Introduction
The Starbucks is an international corporation established in the year 1971. During the first years of its establishment, the company produced and distributed whole bean coffee in their Seattle store. By 1982, the organization had expanded and opened five more stores selling coffee beans and had a roasting facility. They sold their products at wholesale prices to the local businesses. Howard Schultz became the new manager of the retail stores. His aim was to develop the business at a slow pace but with a solid foundation. By the year 1988, Starbucks had grown to 20 new stores.
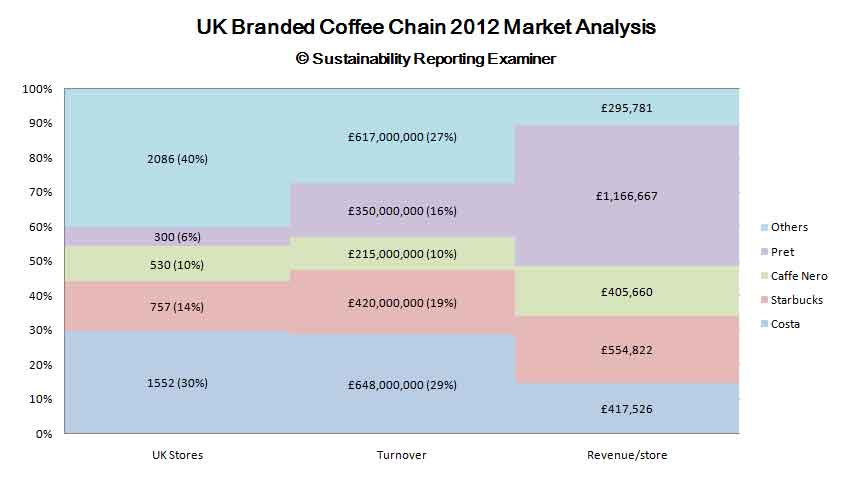
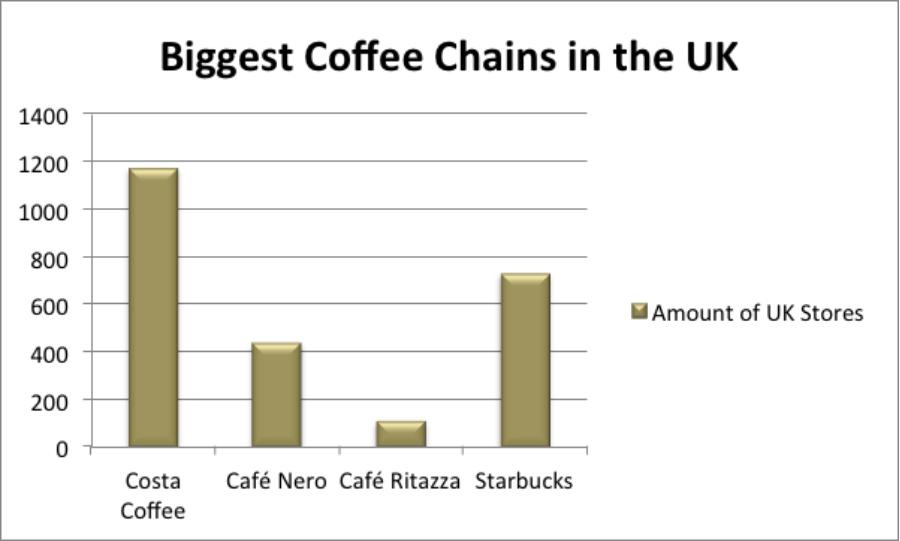
Eight years later, the company had 870 stores across the world. Currently, the company has thousands of stores across the world. The United Kingdom is one of its major market shares in the world. It is the second largest coffee business in the UK after the Costa Coffee with more than 700 stores in the country. Café Nero and Café Ritazza follow it with 400 and 100 stores respectively. Other competitors in the market are McDonald’s and Dunkin Donuts. With its long-term brand reputation, Starbucks could capture more market share in the UK if it improves its operational strategies in the region.
