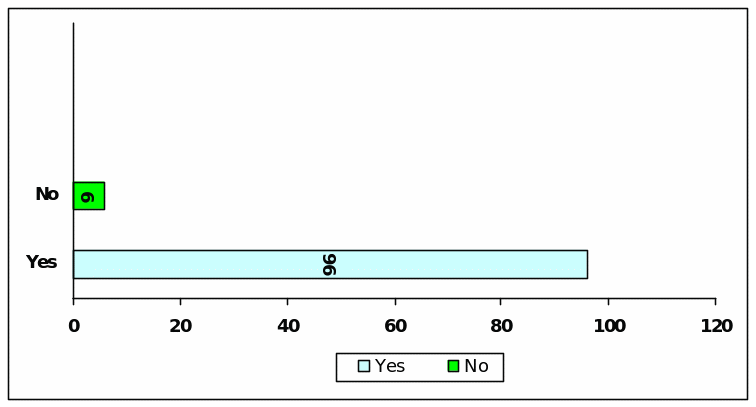
Question (G) : Tolerance level of Earnings Management
In reply to this question, 37 of the respondents are in favour of practicing earnings management but 63 respondents were against to allow any earnings management and argued for more transparency.
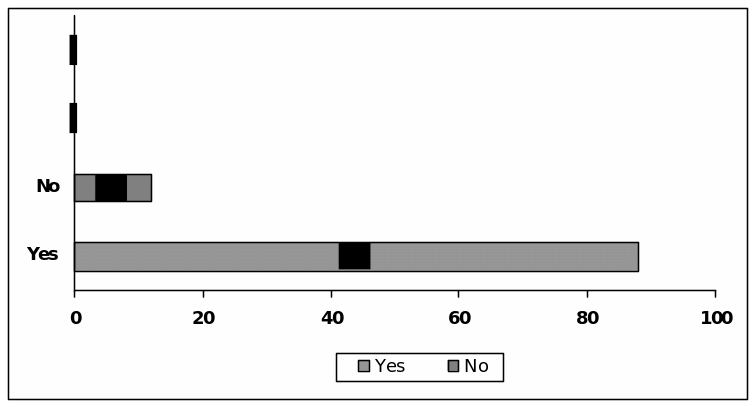
Question (H) : Perception about the Earnings Management of Kelong and WorldCom
Among the respondents 88 pointed out views that the fraud of caused for earnings management while 12 respondents disagreed.
Question (I) : Managements intention to Kelong and WorldCom Fraud
Reply to this question presented the option that 76 respondents seems the fraud was intention of management but 24 of them think it was situational evidence rather than management’s direct involvement.
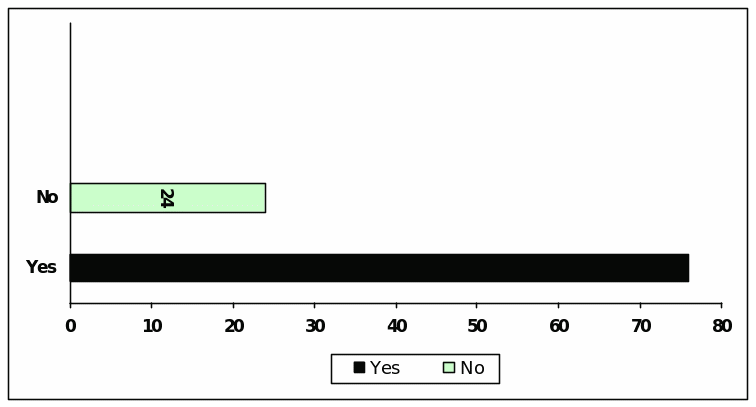
Question (J) : About the settlement of Kelong and WorldCom Fraud
Among the respondent 46 think that the settlements of Kelong and WorldCom Fraud were health for capital market but 54 respondents argue for further trail.

Question (K) : About the settlement procedure of the Fraud
In rely to this question, 76 respondents demand for criminal litigation against the Accounting Magicians but 24 differs this views.
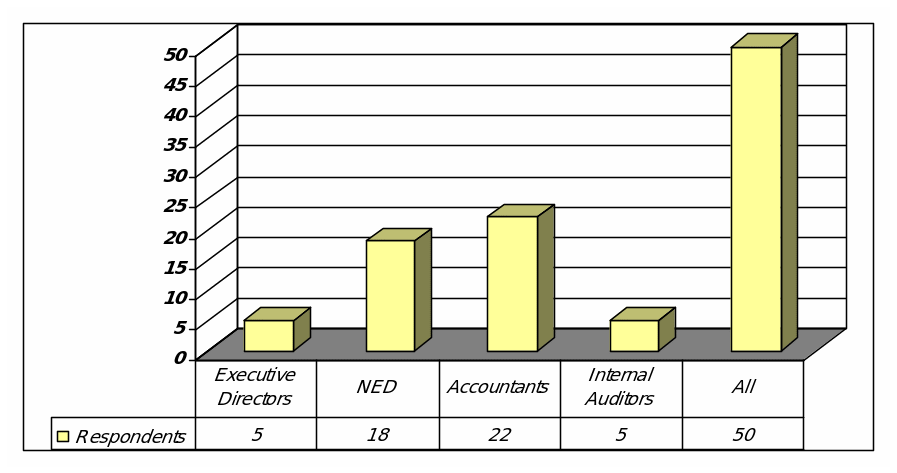
Question (L) : Influence to practice earnings management
Among the respondents 5 of their views is that the Executive Directors are influential to practice earnings management, 18 of them blame the Non-executive directors, 22 of them points to the Accountants 5 of them blame Internal Auditors and 50 of them blame all including External Auditors, SEC, FASB, and Media.
