Introduction
Today, we are moving at a faster speed through technology at every aspect of the business, while e-commerce has been recognised as the most modern aspect of that technology. It influences organisations for discovering newer customs for expanding the competitive marketplace; draw the attention of customers through customisation of their offerings, and format the overall process and functions to ensure efficiency and effectiveness via differentiation.
Background of the problem
The process of conducting a commercial transaction through digital networks, the internet, and other similar technologies can be termed e-commerce. While retailing involves direct selling to the end-users, multi-purpose business involves serving such multiple products and services to customers, while differentiation is the process of presenting an entity or its offerings unique from market competitors. Various patterns of e-commerce applications are helpful in obtaining comparative uniqueness of retailing/multi-purpose businesses in terms of internet service, network facilities, cable networking, and digital channels or even ease of selling through online networks. For this reason, many mega or even local retailers today are inclined today to successfully implementing visual attractiveness and usability of those techniques for trafficking more customers. In this report, the global branded venture capitalist named Virgin Group has presented to analyse their success of winning competitive uniqueness through integration with e-commerce strategies. It sets for obtaining financial, innovative, quality, amusement, and vision of differential advantage with presently recorded revenue of £11 billion and five basic pillars of corporate domains in cellphone, leisure, travel, amusement, and financial retailing.
Rationale for the research
Although the evolution of e-commerce has originated for the basic purpose of venture capitalisation, the modern business environment is more complicated with diversified customer needs and expectations for which retailers have pressurised most since they have to keep deeper conjunction with customer feelings. Under this circumstance, they have to initialise several steps, which could use to create different images of their organisations for generating a greater customer base. Customers are generally interested in getting various benefits, including product mix, price efficiency, prompt service, well- communicated promotion, bundling package and information delivery etc. All of those tasks can be well associated by different e- technologies through developing communication, transaction, distribution channels, improved customisation and business processes, involvement in e-trading, modified structure and level of specialisation, making a strong tie with present customers through IT and gathering newer ones. Another important technique involves innovation of new offers, which is possible to develop via the internet as an effective means of accumulating information, customer identification, and product introduction. Similarly, bundling strategy is also mentionable, which can be used by the multi- retailers for increasing the advantage of entire offers by taking away customers from others offers, generation of financial leverage and counteraction of alternative products from existing and new rivals. Therefore, e-commerce strategies can be effective here for creating such a traditional level of customer satisfaction along with meeting both organisational and individual exchange objectives. The success factors in integrating this idea could visually explain as below:
Research question and objectives
The required dissertation has been formulated to answer the basic research question as:
- Which e-commerce techniques are most influential for developing a competitive advantage for the acquisition of customer satisfaction for a retailer or multi-service operator?
- The answer to this question will enable a marketing manager foe implementing various forms of e-commerce tools to differentiate corporate offerings far from the competition by increasing customer level of satisfaction.
Up to this question, five research objectives will establish as:
- Identification of how does the e-commerce process work in the retail business of multi-product firms as an innovation-driven factor in Virgin UK?
- Identification of the development phases of e-commerce as a strategy of Virgin UK along with the possible initiatives for further advancement;
- Recognising the shift of e-tailing of multi-product firms towards the practical development of competitive strategy;
- Measuring the extension of the e-commerce process of Virgin UK is inefficient for the vision of providing competitive advantage associated with the paves of improvement for the benefit from ICT.
- Identify the development of modern m-commerce applications for increasing organisational capabilities from internal and external content.
Scope and limitations of the study
The potential scope of conducting this study extends from notification and analysis of every aspect of the creation of unique value that Virgin UK had already conducted. And as the research field is indicating, such kind of value generation is an ultimate criterion of understanding and implementing the most significant tools and techniques of e-commerce that are also several issues of marketing, management, customer service, IT, IS and internal process development.
Some integral limitations have also confronted this task, as:
- Limited time for making an expanded research work;
- Obstacles in gathering primary data because of lack of cooperation of target respondents in defective and incomplete answering as well as the reluctance of giving adequate time for giving information;
- Limitation in budgeting and planning framework;
- Clutter of unusual and unnecessary information in secondary sources.
- Limited support for gathering information from private and press sources.
- Complicated analysis and conversed shape of actual data with irrelevant ones;
- Difficulty in co-relating technological issues with vast and multi-product retailing procedure of Virgin Company.
Literature Review
The chapter has been devised to form the general theoretical background of the study. The definitions and proliferation of various variables have been depicted to form the basis for analysing the performances of Virgin UK.
E-commerce
E-commerce is the process of enabling digital transactions between and among assorted institutions and persons (Laudon & Traver, 2007). Here the term digital transactions comprise every type of digitally reconciled transaction. Moreover, these transactions took place through the exchange of value athwart institutional or individual borders by means of products or services (Laudon & Traver, 2007). More succinctly, e-commerce is the process of buying and selling over digital media (Kalakota & Robinson, 1999).
Types of E-commerce
E-commerce is mainly of three types, which are B2C e-commerce, B2B e-commerce, and C2C e-commerce (Laudon & Traver, 2007). The study predominantly focuses on B2C e-commerce and B2B e-commerce:
- B-to-C E-commerce: the consumers of these segments purchase products for final consumption, such as Amazon.com.
- B-to-B E-commerce: the customers of the segment purchase goods or material supplies that become part of final products, for instance, E-city.
The benefits of E-commerce
E-commerce provides businesses with various benefits, such as a large market base, low operating costs etc. Hoffman et al. (2004) stated that e-commerce generally results in marketing, distribution, and operational benefits. The most prominent benefits of e-commerce are as the following (Kurnia 2007and Callon, 1996):
- Innovative applications: it uses newly innovated applications, and hence the firm frequently enjoys a strategic advantage. For example, FedEx provides consumers with parcel tracking amenities.
- Competitive weapons: e-commerce has also been used as the key competitive weapon for organisations. To exemplify, a one-click shopping system of Amazon.com is the firm’s competitive weapon.
- Changes in processes: a firm can usually cover a large geographic area through its e-commerce process. Hence, a number of alterations occur in the operation of the business.
- Links with business partners: An entrenched e-commerce process allows the firm to manage its partners sited in different areas. Hence, its efficacy and aptitude have to achieve in the process.
- Cost reductions: the implementation of e-commerce usually let firms to enjoy large cost reduction. For example, a usual bank transaction in the USA costs almost $1.07, whereas its processing cost in the web-based system is 1 cent. Again, a traditional air ticket processing cost is $8, whereas the e-ticket cost is only $1. Kiggundu (2002) argued that since the cost of operation is low in this method, the cost reduction is usually availed by all firms.
- Relationships with suppliers and customers: the process paves the way to get real-time feedback from suppliers and customers, and in this way, the firm enjoys strong bargaining power over these two parties.
- New products: to persuade consumers of any particular segment, a brand needs to construct something new and offer a number of new attributes. These are required to have a competitive edge in the marketplace.
- Competitive intelligence: updated IT applications in this course would generally help a business to increase its competitive advantage. IT applications should frequently restructure by collecting information regarding products, markets, and competitions.
E-commerce business models
There are several e-commerce business models to institute the system and to build business strategies accordingly. Magombedze (2004) argued that no business model is well enough to suit every e-commerce activity.
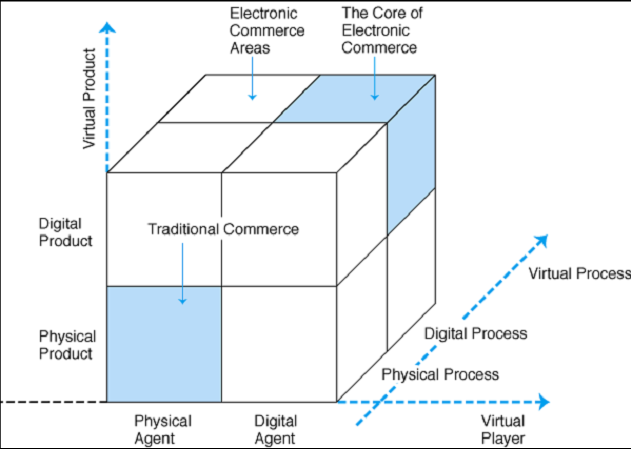
- The Electronic Areas Model: e-commerce could be either used for integrating the probability in a traditional business structure or as a completely new electronic venture. It discerns traditional business from electronic business through product, agent, and process. The following model shows the relationship of an organisation allied to technology, but it does not pursue any strategy for its success.