Competitiveness in the Industry
The success of Starbucks Coffee is based on the effectiveness with which it addresses the negative aspects of the five forces in its UK industry environment. Through the model of Five Forces developed by Porter, the company is able to identify the external factors that influence its business operations. The analysis of its competitiveness depicts the intensities of the external forces on its operations. Through the forces, the company is able to highlight its current conditions in the industry based on emerging issues relevant to the coffee business in the UK. Apart from the suppliers bargaining power, Starbucks Coffee faces various challenges in relation to the five external forces (Dobbs 2014). Therefore, the company must ensure it addresses the issues related to the competitive rivalry, customers’ bargaining power, substitutes, and new entrants.
In terms of competitors’ rivalry, Starbucks Coffee encounters many competitors with equal financial resources and capabilities such as specialties and strategies. For instance, Costa Coffee and Café Nero are its major competitors in the UK market as shown in Appendix III. In addition, it competes with other specialty coffee firms. The switching cost plays a major role in enhancing the stiff competition in the market. To maintain the huge market share it currently enjoys, Starbucks must put competition on its priority list by adopting better practices than those of the competitors (Koehn 2002). For instance, apart from the pricing strategy, it should improve the quality of products and services.
In the UK coffee industry, customers have high bargaining power. The bargaining power of customers has a direct influence on business operations. In the Starbucks Coffee, three external factors attribute to the customers’ stronger bargaining power (Fridell 2012). First, low switching costs in the UK coffee industry give customers different prices for the same product. The second factor is the availability of substitutes. Customers tend to buy what is available in their locally provided it serves the intended purpose. Therefore, the company is unable to capture customers in places where substitutes are readily available. Customers who buy coffee in small quantity prefer small businesses to large companies such as Starbucks (Starbucks Coffee Company 2015).
Suppliers bargaining power in the coffee industry within the UK is lower than other forces within the Porter’s model. There are many suppliers in the industry with high-quality products. As a result, many of them supply their products at lower prices to firms in the industry (Palmer 2015). The overall supplies of raw materials are larger than the demand. Therefore, suppliers must adhere to the specific needs of the firms in order to survive. Subsequently, the influence of supplies on the business operations reduces. In terms of acquiring production goods, Starbucks Coffee and its competitors do not need to prioritize the concerns related to supplies (Dobbs 2014).
Substitute products pose a serious threat to the Starbucks Coffee. Other than products from the major competitors such Costa Coffee and Café Nero, many small firms have emerged. The main threats in the market are the small firms that produce small quantity and offer their products at lower prices. At the same time, they tend to meet specific needs of customers in terms of quality products and services. It is because of the closeness they have with customers (Burke, Van-Stel, & Thurik 2010). Coupled with low switching costs, it becomes difficult for Starbucks to maintain its customers for a long period.
A threat of new entrants in the market is moderate. It is important to note that majority of customers of the company are high-income people, who are also the highest population group in the UK market (Hitt, Ireland, & Hoskisson 2012). For a new entrant to serve the Starbucks’ market, it must have enough financial resource to establish a visible business. On the other, high cost of brand development might discourage new firms. There are various brands in the market and this makes it difficult to build brand recognition (Burke, Van-Stel, & Thurik 2010). However, the moderate cost of entry and establishment of the supply chain can attract more firms into the market.
Strategic Position of the Company
The Starbucks Company has positioned itself among the market leaders in the UK coffee industry. The company’s ability to provide high-end-café beverages contributes to its success in the UK market (Gilbert 2015). The strategic position of the organization does not have its basis on the prices of the products it offers. Instead, it practices premium pricing by offering products of very high quality. It also depends on the brand reputation and long-term experience in the industry. Since most of the rival organizations in the UK market base their strategic positioning on the pricing, the Starbucks has varied positions. It is due to the dynamic nature of the industry. In order to remain relevant in the market for a longer period, it uses quality services, technology, pricing, and quick delivery to respond to varied needs of customers. For instance, it introduces low-priced products among low-income customers to compete fairly with other firms in the industry (Thomas 2013).