Section 4: Concern with Regulatory Framework
Question (M) : Support to SOX and Company Act 2006 to prevent (EM)
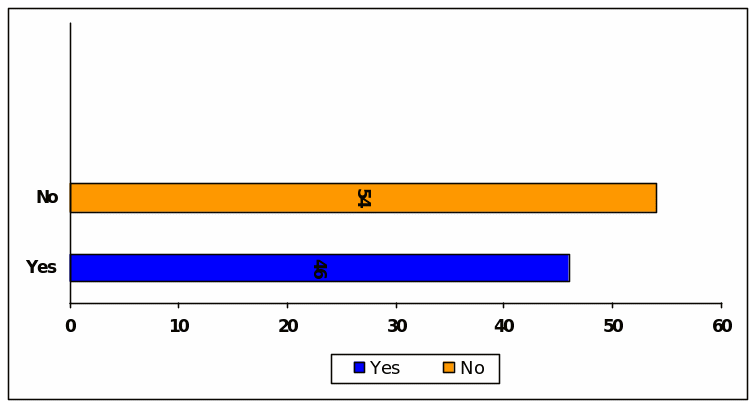
In reply to this question 58 of the respondents mentioned that the new legislation after Kelong and WorldCom Fraud such as SOX, and Company Act 2006 is good enough to sustain healthy capital market environment but 42 disagreed.
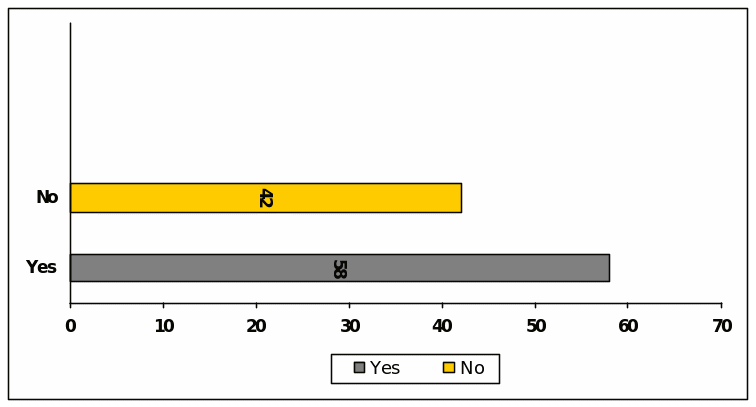
Question (N) : Political consideration under the new legislation
In reply to this question, 67 of the respondents seem that the scope for political consideration under the new legislation can brings massive fraud in the capital market but 33 of them disagreed with this view.
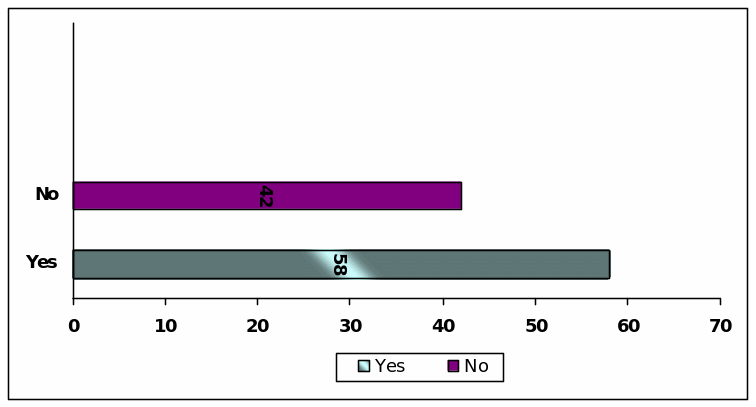
Question (O) : Growth of Share Price at Fixed Rate
To answer this question, 70 of the respondents the continuous fixed growth of share price is a significant issue for investors while 30 of them differs arguing that it is a motivation to practice earnings management.
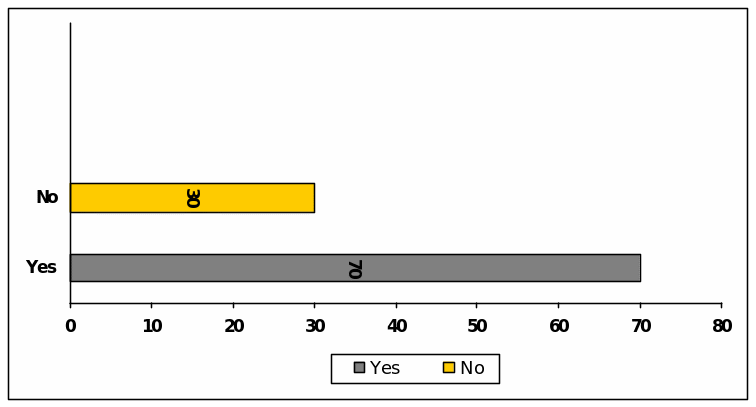
Question (P) : Auditors role at to practicing earning management
Reply to this question presented the option that 79 respondents think that the Auditors create pressure to practice earning management while 21 disagree with this view.
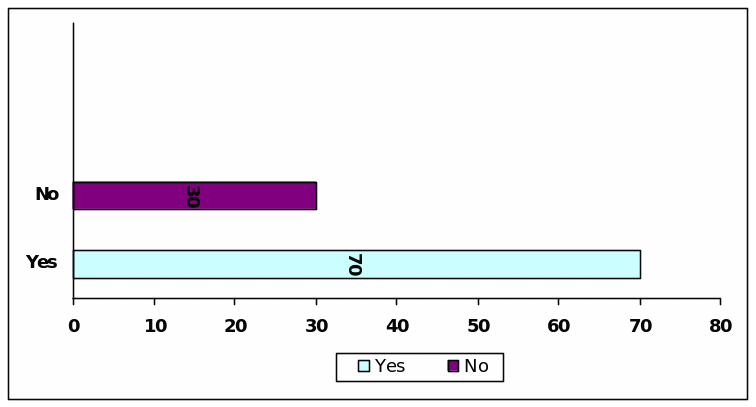
Question (Q) : Views of discretionary accruals
In reply to this question 59 of the respondents mentioned that they think that the incremental accruals provide indication of good economy while 41 respondents disagreed.