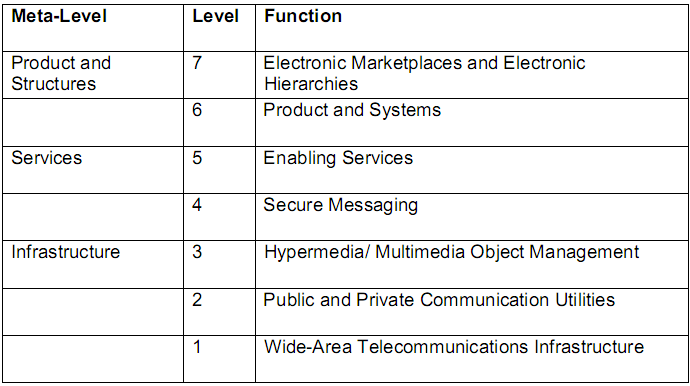
- The Hierarchical Framework of E-commerce: the model formulates three levels of e-commerce, i.e., product and structures, services, and infrastructure. Each of these levels depends on the previous levels to acquire strength. Hence, the more the precedent levels will be strong, the more will be the antecedent levels (Zwass, 1998). In this context, the bottom-up approach has to apply to build strategies for e-commerce businesses. To get success, the organisations need to have strong ICT systems, wide-area infrastructure, along with strong e-commerce products (Magombedze 2004, p. 22-23). Though the levels of the models are not that flexible to be applied, it illustrates to take care about the key components of an e-commerce process.
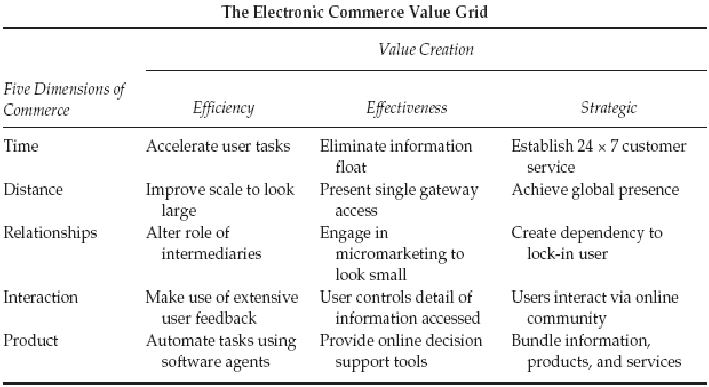
- The Electronic Commerce Value Grid: the business model sorts out the storefronts to gain profitability. A firm needs to work in all five breadths of commerce by using interaction modes to compete in terms of time and distance and provide products to its customers through a chain of relationships. In this perspective, a firm can enjoy competence on the fifteen bases since the efficacy of IT has been measured through efficiency generation, effectiveness, and strategic benefits. Furthermore, the model reveals the idea of information on demand. The model also suggests strategies or strategic choices that can be handy to gain competitiveness over competitors in the marketplace. Yet, the success of the model relies on the firm’s ability to change the business perception and the strategic standpoints to avail benefits of new technologies (Magombedze, S., 2004, p. 24).
Impediments to E-commerce
The adoption and proper functioning of e-commerce have been inhibited by the ICT infrastructures. In addition, the physical infrastructure, trade facilitation, logistics assortment, and regulatory functions regarding value transfer beyond boundaries are also impediments to e-commerce (Magombedze, 2004, p. 32). Some other specific impediments are:
- Ignorance: if the target consumers do not become aware of the e-commerce adoption of an organisation, they will ignore the use of the internet.
- Risk perception (online products and online payments): the value transaction over the virtual network remains vulnerable that increases the risk perception of consumers. On the other hand, the consumer rarely intuitively checks the products sold over the internet, so they might fear low-quality products.
- Cost: the cost of e-commerce adoption is sky-scraping. A firm, which tends to adopt the system, needs supplementary operating costs. Therefore, only financially strong firms can adopt the system.
- Time: the e-commerce adoption for an organisation is a time-consuming task. Hence, the firm employing the system may lose its strategic advantage due to the earlier adoption of the same technology by competitors.
Driving forces of E-commerce
Driving forces mean the actors who have the potentiality to change an industry’s structure and performance.
- Innovation and improvement: innovation of new IT applications and improvement of existing applications can modify the e-commerce industry. The changes of the IT application and other technologies take place very rapidly around the world (e.g., no hardware technology actually remains prominent for more than three months). Thus, the costs of adopting e-commerce become less, and new players start coming persistently in the industry. Additionally, such technological changes help to integrate mobile phone technology in e-commerce (e.g. WAP and Internet). Since the technologies are constantly changing, the next large improvement of the industry will be the high-bandwidth mobile phone internet facility (Magombedze, 2004, p. 33).
- Changes in lifestyles: more and more people all around the world are attaining their personal computers. The scenario is identical for both industrialised and developing countries. Therefore, mobile computing (e.g. Laptop, Mobile phone) is also increasing very rapidly. Thus, consumers will find it more convenient to buy and sell over the internet (Magombedze, 2004, p. 33).
- Technical capabilities of telecommunication networks: one of the major obstacles towards e-commerce adoption is the technical incapacities and less strong telecommunication networks. However, the scenario is continuously altering. Thus, the adoption and application of the system will become easier (Magombedze, 2004, p. 33).
The competitive advantage and sustainable competitive advantage
Porter (1985, p. XVII) stated that the competitive advantage could arise from many sources. These advantages are required to be interconnected with many other activities. The competitive advantage could develop from the significance a firm gives to its buyers that surpasses the costs of producing the significance (Porter, 1985, p. 3). It is actually all about how a firm is able to throughput the generic strategies (e.g. cost leadership, differentiation, and focus) into its plays. It will exist in an industry where there is heterogeneity (ways of earnings), highest limits for competition (making earnings sustainable), deficient mobility (earnings are only possible within an industry), and past bet limits the competition (the earnings are not offset by costs) (Tobias & Soderlund 2001).
To gain a competitive edge over competitors for a long period, the competitive advantage must be sustainable for that long. Barney (1991) argued that resources (those that have value, paucity, exclusivity, and non-substitutability) are only able to have such kind of advantage. Magombedze (2004, p. 33) and Byrd & Turner (2001) have stated that IT is a greatly convertible resource. Hence, it is important but not sufficient to hold a competitive advantage for an extended period of time.
Porter’s five forces model
The five forces model devised by Porter has been used to analyse the standard competitive pressures in a marketplace to know how strong each of these is. Here is an analysis of the impacts of the internet on business and e-commerce in the context of the industrial environment:
- Threats of new entrants: the IT resources are rarely proprietary because of great transferability either through the developer of the resource (i.e., the employee) or by the release of the resource. Hence, the barriers to a new entry in the e-commerce industry are low. On the other hand, since the system does not require intermediaries, the barrier to entry has further lowered (Porter, 2001).
- Rivalry between existing players: as a variety of e-commerce organisations can easily offer similar kinds of products at identical prices, the existing rivalry in a segment is high. Moreover, internet technology is existent in almost everywhere nowadays; hence, new competitors from different country origins are gearing the competition more rapidly.
- Threats of substitute products: the threats of substitute products are increasing due to the existing proliferation of the internet and the easy access to e-commerce marketing around the world (Porter, 2001).
- Bargaining power of buyers: the e-commerce businesses are growing rapidly and are giving customers more choices at competitive prices. Hence, the switching costs are decreasing, and the bargaining powers of buyers are increasing.
- Bargaining power of suppliers: Although the suppliers are getting more customers, the bargaining power of e-commerce businesses over their suppliers are increasing due to the easy availability of the internet. Again, the decrease of intermediary intervention in the marketplace also narrowed the bargaining power of suppliers.
The Strategies
Strategy means the planning intended to attain a specific goal. There are several strategies and/or perspectives of strategies those firms usually hold to gain a specific goal.
Porter’s generic competitive advantage strategies
The generic competitive advantage strategies have been used either to defend or to offend the market forces to create a sustainable position in the industry, to keep up in the market competition, and to generate extraordinary profit (Porter, 1985, p. 11).
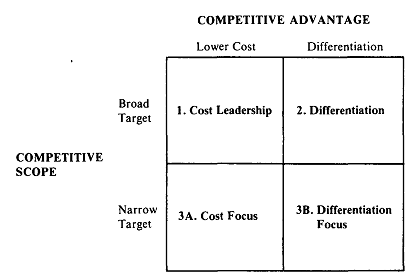
- Overall, cost leadership: the basic notion here is to provide customers with products at a lower cost than that of its competitors. In order to gain such kind of advantage, the firm needs to have an efficient value chain system. The focus is to trim down costs from the purchase of raw materials to the delivery of the products to the end-users. Here, the businesses think that their consumers are only seeking low-cost products (within relatively low effort), and they are not enthusiastic about the brand name and marginally enthusiast about quality. The use of e-commerce further opens the door of cost leadership as it decreases transaction costs and distribution costs through a large cut off (Lumpkin et al., 2002).
- Lumpkin et al. (2002) further described the way e-commerce could lessen costs such as inventory cost through the just-in-time approach, less work-in-process, less workforce and costs and thereby, collaborative design approach etc.