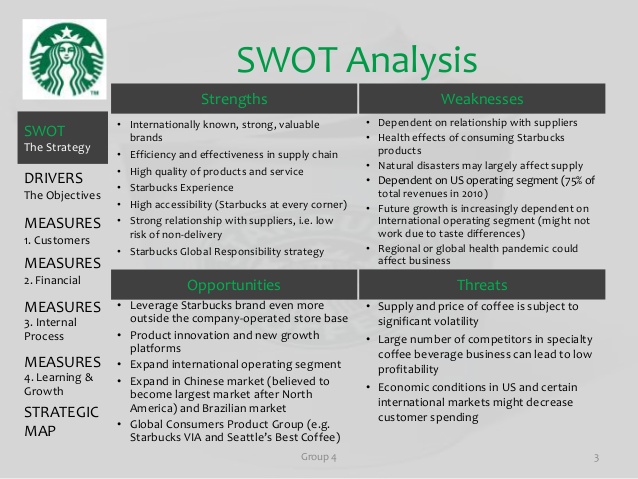
Because of the different strategies employed by the company, it has several strengths and activities shown in Appendix II, which help in maintaining its competitive edge in the market. Some of the strengths include brand recognition, high quality and premium products, desirable locations like in the United Kingdom and a large and loyal customer base (Rosenbloom 2012). Many of the customers in the UK market are willing to pay higher prices for the premium quality products, which is an added advantage. Even though the Starbucks Coffee dominates the UK coffee industry, the kind of competition offered by the upcoming smaller companies is worrying. As such, it has to come up with better strategies to enhance its stake in the industry (Uphill 2016).
Analysis of Potential strategies
The Starbucks Company can use the international strategy to enhance its competitive advantage in the UK coffee industry. The marketing strategy involves making new market ventures in various nations of the world using it brand reputation. By investing more in the international markets such as the UK, the Company is likely to have new opportunities. For instance, UK cities are the major destinations for international travelers. A foreigner who had already used the brand in their home countries is likely to use it again while in the UK (Michelli 2012). Because the Starbucks is a popular brand, it can easily expand its market base to travelers who come in the country. With the lower taxes and tariffs on coffee in some of the emerging nations, the company is likely to improve on its market share nationally and globally (John 2012). The increased demand for globally branded products puts the company in a better position to compete for a larger market share in the international arena. As it moves to the other countries of the world to invest, its brand name becomes the stepping-stone needed to achieve the success (Wickizer 2011).
The new market venture is also likely to increase the market base of Starbucks Coffee. The majority of the consumers of the coffee products within Europe prefer premium quality products irrespective of the prices. Such consumer behavior is a great opportunity for Starbucks in the UK. As such, the organization can easily succeed in the European market (Clark 2013). Once the number of customers of the organization increases, it will be in a position to register more sales and profits. Therefore, it can use the profits to employ the best marketing and advertisement strategy to beat its major competitors in the market such as Costa Coffee and Café Nero (Starbucks Coffee Company 2015). The revenue obtained from the new market ventures could also be used to promote the different corporate social responsibilities of the company (Simon 2011). With enough capital base and revenue, it is easy for the organization to comply with the different regulations and pay the relevant tariffs on the product. Even if the tariffs may be higher in the UK market, the firm will be still in a better position to make proceeds (Schultz 2012).
The other potential strategy for its competitiveness in the industry is to establish a direct link with customers who need individualized coffee products. The organization should acknowledge the continuous growth of customized consumption of coffee products. Because of that, the use of smaller shops and cafés, as opposed to the larger stores, could be a good strategy for the organization in the UK (Palmer 2015). Because the smaller cafés are gaining a significant market share in the industry over time, it is important that the company follow suit. The approach would improve the utilization of the smaller shops and stores to advance their customer base and market share in the country (Schultz 2012).
Starbucks organization should increase awareness on health and environmental concerns through its corporate social responsibility (Pham-Gia 2012). Through marketing and advertisement, its marketing team should promote the brand as the best and demonstrate how it helps in reducing the carbon footprint in the coffee industry (Mangold 2010). Once the organization uses its marketing platform to promote health benefits of its coffee products, the consumers are likely to go for the brand. In the modern world where lifestyles have caused serious diseases, people are concerned about their health. Therefore, talking about health benefits that come with the Starbuck’s products may significantly boost its customer base (Clarke 2012).