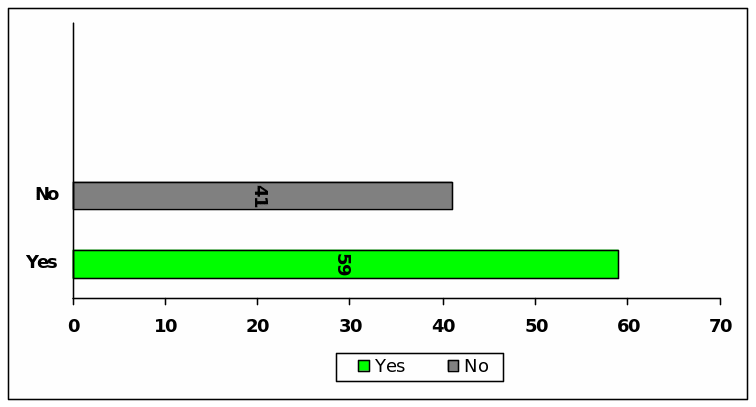
Question (S)
About Accounting standards
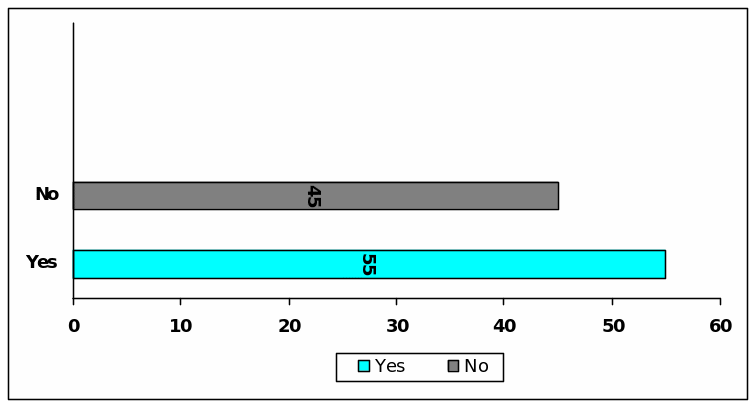
To answer this question 55 of the respondents bring up that the accounting standards such as GAAP has inspired to practice earnings management while 45 of them differs with the view of unifying accounts has aimed by the accounting standards.
Discussion & Findings
Role of Earnings Management to Collapse Kelong
Xueqing et al (2009) mentioned that a the beginning of journey in 1984, Kelong was a township public enterprise and in 1996, it has nationalized by selling 41.96% shares to government and 10.49% shares have taken by it’s employees, rest of the shares have traded on the Hong Kong share market. During 1997, Kelong has earned 3.4 billion Yuan/US$419.8 million with a profit of 660 million Yuan/US$81.5 million whilst they have traded 20% of their shares in their domestic refrigerator market. In contrast, of remarkable performance in the local market, Kelong has masking complex dilemmas of mismanagement as well as domestic competition. Consequently, in October 2001, Kelong’s 20.64% of aggregate shares have bought by Mr. Gu Chujun chairperson of the GED14 and Kelong has controlled by the Kelong (Ronshen) Group. As said by Kelong’s mid-year annual report 2001, their per share price was 4.17 Yuan/ US $ 0.52 and in August 2004, Kelong has declared they have inflated profit by 112 million Yuan/US$13.8 million but in early 2005, they have lost 487 million Yuan/ U$60.1 million and again get profit of 159 million Yuan / US$19.6 million. In between 2001–05, accounting misrepresentation, imbalance transaction, and fake inflated profit has publicized under supervision of Gu and his fraudulent acquisition series has broken by an arrest and 10 years confinement during 29th July 2004. (Xueqing, 2009)
Kelong collapsing history and accounting misinterpretation has an outcome of a series of fabricated financial data and accomplishments of following masterminded equation. Principle financial indicators like inventories, bank loan interests, mortgage, and tricky financial statements of Greencool have strappingly displayed fraud sign. For instance, in 2004, Kelong mother-company has stated 1.7 billion other receivables but in practice, it was only 120 million Yuan. Greencool Kelong financial fraud has defined as high-tech resources, which have rare to operate. In short, resource restructuring, related party business deals, domestic government aid during auditing, unacceptable accounting expertise, auditing complication have driven key role in this case (Anon, 2010).
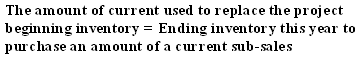
Role of Earnings Management to Collapse WorldCom
The WorldCom has started their business in 1983 and within 15 years, it has turned the company as an international telecommunication very shortly. In the American archives, massive growth like WorldCom has too rare moreover, among 1985–2001, it has acquired more than 60 companies to deliberate wide-ranging geographic exposure. At the end of first business year WorldCom has earned around $1 million and its CEO15 was Mr. Bernard Ebbers who was absolutely inexperience in telecommunication industry. After certain period, WorldCom has disastrous to keep nits elevated growth rates, profit margins and expected returns due to congestion of the transmission aids. In 1989 after a set of significant resale transaction and merger events WorldCom was signed on the NNMS16. In between 1990–95, WorldCom has insistently extended and annual revenue has become $948 million and $3.9 billion respectively in 1992 and 1995. In 1996, its annual revenue was around $4.8 billion but failed to merge with MCI by the British Telecommunications. In terms of merger by a pursuant 1.2439 shares of the WorldCom has taken by the MCI and conversely the British Telecommunications has collected $51 for per share of the MCI. At the end of 2000, the WorldCom has denoted as telecommunication giant and during this period, they have earned more than $39 billion with a $24.9 billion long-term debt. From 2001, WorldCom has suffered from severe downturn and their share prices has fluctuate between $(12–24) whenever in 1999 their share price was $90 per share. In July 30, 2002, NNMS has delisted WorldCom from their stock market and consequently, WorldCom’s top management was filed bankruptcy and hence resigned from their post at 27 October 2002 (Find Law, 2002).