- Differentiation strategy: the strategy has been devised based on the uniqueness of an organisation, which is unparallel to its competitors (Porter, 1985, p. 14). Grant (1995) argued that the brand image, quality of products and services, and the brawny status of the sellers are the key characteristics of the differentiation strategy. Mass customisation is also necessary for this respect (Lumpkin et al., 2002). Therefore, in the e-commerce era, utility such as mass customisation over the internet helps the organisation to minimise costs of operating the business along with unique product offerings and maintenance of quality and brand image. Grant (1995, p. 23) argued that the internet advantages towards the differentiation strategy are shortening customer response time, real-time information proliferation, rapid and fast feedback etc.
- Focus strategy: in this strategy, the firm usually focuses on a narrow market segment (i.e., niche market). Thereafter, the firm applies either the cost leadership strategy or differentiation strategy to the niche market. In this e-commerce era, small sellers also find it useful to access previously non-accessible markets. The most important benefit of the strategy is less concern about scale economies. Grant (1995, p. 23) argued that internet advantages in this respect are personal selling (i.e., permission marketing), niche-specific portals, procurement techniques to collaborate buyers and sellers and so on. Here, the firm should improve both primary and secondary activities of the value chain to compete better with others.
The E-commerce strategy
The functional e-commerce strategy of a company contains its objectives as well as the specified actions to achieve those objectives. The functional strategy can be a part of other strategies (i.e., IT strategy) or can collaborate with the strategy of other functional areas (i.e., e-marketing). Dvorak and Kriz (2006, p. 16-17) stated that there are seven key factors (divided into two broad categories) to employ the strategy such as the main pillars (e.g., market, technology, service, brand) and means (e.g., management, infrastructure, and training). Here, cost minimisation and knowledge-based approach to management get more importance (DVOŘÁK and KŘÍŽ, 2006, p. 16-17).
The Strategic perspectives
Since there are no specific competitive strategies to gain competitive advantages everywhere, the following strategic perspectives are more important to work out a particular strategy (Gunnesson & Soderlund 2001, p. 8-11):
- Informational economy perspective: here, the adopted idea is that the new technological changes around the globe are quite disruptive because of their immense heading around the world. Moreover, the market space (the virtual value chain) helps the marketplace activities by providing information. The most valued drivers of e-commerce in this respect include time, efficiency (cost and time concerned), and novelty (uniqueness) etc.
- Industry organisation perspective: the strategy from this perspective is usually defensive on the ground of following the external forces in the industry. Here, a firm is required to place itself in the value chain by responding to the industry pressures that have been devised by several examinations (i.e., value chain analysis).
- Resource-based perspective: an organisation can enjoy a sustainable competitive advantage by using its resources that can eliminate its weaknesses, counteract threats, and exploit strengths (Barney, 1991). Here, the resources and their subsets get more importance, such as one subset of those resources may gain a competitive advantage, and another subset may sustain long-term performance.
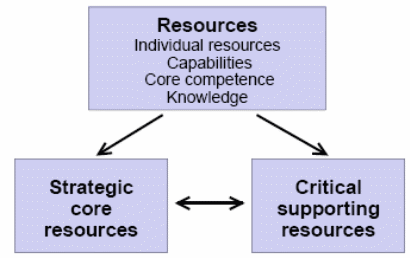
According to the above figure, the strategic core resources are the primary resources for competitive advantage, and the critical supporting resources usually lie in the line of core resources. The core resources are varied and non-transferable around the industry (Barney, 1991). Furthermore, these should be rare, valuable, not substitute, not imitable.
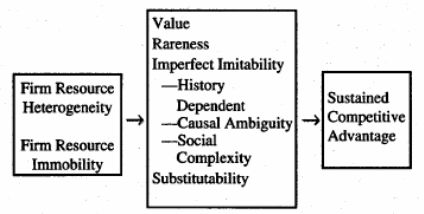
- Networks and Relationships Perspectives: the theory focuses on leveraging external contacts to gain a competitive advantage. These external contacts may include contacts with suppliers, competitors etc. To create a relationship online, organisations need to regard information, transaction, and interaction online.
- Market Orientation Perspective: this is an organisation with a wide function of initiation of market intelligence, communication of the intelligence, and making a response to the intelligence. There is a strong need of changing marketing orientation according to several environment moderators (i.e., market growth, buying power etc.).
- Brand Perspective: building the strategies on branding requires thinking about brand awareness, brand image, and brand extensions.
Innovation (Innovation-driven) Strategy
E-commerce is completely a result of technological innovation. The IT advancements are also a determinant of competitive pressures in the marketplace. There could be several kinds of innovation, such as sustaining innovation (increasing consumers’ benefits by improving the product) and disruptive innovation (changing consumers’ benefits completely and differentiating the core performances in the short run). Here, the e-commerce firms must develop their products considering whether these are marketable online. If yes, then only the firms could go for technological support.
Capabilities of e-commerce to generate competitive advantage
E-commerce can influence a firm both strategically and through operational effectiveness:
- Operational effectiveness: e-commerce is perhaps the most commanding device because of its universality. Since the technologies are universal with common standards, firms can easily integrate them, investing a large number of resources (Porter, 2001). Though various researchers argued against the durability of its effectiveness, Malhotra (2009) stated that in the future other similar firms would share these developed resources of one firm.
- Strategic positioning: nowadays, competing on operational effectiveness does not work. Rather the firms now need to head competition through gaining a cost advantage and/or price premium (Porter, 1985). Magombedze (2004, p. 45) stated that the firms now require exceptional value-chain and create the elements of the value chain as a self-reinforcing system so that the competitors find it impossible to just imitate a single aspect of any system.
- Achievement in the competitive advantage strategies: The firms should focus on their cost centres more to make every operation efficient (Lumpkin et al., 2002, P. 6). Magombedze (2004, p. 45) advised e-commerce integrated firms to further differentiate their products and to eliminate over costing tendency. Again, he argued that the niche market must spread enough to let firms enjoy more profit.
The present scenario of E-commerce in multi-service operations around the world
In the USA only, the total sales volume of B2B and B2C e-commerce firms was 1.679 trillion dollars in 2003. It has been forecasted that only B2C sales would be $329 billion in 2010 worldwide. In 2004, there was 95% e-commerce trade in the developed countries and Africa, along with Latin America accounted for only 1% (Kurnia, 2007, p. 1). In 2000, e-commerce shopping amounted to £50 billion. In 2004, the total B2B sales outstepped B2C sales by 87% (Lincolnshire Chamber of Commerce, 2007, p. 1). On the other hand, almost half of the UK consumers (about 28 million people) purchase online regularly, which amounts to £1,312 annually. Most interestingly, e-commerce has also been thought of as the greenest shopping medium. The Heriot-Watt University, UK discovered e-commerce as twenty-four times “greener” than going to shop by car and seven times “greener” than going to shop by bus (E-Commerce, 2009, P. 1).
The Virgin UK
By the end of 1999, the Virgin UK had employed e-commerce in all of its parts, starting from the giant “Virgin Atlantic” to the most miniature “Virgin Bride” (Virgin, 2009). This e-commerce proliferation mainly refers to B2C e-commerce. The Electronic Commerce Value Grid model is the most appropriate to describe its operation. In order to create a competitive strategy, the brand perspective has been widely used (Murphy, 2008, P. 15). The focus strategy and cost leadership have been used more than that of the differentiation strategy. On the other hand, the groups have come to adopt the strategic positioning successfully and thereby enjoy economies of scale and high profitability (Murphy 2008, p. 15-18).
Concluding Remarks
The firms using e-commerce have usually benefited from cost shrinkage, business partners’ integration, and overall competitive advantage. However, the technology and other relevant factors are subjected to frequent imitation. Therefore, the creation of mutually interdependent aspects of technology is essential to uphold competitive advantage. Moreover, the application of different strategic perspectives surged in order to define the actual strategy of any e-commerce firm through Porter’s three generic strategies, the e-commerce and the innovation strategy, have been suggested historically. On the other hand, strategic positioning has been considered the most appropriate thing since the operational effectiveness perspective highly relies on it.
Methodology
The basic objective of the methodology is recognition of the points, which are helpful to adjust the selected methodology of the research with its five objectives and the main question presented in the study. So, several steps should maintain in this issue as below:
General notions
There are two types of methodology involving quantitative and qualitative research. The first one involves seeking an opportunity to quantify data by implementing some statistical module like- survey questionnaire, while the second one is an exploratory and unstructured process using a small sample for providing general insights of the problem like- focus group or depth interviews. Here, it had conducted qualitative research by interviewing the top-level executives and technical experts of Virgin and a survey in terms of questionnaire among 100 users of their products and services.
Qualitative method validity
Here, we have used an interview method that had conducted among five technological experts and five top-class executives of Virgin UK. Through this pattern of purposeful discussion, relevant information could collect that are valid and reliable in nature. Therefore, we have prepared a semi-structured questionnaire which having some specific themes and questions posing a capability of informal exploration of corporate e-commerce implications. The interview had covered the following criteria:
- Who should be interviewed and why?
- Where should the interview occur?
- What data are required from the respondents?
- How have the objectives of the interview been represented?