Recommended strategy
Starbucks Coffee has been using various strategies to maintain its position in the coffee industry within the UK market. However, the most important one has to do with the pricing strategy. As shown in Appendix I, the organization is strategically positioned in the industry based on the premium quality of its products and the high prices it offers. Through the partnership, the firm could reduce the coffee prices. Once it collaborates with the other organizations, it will be able to sell some of its products at the prices that are convenient to the consumers (Gilbert, 2015). However, the most important thing is that it should not openly reduce its prices because that may lead to losing of brand pride it currently enjoys. Therefore, it is better that the organization should maintain the premium pricing strategy but continue producing the best quality products in the coffee industry (Starbucks Coffee Company 2015).
Conclusion
The Starbucks Company has been one of the dominant organizations in the coffee industry. From the above discussions, it is evident that the company is still among the market leaders in the UK coffee sector. The firm is strategically placed at the top in terms of the competitive sphere. It is because of the premium quality products, a long-term brand recognition, and loyalty. There are different strategies it can use to maintain its large market share in the UK. The best of these is the maintenance of its premium pricing strategy, high quality, value, and prestige of its brand name. By implementing the various strategies mentioned above, the organization will reach greater heights in the UK coffee market and the industry as a whole.
List of References
Burke, A, Van-Stel, A & Thurik, R 2010, Blue ocean vs. five forces. Harvard Business Review, vol. 88, no. 5, pp. 28-29.
Clark, T 2013, Starbucked: a double tall tale of caffeine, commerce, and culture, Little Brown, New Delhi.
Clarke, R 2012, Buyer power and competition in European food retailing, Edward Elgar Pub, Manchester.
Dobbs, M 2014, Guidelines for applying Porter’s five forces framework: a set of industry analysis templates, Competitiveness Review, vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 32-45.
Fridell, G 2012. Fair trade coffee: the prospects and pitfalls of Market-driven social justice, University of Toronto Press, Toronto.
Gilbert, S 2015, The story of Starbucks, The Creative Company, London.
Hitt, M, Ireland, D & Hoskisson, R 2012, Strategic management: concepts, competitiveness and globalization, Cengage Learning, Cambridge.
John, S 2012, Coffee and tea industries and the flavor field, Sage, Manchester.
Koehn, F 2002, Howard Schultz and Starbucks Coffee Company, Harvard Business School, Cambridge.
Mangold, C 2010, The Starbucks company. success strategy and expansion problems, Grin Verlag, Manchester.
Michelli, J 2012, The Starbucks experience: 5 principles for turning ordinary into extraordinary, McGraw Hill Professional, New York.
Palmer, E 2015, Handbook of research on business ethics and corporate responsibilities, IGI Global, London.
Pham-Gia, K 2012, Marketing strategy of ‘Starbucks Coffee’, Grin Verlag, Manchester.
Rosenbloom, B 2012, Marketing channels, Cengage Learning, London.
Schultz, H 2012, Pour your heart into it: how Starbucks built a company one cup at a time, Hachette Books, Columbus.
Simon, B 2011, Everything but the coffee: learning about America from Starbucks, University of California Press, Nashville.
Starbucks Coffee Company, 2015, Company Information, Starbucks Coffee Company, Seattle.
Thomas, J 2013, New product success stories: lessons from leading innovators. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Uphill, K 2016, Creating competitive advantage: how to be strategically ahead in changing markets, Kogan Page Publishers, New York.
Wickizer, D 2011, Coffee, tea, and cocoa: an economic and political analysis, Stanford University Press, Cambridge.
Appendices
Appendix I: An elaborate SWOT Analyses of Starbucks
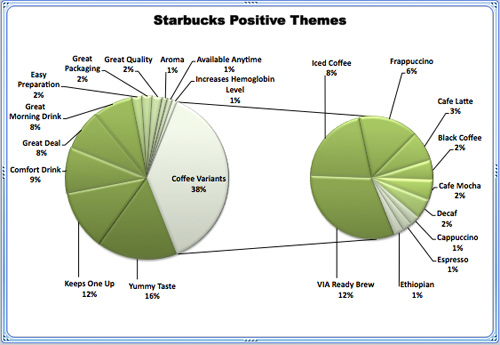
Appendix II: Starbucks positive themes
Appendix III: A diagram show the biggest coffee chains in the UK
Appendix IV: Customer Measures for the old and new markets of Starbucks

Appendix V: An analysis of the branded coffee chains in the UK, 2012