Gavious (2007) pointed out three key issues have played behind for collapsing as well as accounting misinterpretation of the WorldCom. These three have included acquisition strategies for mammoth corporate growth, unethically utilization of loans by senior executives and finally, threats towards the corporate governance of WorldCom, which have run through chumminess as well as unproductive dealing internationally. Cynthia Cooper, internal auditor of the WorldCom case study who has disclosed $2 billion unauthorized capital expenditures along with $4 billion miss-collected outflows and fake accounting entrances. Lack of integrated operations among diverse division has resulted unfastened of $13,000 from IPOs17. Alternatively, WorldCom has terminated three central MCI technical services to unfasten 12 incompetent and duplicate centres. Installation of expensive Clercs18, borrowing loans by the top management at lower interest rate for instance, $341 million loan at only 2% interest has reasonably inferior than WorldCom’s marginal return (Moberg & Romar, 2009).
Changes of EM Practice due to Kelong & WorldCom Fraud
Kelong
Due to accounting misinterpretation of the Kelong, eleven investors (both medium and small) have severely suffered and for another 202 victims petitioner of the case could not drawn any mediation. 15 April 2005, High Court of China was heard about the merger of the Kelong. After collapse of Kelong in 9 April 2009, minority shareholders of the company was filed, a case in opposition to the false accounting statements of Kelong and trial off the Kelong scandal of 202 was took legal action of returning 2922 million Yuan. Throughout 142 trial sections and negotiation, mediation was closed at 1575 million Yuan. Conversely, compensation decision of the Chinese High Court fined 3.1 million Yuan at conclusion of one case and another 15 cases were withdrawal, in terms of court claims other 31 cases were discharged and additional 13 case has yet pending. During trial period, presiding judge of the Kelong case has required demeanour mediation between two surfaces where 60% support appeal side and 70% was demand compensation. Under this circumstance, Kelong’s attorney was decided to return with the arbitration program after High Court decision. Among aggregate 202 cases excepting 11 cases other proceedings was applied for appeal since amount of fine was not satisfactory figure.
During 2006, the CSRC19 was circulated a printed resolution to classify administrative punishment against the Kelong and its associate’s false accounting/financial statements before their stock was sold in between 2001–05. The Supreme People’s Court was taken a legal understanding that the investors who were lose their investment or in another term non-subjective aspects of the financial systematic risk was smashed would be compensated. After a long term trial and appeal of two parties Kelong chairman was fined around 6.8 million Yuan with 10 years confinement and his another six associates was kick out from Kelong (Xiao, 2010).
WorldCom
In US, financial scandal history the WorldCom case has stayed at peak. Post fraud phenomenon of the WorldCom has much severe that its impact on US economy has experienced durable affect specially employees of the WorldCom and minority shareholders. Following are the post fraud facts of the WorldCom (AICPA, 2005).
- In order to save around $1 million, more than 17,000 employees of the WorldCom were lost their job.
- In terms of intangible assets, the WorldCom might be written of about 50.6% billion.
- Special investigation panel was constructing where former US Attorney General as well as the FASB former chairman was selected as member of the panel headed for reviewing accounting practices of a private traded company in US as said by GAAP.
- The WorldCom was then trying hard and soul to shelter their loans.
- The CEO of the WorldCom Mr. John Sidgmore replaced Ebbers as well as stated that he and his associates wanted to carry on continuation of the WorldCom. Moreover, he declared to expose embezzlement team and punished them as per regulation of the US Business Criminal Law.
- During 2004, whenever the WorldCom has let off bankruptcy it has amended its name as MCI.
- Court has approved debt or credit cutback
- Operation division of the WorldCom has decided to spin off their several business units.
- Scott Sullivan, the CFO of the WorldCom has impeached in August 2002 by the grand panel of judges resting on 1 tally of fraud moreover, another 6 tally of securities fraud have filed case against false accounting statement approximately $8 billion. However, not yet then Mr. Sullivan pleaded guilty for his falsified movements. Finally, during 2nd March 2004, consequence of a superseded accusation Mr. Sullivan pleaded guilty for his falsified movements as well as conspiracy towards three federal scandalous charges and punished 25 years confinement. At last, the judicial panel has come to an end that they would have scrutinized against Ebbers and at the end of his trial Mr. Sullivan have to be sentenced.
- In September 2003, the Oklahoma Securities Laws has contravened by not pleading guilty towards fifteen-offence tally and successively Attorney General of the Oklahoma afterwards has refilled about those occurrences.
- 19th January 2005, Federal jury panel has started trials lying on charges of Scott Sullivan offences and potential result would be 25 years though he has expected that jury panel would be testified against him.
- During January 2005, ten former directors of the WorldCom have agreed to compensate $54 million to their minority shareholders because of negotiation. The compensation payment was paid by two instalments one has compensated by the directors of the WorldCom amounted around $18 million and the liability insurance has compensated the rest of $36 million.
- 28th February 2005, due to class action dilemma former directors and auditors of the WorldCom has not possible to come on and begun trials.