The information obtained from that way were confidential whether the higher-level executives and e- experts had been chosen for their clear understanding about the ongoing critical e-technological orientation and active participation for the strategic decision-making process of Virgin, which is enclosing key research area of that company. The major issues upon which the interview had been conducted are:
- Present e-business offerings.
- Forthcoming technological ideas;
- Dependency of long-term decisions on e-commerce strategies.
- A technological overview of the company;
- Branding via e- techniques;
- Limitations in such practices,
- Identification of competitive forces etc.
The overall interview session has been divided into several parts as:
- Introduction: Common questions regarding the fundamental basis of the problems have been addressed with an adequate level of confidentiality.
- General conversation: Open-ended questions have been used to obtain information about facts from the interviewees involving two parts as identification of e-commerce influence for differentiation and discussion over this fact.
- Ending: Consists of asking for additional data and literature source personal perception towards the interview.
Approach and data collection
The methodology has developed upon research approach considering both exploratory and descriptive research design as well as inductive causes. Therefore, a primary foundation is essential to design with conduction and reasonable analysis. The approach is significant for the foundation of qualitative research since it carries out the designing of research, which is the ultimate answer to the presented research question. It had also shown usable methods of data collection depending on the logical reasoning.
Exploratory research has been used for gaining a simple definition and understanding of the problem as we’re going to take such initiative by conducting expert and top personnel interviews. The descriptive design had met the need of defining characteristics of the target market that has taken in the form of a customer survey method. Therefore, the result depends upon data collection and measurement techniques and types of doing so. The description would be inductive or deductive, while the former starts with a question and then explains it, and the latter one starts with the issue by working upon the history of that. Here, we had gone forward with an inductive approach for establishing theory from the collected data for the discovery to reach concluding points toward e-commerce and the competitive advantage of Virgin group.
Reliability and validity
Reliability can calculate the random error absence that could be avoided by standardised surveys while preparatory information has launched to both kinds of respondents.
To maintain inner validity, we had conducted the survey and interview with different people with tactics of handling external misinterpretations. Outer validity has been maintained through a generalisation of the findings with the assistance of existing theories and explanations that are more explicit.
Data analysis
During the period of conducting survey and interview prior to final analysis, the interviewer had approved such information and senior technological staff of Virgin and after all the unrelated data has abolished for the avoidance of bias. Here, the “laddering” technique has been conducted through tailoring interviewing structure with a serial of directed probes with specific sets of connections among values, theories, and results. Then a classification has followed with a phenomenology system explaining features, results, and values classify condition and action. Attributes explain the environment and facts evolved through an inductive approach as a holistic description of alternative management tactics. Values are empirical proofs explaining the reasons for changing, and consequences are results explaining that what was to happen for the 1st two drives. By adjusting these three, a holistic view of e-commerce, competitive advantage, and strategic orientation has been conducted.
Secondary data sources
Secondary data are processed data that already exist acted as a major source of information for the preparation of this research work. However, various secondary data sources include national and international business journals and reports, business directories and magazines, books, newspaper articles, chamber of commerce reports and corporate web pages and internet articles.
Primary research sources and major focus areas
The chosen methodology has been classified into two parts. At 1st part, it was a descriptive interview with the mentioned corporate bodies in the UK office. That interview emphasises various issues of the problem. Then the question of research strategy may arise for which an inductive, qualitative standard has been used for clear data analysis. Here, the thoughts of several strategic schools could be accomplished involving development, implementation, experimentation, and discussion. So, a rational viewpoint has been used here while the data analysis and suggestions are going to go after in some sequential order.
In the 2nd part, a questionnaire has been adjusted with this report for generalising perception of Virgin to further show corporate image among general people. The sample respondent age had estimated from 18 to 60 who are regular users of their multi-products and enjoy various online and networking services from them. The locations of this survey were XYZ Street, south London, ABC Street from north London and MNK Road from west London, the UK, where a mixed approach of open and closed-end format had been used.
Results and Findings
Business achievements in serving huge customers through multi-task
Virgin Media (2009, p. 8) pointed out that Virgin UK has been recognised as the largest communication and entertainment company for offering “quad-play” in association with television, broadband, mobile phones. It has landline services while it had achieved the largest customer base of merely 56% at the end of 2008, among who most were “triple-play” people for the extraordinary network performance of the company. The company also relies on and implements superior, deep fibber access networking for delivering speedy and better-qualified services than the general digital customer line or some other DSL retailers.
Pirvanescu et al. (2008, p. 22) offered that at the same time, it follows wide diversification in serving the residential customers by developing their own media brand. This personal, locally distributed and cabled communication web has expanded everywhere so that the user can easily access it, and because of such initiative, the company is now a significant gainer of a giant market segment of nearly 12.6 million households. Along with covering the major urban areas and megacities of Wales, England, Scotland, and North Ireland, Virgin has also been concerned to meet the needs of customers. Customers who stay outside of the cable channels by providing telephone and broadband facilities through the help of other mobile networks with the implementation of “off-net” service commonly known as “Virgin Media National” as an indicator of achieving the goal of frequent and non-frequent users who face hindrance in consuming other organisation’s communication advantages. (Tobias & Soderlund 2001 p. 33) As a result, Virgin creates competitive advantage through an organisational map, such as-
Diversified offerings in the cable network segment
Molla & Licker (2001, p. 23) addressed that within each of that patterned product options, Virgin differentiates itself by granting customers for making a preference for several bundles and duties. It also indicated by M, L, XL, XXL size while the company tailors its packages and charges are structured for making customer enthusiasm of purchasing multiple products and offerings and thus creating a new dimension of e-trade. In this situation, it offers discounts and other benefits to the customers for making multiple network functionality. However, playing off those integrated electronic commercial products plays a major role in improving the rate of customer retention through a gradual maturity in video- in-demand, controlling fault, and other operational development. (Abdul 2002, p. 11)
Network benefits in the identification of addressable markets
AgMrc (2008, p. 14) explained that, especially in the UK, Virgin Media has imaged for pressuring cabinets. Since then, the construction of twin cables has been applied for providing flexibility in service broadband lines through both copper and coaxial cables. Recently, the company has been obliged to performing such a function with the latter one. In addition, its networking technology is capable enough to be close to the user’s residence than other major competitors. Then, Virgin’s networks are interactive with users linked with the network by enabling the company for making additional functionality of transmitting video-on-demand by set-up box. Because of delivering numerous bundled services at a fixed price, Virgin has created a distinguished culture of customer service by integrating e- goods rather than any equivalent players in the minds of their target buyers because they do not pose the capability of putting forward the tow- way communication with a persistent limitation of using other e- tools. They also face a problem in the limited capability of serving digital service lines for delivering high-speed access through ordinary telephone lines over of present copper-based network of BT since it is promising to enhance further development of assisting networking technologies with lower capital requirements to maintain operational cost-efficiency. (Abdul, 2002, p. 8)
Operation of broadband internet in an effective manner
Tobias & Soderlund (2001, p. 32) have described, and the users of the internet mostly prefer Virgin’s broadband service because of higher speed and richness and a direct linage with the corporate network. The year 2008 was significant in this regard since it offered that e-commerce product strategy for promoting customers from 4MB to 10MB by increasing corporate strength from 20MB to 50MB service level by making it on hand at the entire broadband process for future successive years. Similarly, those services now enlighten the use of three- tiers to stand out more competent than other firms by delivering that advantage of a maximum of 10MB for L size users, 20MB for XL size users and 50MB for XXL size users. Customers will be able to maximise their benefits from such tabulation with an option of unlimited consumption along with PC enabled software security system. Other factors in relation to this issue are:
- Virgin expects to enhance its present market share by communicating its e-benefits in communicating hyperactive quality broadband services for attracting both real customers and potential prospects.
- Since the last year, it has been delivering that item by using BT’s domestic network and individual connections from C and W to people who have indirectly engaged with the company networking. Here, it has also arranged of itemised pricing and attributes packages associated with customisation process that effort had resulted in merely 252000 users enjoying its broadband service.
- To increase the level of sophistication and competitive dynamics, Virgin had introduced a web-based portal as viginmedia.com, which proves its multi-performance in transmitting movies, music and TV functions. Rather than many other similar types of e- tailors, customers like to administer their mail accounts and customer care data easily via the Virgin website, which is also generating supplementary profits through search engines and advertisement. The company is experiencing an extreme level of competitive uniqueness by using cross-promotion of the overall range of products. Recent year has identified for making extra amusement and customer care factors in the corporate website through an influence on managing and controlling online accounts and support services.