Accounting Practice during Kelong & WorldCom Fraud
Kelong
Chinese accounting standards practice has been formed through three environmental forces socio-culture, political style, and transformation of economy. In broader form, Chinese accounting has split through two eras where the first one has governed through communist command and the second has encouraged taking profile accordance with the market oriented model after liberalization. As said by Chinese government, second stage has now denoted as “the open door policy” which has technically attached with modern western guidelines. Since 1980 after started of the economic reform, Chinese Finance Ministry has started to follow IAS20 (amended in 1993) in consistence with their culture and politics. In order to encourage foreign investments like joint venture, FDI, IAS has modified as the ASBE21 and governed by the finance ministry. As circulated by the finance ministry, Chinese SOEs and the SME sector has also noticed to follow recent accounting attachment (Solas & Ayhan, 2008).
As said by the IAS 34 conditions Kelong has constructed their short-term financial reports from the last decade and therefore under supervision of the IASB22 Kelong has published their annual reports. According to IAS 34 circumstances, Kelong has included in their financial information asset and liability figure, both segmented and aggregate income and expense, advisory notes in few cases ands firm’s financial position and performance growth in market. Alternatively, Kelong has prepared their complete financial statements on the word of IFRSs23, which has also circulated by the IASB (Kelong, 2008).
WorldCom
Being incorporated in US as a private limited company, WorldCom has entailed to follow GAAP24 in conjunction of the SEC during reporting their both annual and short-term or quarterly financial statements. Purpose of the SEC conditions have justified whether accounting professionals of the WorldCom accurately practiced satisfactory accounting standards at a particular time. Alternatively, highest authority of the GAAP has strictly required complying with FAS25, which has issued by the FASB26, APB27 and SOP28 attached with the AICPA29. It would be treated as fraudulent tasks if the SEC circumstances would not be comply with the GAAP. Since 1998–2001, WorldCom has figured itself as an emerging international telecommunication company in terms of their net income, which was applied, to their common shareholders. But in 2001, the Arthur Anderson auditing company has identified that the WorldCom published annual report and financial statements has fail to kept their trustworthiness moreover has not equipped in proportion to the GAAP. In between 21–24 June 2002, Anderson audit committee has disclosed and confirmed about the fraudulent movements of WorldCom (Cotchett et al, 2003).
Legislative Measures for Kelong & WorldCom Fraud
Kelong
After collapse of the Kelong, securities regulators of China has inspect and weigh up that Gu has inflated Kelong’s profit from 2001–05 and large amount of capital has transferred from Kelong’s account into his personal account. After collapse of the Kelong, all of his embezzlements have disclosed and point has to quote that besides Kelong Gu has also operated another 5 publicly listed organisations and his mastermind acquisition series has continued over decade’s earliest half period. After Gu has arrested in September 2005 and several consequent trials has punished for 10 years detention. Additionally, High Court of China has fined him around 6.8 million Yuan or $992,700. Besides fine and jail ha has also ordered to repayment almost 165 million Yuan as his embezzlement and conspiracy at the Kelong home appliances (Reuters, 2008).
Before collapse Kelong was the one of finest home appliance provider in China in terms of their CFC free refrigerator and air conditioner. In recent times, they have started to manufacture TV sets. CSRC30 has started to scrutinize against Kelong form September 2005 after Gu was arrested. Before 2005 scandal, from 2002 to 2004, Greencool Kelong has fined by the securities regulator of China for several accounting fraudulent statements. In those times, it has fined about 600,000 Yuan or $75,000. Post collapse of the Kelong excluding Gu another six non-executive director or former top management of the Kelong has fined between (50,000–300,000) Yuan or ($ 6,250–37,500).
CSRC investigation has also discovered that in the Kelong annual report 2004, there have 60 million Yuan or $ 7.5 million deficit and 50% growth in 2005. Conversely, Kelong has failed to publish their first-quarterly annual report in 2006. Following a few stock exchange notices to present financial reporting Kelong was still fail to report and finally 31 August the stock exchange of China filed against Kelong and delisted from their security house since September 1 2006. Kelong’s delisting from stock exchange was passive decision of the CSRC as a result since first August 2005; investors of the Kelong have continued their share maintaining but would not be traded in future (The China Daily, 2006).
WorldCom
Several legislative actions have taken against WorldCom’s top management. Following g are the legislative measures against WorldCom by US SEC (Cotchett et al 2003).
- In 24th June 2002, US SEC and Business Criminal Charges have impeached Scott Sullivan CFO of the WorldCom to resign from his post before next board meeting. However, Mr. Scott Sullivan refused this charges and then in August 2002, SEC has opened a file against securities fraud conspiracy as well as another criminal violence and Sullivan has not pleaded guilty willingly to the charges.
- Controller and the SVP31 of the WorldCom Mr. David F. Myers has charged in September 2002 and he has pleaded guilty to the charges like filing forged financial statements with the SEC, securities fraud conspiracy and one count for every securities fraud. Additionally, Myers direct report to Sullivan indicted embezzlement of tax payments, general accounting, receivables of the accounts, payables of the accounts, payroll, accounting of property, budgeting, reporting to the management and controllers’ group of foreign deals. On behalf of Myers acknowledgement in 27 September 2002, Washington post report declared that financial statements of the WorldCom have not follow GAAP during documentation.
- Buford Yates, Jr. who had supervised general accounting division of the WorldCom October 2002, Yates has pleaded guilty for the security fraudulent movements after he has charged. Under his supervision, WorldCom has prepared its closing financial statements and had a strong inspiration for the accounting scandal of multi-billion dollar. Aim of these fraudulent movements has occurred to mislead people who have interested to invest in WorldCom as well as fulfil anticipation of the securities forecaster through unacceptable utilization of GAAP.
- As said by Yates in Montreal Gazette 8th November 2002, in October 2000 for the first time he has conducted misreport tasks of the WorldCom. Additionally, in April 2001, according to Yates guideline WorldCom annual report has declared about their fake large amounted operating expenses similar to their capital expenses. All of these counterfeit movements has guided under supervision of Myers.
- Another two-scandal hero of the WorldCom Vinson and Normand has charged to participate during the prohibited plan of the Myer and Yates. They have performed consequently in the management and reporting division and legal entity accounting department. After they have charged both of them had pleaded guilty.
- To occupy a conciliation defrayal with the SEC, Myers and Yates had stepped at November 2002.
- At middle of November 2002, WorldCom had filed a bankruptcy case in cooperation with the US Bankruptcy Court after settlement with the SEC of $1.8 billion accounting fraudulent and inflate company profit around $9 billion. Additionally, WorldCom has reported net operating loss of $108 million but fail to publish their monthly operating reports.
Non-executive Directors Rome to Practice EM Fraud
In implementing corporate governance role, the non-executive director (NED) has central role. In Cadbury Report 1992 as well as SOX Act 2002 have also brief discussion about the duties, responsibilities and prohibition of the NED. It has to be pointed that the NED has not any responsibility to perform executive directions as well as taken remuneration, they have appointed to focus on board matters like auditing, structuring composition and remuneration package and nomination. Additionally, NEDs have required bringing independency, neutrality, enriched experienced, skilled knowledge and outgoing personal attributes among the board members. As said by SOX Act 2002, following are the prohibited task of a non-executive director. (Board Source, 2003)
- Selection procedure on the basis of network contacts rather than merit
- Act an executive director through weakly contribution attributes
- Unsatisfactory number of the NEDs as well as in variety on the board has negatively impact on company
- Conflict of the full time directors has born through utilizing prying eyes scrutinizing and performance evaluation
- Limited time distribution for the NEDs meeting
WorldCom
NEDs of the WorldCom has unethically withdrawals of large amount of loans as well as performed fake accounting entrances. Before collapse of the WorldCom, NEDs of the company has take out around $341 million credit at just 2% interest rate. Additionally, there have also $2 million unauthorized capital expenses along with $4 billion miss-collected outflows. (Moberg and Romar 2009)
Kelong
Behind collapse of the Kelong illegal fund transfer of its former NEDs GU and his six associates have played vital role. Among them Gu has shifted large amount of capital from Yaxing to the Yangzhou Greencool. As stated in the Greencool’s official record Gu has transferred around 63 million Yuan or $7.8 million. (Xueqing et al 2009)
Accounting Practice during Kelong & WorldCom Fraud
Hunt et al (1997) explained that embezzlement, fake accounting and financial statements, transfer of money from company account to personal account, illegal earnings, inflate profits, fraudulent with securities exchange and so on have been treated as corporate earnings management threats. Most of them have origin through internal conspiracy of an organisation. Accountability, transparency, updated accounting monitoring, control of internal expenses, reduce loan withdrawal by the non-executive directors and reduction of the role of NED have the primary solution of reducing corporate earning management threats. Risky business companies like WorldCom and Kelong have faced internal threats due to absence of clarity or gloomy accounting statements. Since in several cases, addressing fraud would have entirely difficult.
Abarbanell and Lehavy (2002) added that better business performances has outlined through management accessibility, database-monitoring appliances, capability to analyse audit-log. Conversely, due to conspiracy of the small managers group, procurement fraud of high risky shares, sales fraud in securities houses or in terms of cooking the books. Taylor (2008) pointed that under these series of embezzlement WorldCom, Kelong, Enron, Tyco’s undersized group of mangers had exploited their authoritative privileges (Kim et al, 2003). As evaluated by the ACFE32, 60% of corporate fraud has performed by the high profile management members and 73% fraudulent has committed by the reliable workforce who have diversely worked in the significant departments of an organisation such as finance, accounting, manufacturing and sales. To overcome these threats corporate bodies would be get privileges by (Taylor, 2008) –
- Utilizing DBAs33 in terms of intercept payment ort unusual funds withdrawals
- Make restriction for the mistreatment of corporate credit cards by the managers
- Regular updating of the general ledger accounts to be alert of the financial managers movements
- Analysis of the continuous business deal supervising
- Superior development of the artificial-intelligence-based investigations have better potentiality to protect current and probable falsified activities
Conclusion & Recommendations
Recommendations
Conducting the investigation with the case study of Kelong and WorldCom, this dissertation would deliver following recommendations
- It has observed from the case study of WorldCom and Kelong that the settlements of the lawsuits for aggressive earning management and coherent corporate fraud, there were absence of strong securities litigation by which the recovery of wealth and punishment of accounting magicians could ensure. At WorldCom case, the government officials stood as major claimants who were promised to the media for recovery while in the Kelong case, major investors were pretenders, but small investors kept outside of settling and later on, the mentioned fraud the security regulation has revised. However, this dissertational effort identifies that the there are more scopes for the corporate world to commence earnings management within the new regulatory framework and suggests for more stick security legislation.
- Afterwards of WorldCom and Kelong fraud introduction of Sarbanes Oxley Act will produce special consideration to appointing directors and non-executives of the board but still there is provision of political consideration that would ultimately dive to further unholy alliance and may bring gigantic corporate fraud in near future. Taking into account of such possibilities the researcher would suggest the lawmakers to identify more such risky probabilities and integrate criminal offences with the SOX that can ensure transparency and direct to what extend the punishment would be sentenced for earnings management.