Diversification in manufacturing of cable and dish TV
Figueiredo (2000, p.15) explained that Virgin is one of the most prominent companies in the UK in supplying a greater range of analogue and digital as ATV and DTV to more than 3.6 million households while most of them are DTV users. The company keeps its technological expertise and practical capability in implementing e- techniques in such products via increasing accessibility of more channels, high-tech interactivity, and the like. ATV also serves more than 60 channels; in contrast, DTV users are able to get an integrated VOD facility, which has generally referred to as “Virgin TV on Demand”. Further, its networking effort allows the company for serving a broader range of communicative advantages termed as “always-on” linkage from root network to viewer’s living point. Examples of various integrative amusements involve e-mails, games, news, on-screen information procedure. Other than the “red button” function has very much popular today conducted with BBC and other commercial newscasters in whom the former one is highly useful that permits a customer to press the red button and view the preferred item. Another notable item by which Virgin acquires wider appreciation from its audiences is giving of free-to-air DTV service that accumulates more than 40 equal channels along with radio VOD access. Some other facts are:
- Virgin modifies its marketed television by implementing customer-oriented e-applications of free choice for scheduling programs apart from any complicated modulation handling with free installation or subscription charge. Combining all those features involved in general TV functionality benefits the users with extra programming conduct, which can be utilised and visualised regardless of time limitation with normal remote control. It also integrates DVD- pattered characteristics like- freeze structure, rewind, and speed. All are applicable in maintaining user control regarding the time and content of their TV that can easily be found out in overall Virgin DTV people. Virgin also delivers three types of DTV containing a daily refresh option, while selection is at free charges to the DTV users regardless of the bulkiness of the package. Moreover, customers face a flexible pricing policy with getting of the additional scope of SVOD or VOD. Users of other brands also pose a chance of using Virgin since it offers a non-branded subscription facility. (Coulthard et al. 2004, p. 61)
- Another offer of Virgin is DVR or Digital Video Recorder, where Virgin Media DVR box, termed as “V+ Box”, is also easy to get for the DTV subscriber. Such a box is of broader storage place of 160 Gigabytes, HD, three tuners, permits users for documenting two programs when he/she is enjoying something else. V+ Box users associated with HD function can enjoy that version on-demand feature. The company’s content strategy has also differentiated since it adopts several techniques for measuring the intelligence of the latest channels and functions for enhancing mutual diversification for the purpose of generating trust in customers thought by means of raising their interest in those options. (Kiang & Chi, 2001, p. 5)
- Virgin UK is a leading provider of fixed-line telephone service on a neighbouring, domestic, and global basis. It is committed to creating differential advantage by providing some extra benefits, like- barring calls for blockage of some specific inward and outward calls, waiting calls, forwarding calls, voicemail, recognition of caller’s channel, three- panels calling and completely listed payments per month. Additionally, it also provides directory supervision facilities in-home and out-home countries. Along with the basic rental charge, it serves M, L, XL alternatives to the fixed subscribers as a variation to direct usage-determined payment. It involves “Talk Plans” for allowing customers with limitless internal and external calls for standard and fixed subscription fees. Here, on- net services are mentionable, as it has offered to merely 4.1 million users. Similarly, its functionality extends to local networking channels of BT to people who are not regular with corporate networks counted as about 105500 subscribers. (Anon 2008)
Communication requirements in corporate retailing
Malhotra (2009, p. 11) argued that Virgin is a company that is conscious about serving individual and organisational bodies, including private and public companies through ntl: Telewest merging along with the transaction with other telecommunication operators. For such merging in working on telecommunication channels, Virgin now can offer various benefits inside the home company where the combination of some other e- products involving extended voice assortment and information goods are served to final customers for assigning more value upon entire business. According to prior knowledge, it is easy to remember that the brand Virgin UK had re-branded in 2007, where such re-branding largely focused on long- term customer bondage. Becoming an active service entity with e-commerce expertise, the company ensures of enhancing an optimised level of increase in brand equity through each of its involvement in legacy transactions with an overall reflection of self-differentiation. Some other advantages relating to sales channels are:
- Virgin occupies two major sales channels named business markets and service providers, which are widely used for supporting their retailing and multi-business operations with buyers. Business markets are a pattern of the private sector that emphasises satisfying the communicative demand of private ground of the UK ranging from tiny to bigger corporations, which are domestic in nature. Management having centralised receiver accounts deal with small entities having 50 to 99 personnel, and the regional accounts, functions and assignment management groups are maintained by pre-selling mechanical experts for the purpose of delivering differentiated functionality proposals to the gigantic and mid-sized firms with more than 100 staff. According to the company philosophy, their internal market presence, as well as optimised service level, is a basic indicator for their running differentiation strategy in such mid-sized market arena while such facilities of this planning have proved in their long-run intimacy with numerous customers. On the other hand, public sectors of business markets are a channel of sales, which have related with definite vertical criteria involving the local authority, health, education, and urgent services. Those can be identified as unique sources of advantages over competitors for delivering sector-wise professional expertise through a thoughtful process of drivers and accumulation methodology of publicly capitalised corporations is in the necessity of performing an active operation of communicative strategy. So, the merged counterpart of Virgin acts as an efficient vendor working with different government structured contacts liable for both growth factors in the individual segment as well as track- documentation endorser with an extra obligation and capability of delivering value to public entities. In 2008, the company could make a profound regional exposure by performing a perfect positioning of multi-service solutions for making it possible for an interrelated shift of health authorities for offering operational and expenditure savings to those businesses, finally, in sales channels of service provider, accounting, and service management groups maintenance bears, cell phone companies, ISPs and system integrators. These channels are exclusive in that sense that it performs as a data connector on both local and principle networking. As a result, greater benefits have been placed upon network wealth with backward solutions linked between two forms. It is helpful for sustaining the market share of generating data transformation services rather than BT along with cell phone players for sophisticated bandwidth linkages for the development of information services and 3G technologies.
Product and service differentiation
Virgin Media (2009, p. 21) stated that Virgin’s intimate partnership with ntl: Telewest Business had made it possible for exposing numerous e-goods, including data and voice products, analogy telephony and data management etc. Its product strategy is concentrated on offering organised services involving VPN (Virtual Private Network) through the internet and Ethernet protocol, while that kind of improvement is associated with insider corporate functions based on the specific time and need of selected segments. This strategy helps the company for being a market leader in Ethernet, introducing IPCCTV and IP, and improving cost savings in conventional services. Inducement of HSC had been effective notification of top bandwidth chucks of few bigger businesses. Some other fields of improvements via e-commerce involved project automation and pioneering web-oriented user interfaces in increasing competence in instalment, charges, payment and network functionality.
Voice goods and service differentiation
Virgin is an industry expert in delivering a complete package of voice products and services. Adoption of IP network has been notable in this case for PC-to-PC video conferencing as an indicator for 3rd generation capacities in the IP era.
Data items offerings
Rajgopal et al. (2000, p. 27) pointed out that those items are offered in three shapes casing congregated, Ethernet and implication procedures. The first one involves using an individual network by which customers can enjoy savings of costs, empowerment, and easiness in handling not available to get from other’s services. Now, Virgin can connect sites beyond the UK through implementing hyper technologies as eight patterns of service passage is possible to be divided into eight groups for assuring complex data implementation at the priority-based transformation. In Ethernet implementation, MEF14 authorisation introduces corporate competence for evolving “any- to- any” and “point-to-point” networks, which are scaled competency and set up with support services of video voice and integrated others. These networks are easy for customers to get with more flexibility and bandwidth. Lastly, Virgin supplies application services for increasing the value connectivity infrastructure of people.
Dealing with customer service
The merging entity is supposed to generate communication necessities of selected segments for providing them with the finest experience. Such e- strategy focuses on 75% selling offers in- life provision while it aims to differentiate full-service mixes to deliver as a competitive advantage to their target groups. (Rajgopal et al. 2000, p. 12)
Serving through mobile segment
Malhotra (2009, p. 11) expressed that the company had introduced this type of retailing from 2006 by a greater acquisition. Today, it has a huge user based network comprising better facilities than other operators do. This item has several attributes, including voice and non-voice options as news, games, and music over 2G to 3G stands. From the year 2008, it had contacted to offer data charging amounts that offer a more competitive framework in the cell phone industry for the issue of enhancing the recreational scope for the users, browsing facilities, linkage and community-based networking. It also maintains liability over basic voice, receiver information, content and broadband data card benefits from their previous T- Mobile while in the same year, along with their general broadband lining, an extra package containing some other extra technological features have been launched. Few initiatives for making market positioning via this segment of the company are as follows:
- Virgin uses a variety of logistics systems for retailing their multiple items to several consumers, like- online and trade channels, telemarketer and customer care booths. Outside of the UK, in the Philippines, it had launched a partnership with the outsourced marketer. Thus, its self-owned retail stores are about 23 in quantity for delivering all sorts of consumer goods, and in recent times, they wish to introduce corporate branded shopping mall kiosks. Here, Virgin maintains a home-based user database for spotting their personal requirements. Eventually, with a successful integration with several e-commerce tools, it initiates customers for making newer buying with upgrading the present ones via a balanced marketing philosophy and growth. (Sultan 2007, p. 10)
- Upgraded customer services have been maintained by in-home services along with hired associates through regular conduct with customers in terms of transmitting necessary information and handling complaints.