- From this investigation with the earnings management Kelong and WorldCom, it is clear that the investors are less efficient to detecting the evidences of earning management while they are most busy to analysing the return from their investment in the stock market, this paper would urge for higher extend to investors awareness and understanding with the fraudulent accounting approach. To making investment decision, Investors must learn to identifying and analysing the financial data to scrutinising the evidence of earnings management rather than depending on unauthentic news or rumours intentionally publicised in the market by the beneficiary directors, corrupt auditors, and negotiators of fraud game.
- The Kelong and WorldCom had commenced massive fraud within the existing securities regulation and sold their securities maintaining the SEC34procedures and both the companies submitted their manipulated financial statements to the SEC with some directors signatures, directors who signed fraud statement has kept far from trail due to their limited liabilities. But to ensure investors interest, this paper would suggest to take them under criminal proceeding, the SOX must be revised with such provision to extend the fraudulent director’s liabilities up to their personal assets as the corporate social responsibilities or ethical motivation has failed to bring any change of serial fraud.
- The accounting scandals of Kelong and WorldCom have raised severe uncertainty with the credibility of accounting statements of listed companies and argued for the compulsory to admittance about the degree of earnings management has practiced to preparing the report. In both of the collapse rather than the directors, there were involvements of auditors and CPA firms, why they not identified the earning management, how they signed the reports in favour their client and why they may not be charged for such massive fraud – all this issues need to be investigated. This paper would like to suggest reducing independence of auditors and taking them into the legal framework for trail if they involve with any further earnings management.
Conclusion
Under the background of Kelong and WorldCom fraud it is clear that the corporate world is far from their ethic and values of transparency and corporate social responsibilities, this are the just their eye wash or nothing more than the advertising language, under the existing company act their limited liabilities have facilitated them the opportunity to commence unlimited fraud. It is notable that the most of the directors and shareholder even who are not concerned with fraud would agree to allow lower level earnings volatility that take place from both actual accounting provision along with accruals management coupled with elevated market value of equity but earnings volatility artificially created by rumour or aggressive earning management may not be desired.
Accounting fraud, accounting magic or earning management what ever we name it, if there is no provision of framing criminal charges against the directors who are involved with fraud and extended liabilities to their personal and family assets, no initiatives would be fruitful to preventing earning management. It is not the discretion of SEC but the US Congress or Chinese Politburo to amend the Company Act considering such provision and the binding precedent or mandatory obligation may contribute to prevent earnings management practice.
References
Abarbanell, J. & Lehavy, R. (2002) Can Stock Recommendations Predict Earnings Management and Analysts’ Earnings Forecast Errors? Journal of Accounting Research, Vol. 41 No. 1. Web.
Ahmed, A. S. et al (2008) Equity Incentives, Corporate Governance, and Earnings Management. Web.
AICPA (2005) The WorldCom Fraud. Web.
Anon (2010) Greencool Financial Fraud Case Analysis and Its Implications. Web.
APB (2010) Briefing Paper – Providing Assurance on the Effectiveness of Internal Control. Web.
Balasubramanian, N. (2010) Corporate Governance, Bank Boards & Directors. Web.
Bayley, L. & Taylor, S. (2007) Identifying Earnings Overstatements: A Practical Test. Web.
Board Source (2003) The Sarbanes-Oxley Act and Implications for Nonprofit Organisations. Web.
CFA Institute (2007) China Corporate Governance Survey. Centre for Financial Market Integrity. Web.
Cohen, D. A. & Zarowin, P. (2007) Earnings Management over the Business Cycle. Web.
Cornett, M. M. Marcus, A. J. Tehranian, H. (2006) Corporate Governance and Pay-for-Performance: The Impact of Earnings Management. Web.
Cotchett, J. W. et al. (2003) Overview of Complaint. Web.
Dechow, P. M. Richardson, S. A. & Tuna, R. (2003) Why Are Earnings Kinky? An Examination of the Earnings Management Explanation. Review of Accounting Studies, Vol. 8. Web.
Dechow, P. M., Sloan, R. G., & Sweeney, A. P. (1995) Detecting earnings management. The Accounting Review, Vol. (70), No. 2. Web.
Find Law (2002) First interim report of dick thornburgh, bankruptcy court examiner. Web.
Francis, J. et al (2003) Accounting Anomalies and Information Uncertainty. Web.
FRC (2006) The UK approach to corporate governance. Web.
Gavious, I. (2007) Market Reaction to Earnings Management: The Incremental Contribution of Analysts. International Research Journal of Finance and Economics, Issue 8. Web.
Gombola, M. (2008) Earnings Management, Fraud, and Compensation. Web.
Goncharov, I. & Zimmermann, J. (2008) Do Accounting Standards influence the Level of Earnings Management? Web.
Gonedes, N. J. & Schnellar, M. I. (1984) Value Maximization and Earning Management via Accounting Techniques. Web.
Hirshleifer, D. (2008) Psychological Bias as a Driver of Financial Regulation. European Financial Management. Web.
Holmstrom, B. & Kaplan, S. N. (2003) The State of U.S. Corporate Governance: What’s Right and What’s Wrong? Journal of Economic Perspectives. Web.
Hunt, A. Moyer, S. E. & Shevlin, T. (1997) Earnings Volatility, Earnings Management, and Equity Value. Web.
Jones, J. J. (1991) Earnings management during import relief investigations. Journal of Accounting Research, Vol. (29). Web.
Kelong (2008) Interim Results Announcement. Web.
Kim, Y. Liu, C. & Rhee, S. G. (2003) The Relation of Earnings Management to Firm Size. Web.
Laux, J. A. (2003), Earnings Management: Friend or Foe? Journal of Business & Economics Research, Vol. 1, No. 12. Web.