- Virgin’s content channels offer non-premium and cable facilities, while additionally, it arranges online auction sites for some proposed consumer items. On 2008, 31 December, Virgin introduced “multiplexed” networking associated with a portfolio of its TV. Further, it poses a joint effort with Setanta Sports Holding Ltd. for offering various integrated services to their DTV subscribers without extra expenses. With a combined team, Virgin earns revenue by posing flexible billing procedures and thus shows customers VMT, UKTV and Freeview to accumulated multi-line phases.
- Three renowned communicative TV channels named bid, price- drop and speed auction TV are acting as auction-sited channels of Virgin, which can use at the user’s satellite channels, digital modules, as well as the internet for making public bids through auction. Freeview is also possible at bid TV, which service has not always been given adequately by other multi- retailers in the industry. (Laudon & Traver 2002, p. 41)
Technological efficiency at the corporate network
Virgin UK is one of the promising investors for developing their corporate cable network with advanced integration with a broadband methodology that had been raised at upward and downward broadcasting speeds by increasing their ability for operating at more than 200 MB each second. In such contribution, the company owns merely 600 hub points, presence points, radio points, and repeater nods etc. It also poses a number of alternative techniques for domestic connection along with locating outsiders with “last mile” process as DSL and the company rents circuits to other local service sellers at lower investment as a source of side transaction at quick placement and the chance of altering with direct line. (Virgin, UK, 2009)
IT support in multiple operations
The company has developed its talented information technology team with superior internal and hired personnel for generating extra positive support. Some basic e-commerce information systems are continuously using involving electronic billing systems, ERP or Enterprise Resource Planning, intranet, intelligence unit, information and data centre, and desktop features etc. The year 2008 had been memorable for making greater competence in incorporated customers care process of paying bills for the development of functional efficiency. Because of such initiative and extra technological sophistication, it is becoming to decommission a large variety of hardware and software usability for removing the reliance on outsourced managerial and technical services. (Virgin, UK, 2009)
General servicing for customer assistance
(Virgin, UK, 2009) clarified that by using the internet, Virgin explores information about distinct lines of products, which are helpful for potential buyers to discover their items and prices with the physical visit of stores by the reduction of customer costs. Moreover, the company’s overall strategy has merely reflected a better example of e-commerce application for becoming brick- and mortar rather than a pure click-and-mortar entity for gaining the satisfaction of overall market partners in the context of competitive leadership. Therefore, a summarised diagram can show the projection of Virgin’s e-business strategic implications, as:
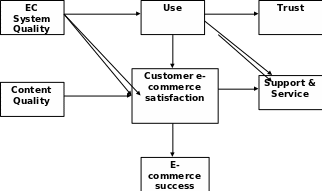
In addition, eventually, the targeted e-commerce success will come up as.
Discussion
Working of E-commerce Process as Innovative Factor in Virgin UK
In this chapter, the discussion has been carried out after analysing the results and findings of the e-commerce process in Virgin UK. The discussion mainly focuses on describing the research questions of the study after implementing it in the target customer group. This portion has been divided into four parts to discuss e-commerce in Virgin UK more easily, which has given below:
Whiteley et al. (1999, p. 13) mentioned that Mike Brown, an investor of Virgin UK, was investing there in the early stages of company development, which was broadening internet space for consumers by concentrating on innovation, brand name, technological advancement, art, and musical instruments according to consumers’ preferences.
However, these days, the world has grown excessively competitive, and this was beyond everyone’s thoughts before a period. This is because, at that time, the concentrations were only on the internet, but now people need to focus on the total e-commerce process in the market. The performance of the site is an important factor in the entire e-commerce process, which has been defined as the quality of e-commerce to maintain difficult tasks. The previous system of Virgin UK depended on reliability, flexibility, customers’ responses, and easy to use dimensions. Right now, they must focus on some other criteria, specifically: (Molla, 2001)
- Availability in 24 hours in a Day
- Software and Hardware Stability
- Page loading Speed
- Architecture of E-commerce
- Appearance of Visual
- Accessibilities to all people
These criteria can undeniably work successfully to influence further use of e-commerce system and customers’ satisfaction of Virgin UK. The success of potential customers can also dissatisfy the non-users of e-commerce of this company.
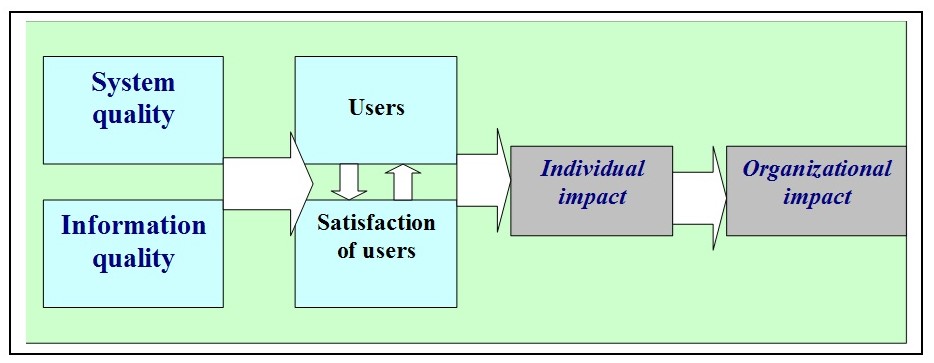
Customers’ satisfaction of Virgin UK according to their e-commerce system depends on a model, known as web evaluation model, which has shown below with the help of a figure: (Whiteley et al. 1999)
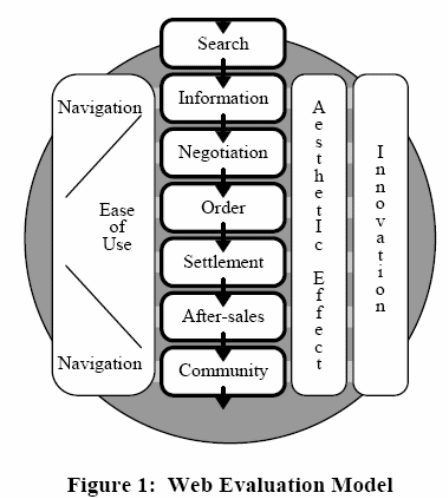
E-commerce services of Virgin UK must be proliferated with interpersonal services and self-service, which can reduce direct interaction with sales personnel of the company. Some other purposes include conducting various activities and extracting information about customers by clicking on the mouse to specific services.
In the above model, it has been seen that consumers want to navigate all types of services with ease through the e-commerce process. The other two important factors that should consider in this company includes the effects of the aesthetical approach and the innovation of the e-commerce system. Innovation can make differentiation of the e-commerce system of Virgin in the competitive field. (Whiteley et al., 1999, p 6) With an annual profit of £ 3 bn, it is showing its innovation in e-commerce system comparing with other private companies in the UK. This company is positioning three factors as innovativeness, those are, fun, innovation, and daringness in the marketplace. These are very important in the marketing and promotional activities of Virgin. The top management of this company is emphasising innovation to extend flexibilities and values towards its customers with the help of the staff and groups of people of the company. (Abdul 2002, p. 29)
The innovative thoughts of e-commerce have been implemented directly to the system, sometimes worked as bare fruit, which had seen when Virgin Mobile was operating to retail in mobile services in network management. Although it has faced failure, the innovation can differentiate this company as a unique service provider in the market and e-commerce process in the UK. (Abdul 2002, p. 12)
Developing E-commerce as Strategy of Virgin UK
For e-commerce, there is no specific single available strategy, as the market is too competitive to capture the advantages of the strategy. (Shin 2004, p. 8)
The company must have to focus on the competitive forces in the market, like new entrants, competition among the same companies, and threats from substitutes etc. Virgin can develop strategies by making sudden changes in the e-commerce process by predicting and handling customers using different models and approaches in the e-commerce domain. From the results, it has been seen that Virgin UK is using numerical simulations to maintain e-commerce conditions as an online retailer in the competitive market. Strategically, e-commerce has developed by managing customer base growth according to competition.
Virgin UK must develop strategies for e-commerce to create competitive advantages with its rivals. To attend competitive advantages, the company has to develop three competitive strategies, which are:
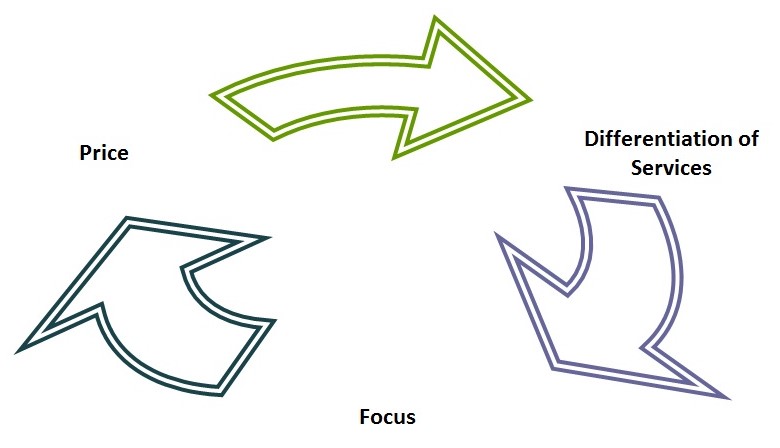
- Pricing Strategy: In upgrading e-commerce, it is the simplest strategy to understand and implement by Virgin UK. In this strategy, it is important to focus on ensuring that the company’s products and services are priced cheaper than that of the potential competitors. For example, by e-commerce, a customer may easily access Virgin UK’s system and other competitor’s systems, so it must be ensured that the prices of its products and services are lower and easily accessible to the customers. (Griffin 2006, pp. 339 432)
- Differentiation of Service Strategy: This strategy also focuses on the product and service differentiation of Virgin UK from their sufficient resources comparing with rivals. Pricing is attracting the cost-concerned customers, but most of the customers are looking for quality of products and services, which could be ensured by this strategy to make customers appreciate them for the quality. The e-commerce system has been developed by upgrading all information of products and services, which would depend on the nature of quality that customers prefer. With distinct product quality with higher prices, customers can have freedom of choice. Therefore, the differentiation of the e-commerce process must be of concern. Hitt et al. (2001, pp. 317- 421)
- Focus Strategy: When the degree of competition is lower in the market, Virgin UK can develop an e-commerce process by this strategy. If the total competitive market has been taken into account, then focus is not an appropriate strategy has to implement. However, the e-commerce development market is smaller than the direct market.
By applying these strategies in e-commerce of Virgin UK in supply chain system, the company can reduce costs by implementing the ability to sell products and services offerings in cheaper. The team of the company can also differentiate its offerings to have better responses from potential customers. The company can also develop the focus to capture small markets according to customer requirements. (Hitt et al. 2001, pp. 317- 421)
Dynamics of Competitive Strategy of E-retailing by Virgin UK
Kotler & Armstrong (2006, pp. 267- 316) explained that the different competitive factors shape the company dynamics and other operations of a firm. The concept of e-retailing has critical effects on the shift or change of the competitive strategy. E-retailing argues that firms like Virgin must think about the presence of these competitive factors and a certain mixture of the key marketing aspects like the product, price, place and promotion. Virgin has different strategies regarding these, but these may not be useful to some extent as the e-retailing concept disputes that the difference in the level of competition may differ. Virgin has many differentiated services and product offerings, which peruse the e-retailing concept to be changed. (Abdul 2002, p. 17)
Virgin UK has identical products that keep apart its e-retailing concept adoption not to price lower than the competitors. There are some tendencies in retailing to price the same as the competitors to the consumer market. The e-retailing concept brings the change, saying it is not important to make the high-quality product features rather change the price strategy. As e-retailing gives the customers the chance to compare different product offerings at the almost same time, Virgin UK should reduce the price. To do that, the firm must reduce the costs that will lead to good market share and profit.
Virgin UK has a good relationship with its suppliers, distributors, and retailers. E-retailing gives the opportunities to increase the closeness of the relationship. As e-retailing helps to do direct and time-to-time communication with the consumers, Virgin UK can give the opportunity to its e-retailer to be familiarised and thus, it is increasing the relationship positively.
E-promotion strategies are another aspect of e-retailing, which has been used by Virgin UK. Like traditional retailing, the firm has to take promotional campaigns, and e-retailing is making it easier. Through these e-promotional activities, Virgin UK has established different strong e-brands. Virgin UK must concentrate that all e-retailing strategies will not work for all brands. Besides, when a company takes an expansion strategy in the case of e-retailing, the company must consider the digitalisation of the framework and infrastructure. Virgin UK is applying the concept of e-brand to expand its business in a disciplinary way, which is focusing on profitability, establishing a value proposition and choosing tradeoffs.. (Abdul 2002, p. 31)
A well-designed website can play the most facilitating role in the case of e-retailing. Virgin UK has a website which has designed to promulgate the company’s offerings. The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) argues some key ways to make a website more accessible and attractive, which Virgin has to follow these are:
- Virgin UK should offer corresponding alternatives to the customers in both auditory and visual ways.
- The firm should not rely on the drawing, only explaining the reason behind the colour. The high contrast of visibility has must be used in this case.
- The website must use the natural language handling spell out.
- There must be some attractive titles and headings.
- The documents or data must be clear, or mechanisms to make the data clear must be present.
- Navigation is another key part of a website where Virgin UK must keep proper concern. The navigation must be easier and easily identifiable.
Efficiency of Competitive Advantages of Virgin UK by E-commerce
E-commerce gives high levels of competitive advantages to Virgin UK. To assess these marketing mix strategies of Virgin UK could be assess:
- Product Strategy: Consumers are now getting it easy to collect information. Thus, Virgin UK can be able to give product knowledge to consumers more efficiently. The firm can highlight its major product differentiations. Besides, as Virgin UK is offering high quality at a lower price, e-commerce gives a chance to its consumers to compare the offerings with the competitors. (Anon 2008)
- Price Strategy: There are some price comparing sites, which are giving the facility to compare different products and their price on a single page. These sites are using the price catalogue of Virgin UK as well as convincing the consumers to go with it.
- Promotion Strategy: E-commerce makes the promotional campaign much easier. A website or a webpage has the ability to express all the offerings at the same time. Using audio, video, animation, and digital displays make the web promotion more attractive.
- Place Strategy: The use of the internet diminishes transportation and delivery costs. Besides, consumers do not need to order a product appearing physically. Thus, Virgin UK centralises its placement strategies based on e-commerce concepts.
The effective competitive advantage of Virgin UK has used through e-commerce can display by two aspects: information sharing and sustaining the competitive advantages. The firm makes all the information available for the consumers on the internet. It gives the consumers the facility to ask any query online. Besides, the competitive advantages, which have carried by e-commerce, has been remained sustainable for more times. (Shin & Chi 2001, p. 19)
Conclusion
Recommendations
Although Virgin UK is one of the most incapable organisations of the country for effective application of various e-commerce tools in order to have unique operational efficiencies than other competitors have, it has some limitations in such technological background which must be identified as well as corrective actions should be taken. Therefore, some suggestions can give from that perspective:
- Along with depending on the internal technological team, Virgin needs to employ some external e-business experts because, in the near future, it will be very much difficult for the company to sustain over existing competitive advantage. Because the industry has been saturated by so many different expertise for individual field with more sophisticated e- knowledge as BT, Carphone Warehouse, O2 and others providing VOIP, IPTV etc. options. Some of them utilise substitute and advanced methods of ADSL+ 2 and better speed.
- Increase the functionality of present DTV services to enjoy by the users who move around many locations.
- Superior e- techniques should supply at lower prices than competitors should.
- Improvement of management and upgrading in-network contents that involves infrastructural modification for latest items, especially for broadband, installation and proper management of e-components and cables, while financial support is a major factor.
- Virgin should simplify some of its critical circuits by eliminating vulnerability for electronic brokerage, viruses, worms, or the like. Therefore, it should ensure much security in information systems, billing processes and transmitting signals via their communication webs. All those tasks focus upon the formulation of a contingency plan for the certain damage of the e-business strategy.
- Concentration on composing superior programming for television like- Sky Sports and Sky Movie channels with high-class interactivity and satellite digitalization.
- The company should be highly careful about illegal access of its network for distorting security, confidentiality, and projected revenue, for which it needs to work harder.
- At many times, proposed e- products are subject to greater technological modification as VOIP, WiMax, WiFi etc. tools are changing with greater speed that requires a sincere analysis for better prediction.
- The company should develop greater adaptability about different rules and regulations for governing e-commerce efficiency imposed by the central UK government. Therefore, operations regarding telecommunication, outsourcing, and pricing policies should be revised enough to avoid any unfavourable public pressure.
- The tendency of gaining over competitive advantage should control since that sort of over-diversification may be a boomerang for Virgin, as all the offerings may not accept by the market like- 50MB broadband. As a result, the conduction of market research on a regular basis is very much essential to understand the level of feedback of consumer choice.
- The company should reduce its reliance level on the T-Mobile network for a complete package of telecommunication services as a termination of such agreement would result in a greater financial and non-financial loss. Therefore, diversification in choosing technological partnerships is necessary for sustaining a longer time in a competitive market.
- Virgin should maintain a stronger and personal control in Media TV and satellite transformational devices as those are interrelated. Any interruption at any component would be resulted in a full system loss, abusing and extra expenditure.
- Greater insurance about dissident parts of the cable network and other pavement-oriented electronic devices associated with that network should give to obtain more confidence from the market. So, a trained engineering and technological expertise team should assign for that task, especially for the objective of securing the company from maximum unpredictable losses.
- Virgin should immediately increase its cable platform capability. As their digital, analogy, VOIP etc., services have served by core channelling, problem in wider access would be very common that can prevent by smooth alteration of UK DTT technique coming from analogy to digital system would be able to raise spectrum performance. Such a feature will be helpful to release modern service functionality by the elimination of present limitations for bearing the latest channels. Additionally, competence in digital TV should enhance for increasing customer satisfaction and revenue.