Lee, K. W., Lev, B. & Yeo, G. (2007) Rganisational Structure and Earnings Management. Journal of Business & Economics Research, Vol. 1, No. 12. Web.
Leung, E., et al. (2002) Financial Reform and Corporate Governance in China. Web.
Liu, Q. (2005) Corporate Governance in China: Current Practices, Economic Effects, and Institutional Determinants. Web.
Malhotra, N. K. (2009) Marketing Research- An Applied Orientation. 5th ed. Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited.
McKee, T. E. (2005) Earnings Management: An Executive Perspective. 1st ed. NY: South-Western Educational Publication.
Moberg, D. & Romar, E (2009) WorldCom Case Study. Web.
Munter, P. (1999) SEC Sharply Criticizes “Earnings Management” Accounting. Web.
Nelson, M. W. et al (2003) How are Earning Managed? Example from Auditors. Web.
Parfet, W. U. (2000) Accounting Subjectivity and Earnings Management a Preparer Perspective. Web.
Rath, S. & Sun, L. (2008) The Development of Earnings Management Research. International Review of Business Research Papers, Vol. 4 No.2. Web.
Rayton, B. A. & Cheng, S. (2004) Corporate governance in the United Kingdom: changes to the regulatory template and company practice from 1998 – 2002. Web.
Reuters (2008) China appliance tycoon to serve 10 years for fraud. Web.
Richardson, S. A. et al (2002) Information in Accruals about Earnings Persistence and Future Stock Returns. Web.
Richet, X. et al. (2000) Between Bureaucracy and Market: China’s Industrial Groups in Search of a New Corporate Governance System. Web.
Saunders, M., Thornhill, A. & Lewis., P. (2006) Research Methods for Business Students. 4th ed. London: FT Prentice Hall.
Sekaran, U. (2006) Research Method for Business. 4th ed. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Spohr, J. (2005) Essays on Earning management. Web.
Solas, C. & Ayhan, S. (2008) Historical Accounting Standards in China. Web.
Stake, R. E. (1995) The Art of Case Study Research. 1st ed. London: Sage Publications, Inc.
Taylor, P. (2008) Insider Threat -The Fraud That Puts Companies at Risk. Information System Scontrol Journal. Web.
The China Daily (2006) Kelong Gets Fined for Accounting Fraud. Web.
UKSA (1992) The financial aspects of corporate governance (The ‘Cadbury’ Report). Web.
Walker, D. (2009) A review of corporate governance in UK banks and other financial industry entities. Web.
Wallison, P. J. (2005), The WorldCom and Enron Settlements: Politics Rears its Ugly Head. Web.
Wang, Y. H. Chuang, C. C. & Lee, S. Y. (2010) Impact of compositions and characteristics of board of directors and earnings management on fraud. African Journal of Business Management, Vol. 4 (4). Web.
Xiao (2010) Kelong case, court action for compensation and robust debate on definition of a false statement. Web.
Xueqing, L. et al (2009) The dramatic collapse of Kelong chairman Gu Chujun. Web.
Yin, R. K. (2003) Case Study Research: Design and Methods. 3rd ed. Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
Young, M. (2000) Chapter 3–Earnings management and fraud. Web.
Zikmund, W. M. (2006) Business Research Methods. 7th ed. Orlando: Harcourt Publishers.
Zhang, H. (2002) Detecting Earnings Management—Evidence from Rounding-up in Reported EPS. Web.
Zhou, H. Xiong, Y. & Ganguli, G (2008) Accounting Standards and Earnings Management: Evidence From An Emerging Market. Web.
Appendix 1
Questionnaire
What is your present integration with the Stock Exchange?
Please mention your gender
What is your Age group?
How long you are in the financial market
Are you familiar with the Kelong and WorldCom Fraud?
Do you have clear perception with earnings management?
Do you suggest to allowing earnings management at a tolerance level?
Would you consider earnings management is the major reason of Kelong and WorldCom Fraud?
Do you blame that the management has intentionally framed the Kelong and WorldCom Fraud?
Do you thing that the settlements of Kelong and WorldCom Fraud were health for capital market
Do you demand for criminal litigation against the Accounting Magicians?
At your consideration, who are the influential to practice earnings management?
Is the new legislation after Kelong and WorldCom Fraud such as SOX, and Company Act 2006 is good enough to sustain healthy capital market environment?
Will the scope for political consideration under the new legislation bring massive fraud in the capital market?
Does the continuous fixed growth of share price is a significant issue for investors?
Do you think that the incremental accruals provide indication of good economy?
Do you think that the Auditors create pressure to practice earning management?
Do you think that the incremental accruals provide indication of good economy?
Do the accounting standards such as GAAP have inspired to practice earnings management?
Footnotes
- Generally Accepted Accounting Principles
- Sarbanes Oxley Act of 2002
- Earning Per Share
- Total Accruals
- SEC
- New York Stock Exchange
- SOX/SOA
- Non-Executive Director
- The Securities and Exchange Commission
- The State Owned Enterprises
- Industrial and Commercial Bank of China
- Foreign Direct Investment
- London Stock exchange
- Greencool Enterprise Development Co.
- Chief Executive Officer
- NASDAQ National Market System
- Initial Public Offerings
- Local Exchange Carriers
- China Securities Regulatory Commission
- International Accounting Standards
- Accounting System for Business Enterprises
- International Accounting Standards Board
- International Financial Reporting Standards
- Generally Accepted Accounting Principles
- Financial Accounting Standards
- Financial Accounting Standards Board
- Accounting Principles Board Opinions
- Statements of Position
- American Institute of Certified Public Accountants
- China Securities Regulatory Commission
- Senior Vice President
- Association for Certified Fraud Examiners
- Database Administrators
- Securities and Exchange Commission