- Virgin should introduce a new e-business application termed LLU (Local Loop Unbundling) in lowering total functional costs for ISP, which is preferable for lower investment for application with an essence of a larger number of customers for getting a handsome ROI.
- From a national viewpoint, Virgin should go with a scheme of expanding their three retail options of DTV, broadband and fixed-line throughout each corner of the zone as improving the present ratio from 95% to 100%.
- It should use a faster level of SIs in each major aspect of operation along with taking of scope of dynamic sales, fundamental integrated IT technology and individual SI channel for salesforce.
- It should take a further step in e-tailing where it will be able to sell of sorts of retail products through pure click play with storage benefits.
- Finally, the company should always apply supervision in self-judgment in terms of keeping the flow of differential strategy, continuous improvement programs, analysing the functions of major competitors in terms of e-business applicability, brand recognition for adding technological value and overall calculation for measuring risk and reward. These issues will help the company to accommodate e- support for significant differentiation.
Conclusion
Although retailing is an older concept, the modern business world is dynamic enough to create adequate charm and scope of more expectation by adding extra value in such traditional retailing. E-commerce is one of those kinds of technological tools that have mostly been used in the creation of dynamism and diversification, especially for that kind of business that has to deal with multiple options, at the same time similar to Virgin UK, which is performing its multi- capacity in adopting and implementing various sorts of commercial strategies by integrating e-commerce tactics to sustain the highly complicated and dynamic business environment where there exist a number of challenges and pressure to be competent enough for meeting versatile demand of ending buyers. In spite of experiencing some limiting factors, Virgin is one of the recognised companies of the country for maximising customer values through information, knowledge, and correspondences. The aim of this research task is to find out a set of e- technologies as means of generating unique values to people that had been shown by clarifying various business operations and methodologies of the company. In relation to its bandwidth, broadband, telecommunication, networking, sales channelling and DSL etc., types of options that are acting as powerful, influential factors for continuous development and unique advantage in the served customers mind. Along with secondary research, the primary research has shown an integral viewpoint of such potentiality from the reliable groups of corporate personnel who employ those strategies and general users who enjoy the benefits of those implementations. Although the presented task was a topic of several internal and external barriers, we have finally been able to adjust all of such problems by combining this practical affair with the relevant theoretical framework and data analysis projection. In such a way, it has expected to prepare a diversified task with maximum effort and labour for reaching a final destination of discovery that there exists a greater impact of e-commerce strategies for the formulation of competitive leadership of Virgin Company for acting as a diversified retailer in dealing with numerous customers.
Reference
Abdul, R. 2002. Virgin corporate strategy Case Study. [Online] 2009. Web.
Anon. 2008. E-commerce- Tutorial three: e-commerce and competitive advantage. [pdf] Web.
Barney, J. 1991. Firm Resources and Sustained Competitive Advantage. Journal of Management. vol. 17, P. 99-120
Callon, J. D. 1996. Competitive Advantage Through Information Technology. New York: McGraw Hill.
Coulthard, D. Castleman, T. & Batten, L. 2004. ECommerce Strategy in a Multi-Sector Trading Environment – Quandaries for SMEs. [pdf] 2009. Web.
Dvořák, J. & Kříž, J. 2006. E-Commerce Strategy for Companies. [pdf] 2009. Web.
Figueiredo, J. M. 2000. Finding Sustainable Profitability in the E-commerce Continuum. [pdf] 2009. Web.
Forsman, S. 2000. Framework for Resource and Competitive Strategy Analysis: A Case of Local Food Processing Firms in Finland. Agricultural Economics Research Institute.
Grant, R.M. 1995. Contemporary Strategy Analysis: Concept, Techniques, Applications. 3rd ed. Blackwell Business: Oxford.
Griffin, R. W. 2006. Management. 8th ed. Boston New York: Houghton Mifflin Company.
Gunnesson, T. & Soderland, K. 2001. Creating Competitive Advantage In Mature E-Retail Markets. [pdf] 2009. Web.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & Hoskisson, R. E. 2001. Strategic Management. 4th ed. South-Western Thomson Learning.
Hoffman, D. L., Novak T. P., & Chatterjee, P. 2004. Commercial scenarios for the web: Opportunities and challenges, Journal of computer-mediated communication. Vol. 1.
Kalakota & Robinson. 1999. e-Business – Roadmap for Success. Addison-Wesley Longman Inc., Reading, MA.
King, V. & Wirtschafts N. 2009. Development of an E-Commerce Strategy and Implementation with operative Marketing on the example of the internet platform Evaluba AG. [pdf] Web.
Kiggundu, J. 2002. Designing e-commerce strategies, Roles of Governments and non-government actors. Printice Hall.
Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G. 2006. Principles of Marketing. 11th ed. Prentice-Hall Private Limited.
Kurnia, S. 2007. Identifying e-Commerce Adoption Driving Forces and Barriers: The Case of the Indonesian Grocery Industry. [pdf] Web.
Laudon, K. C., & Traver, C. G. 2002. E- commerce- Business, Technology, Society. 4th ed. Dorling Kindersley Pvt. Ltd.
Lumpkin G.T., Droege S. B., & Dess G.,G. 2002. E-Commerce Strategies: Achieving Sustainable Competitive Advantage and Avoiding Pitfalls. Organisational Dynamics, Vol. 30, No. 4, P. 325-340.
Magombedze, S. 2004. ECommerce-StrategiesThe-Relationship-Between-Ecommerce-Competitiveness. [pdf] 2009. Web.
Malhotra, N. K. 2009. Marketing Research- An Applied Orientation. 5th ed. Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited.
Pirvanescu, A. Badica, C. & Paprzycki, M. 2008. Developing A Jade-Based Multi-Agent E-Commerce Environment. [pdf] Web.
Porter, M. E. 1985. Competitive Advantage. Prentice Hall: New York
Porter, M. 2001. Strategy and the Internet. Harvard Business Review, P. 62-78
Rajgopal, S., Venkatachalam, M. & Kotha, S. 2000. Does the Quality of Online Customer Experience Create a Sustainable Competitive Advantage for E-commerce Firms? [pdf] 2009. Web.
Sultan, S. S. 2007. The Competitive Advantage of Small and Medium Sized Enterprises: The Case of Jordan’s Natural Stone Industry. [pdf] Web.
Tobias, G. & Soderlund, K. 2001. Creating Competitive Advantage in Mature E-Retail Markets. [pdf] 2009. Web.
Virgin Media, 2009. Virgin Media Response to the Government’s Digital Britain Interim Report. [pdf] Web.
Virgin, UK, 2009. The Company Annual report 2008. Web.
Whiteley, D., Hersey, I., Miller, K. & Quick, P. 1999. Internet e-Commerce: buying the book and catching the plane. [pdf] 2009. Web.
Zwass, V. 1998. Structure And Macro-Level Impacts of Electronic Commerce: From Technological Infrastructure to Electronic Marketplaces. Wiley: New York
Appendix
Customer survey questionnaire:
- What first comes in your mind when you think of Virgin brand? Answer: ……………………………………………………………………………
- Which pattern of offered products by Virgin you consume like most? Answer:
- General retailing
- Travel
- Leisure
- Mobile
- Entertainment
- What is the most important factor according to your consideration while choosing Virgin’s network? Answer:
- Flexibility
- Speed
- Accessibility
- Others
- Which is your most preferred feature of Virgin TV? Answer:
- Free of choice scheduling program
- Pricing
- Less complexity
- Others
- Have you ever used auction site of Virgin? Answer:
- Yes
- No
- How it is different from other company’s procedure? Answer: ………………………………………………………………………………
- How do you feel while using such option? Answer: ………………………………………………………………………………
- Do you like to shop Virgin products through internet? Answer:
- Yes
- No
- What is the most important feature of broadband internet service? Answer:
- Speed
- Richness
- Direct linkage with corporate network
- What is their most attractive offer in delivering fixed line telephone service? Answer:
- Barring calls,
- Waiting calls
- Forwarding calls,
- Voicemail
- Others
- What is the most significant issue for which you are loyal with Virgin brand than other companies? Answer:
- Quality
- Integration with technology
- Bundling offer
- Price leverage
- Others
Corporate personnel interview questionnaire:
- According to you, what is the basic comparative advantage of Virgin that makes it differentiated than other market players? Answer: ………………………………………………………………………….
- Do you feel that it is essential for a multi- option business to make technological implementation at each phase of production and marketing? Answer:
- Yes
- No
- How can you explain such essence? Answer: ……………………………………………………………………………
- What is role of e- commerce in such orientation? Answer: ………………………………………………………………………….
- How much support and incentives does the top management provide for e- commerce implementation in developing brands? Answer: ……………………………………………………………………………
- What are the major technological threats that are you facing from this market right now? Answer: …………………………………………………
- How much user friendly are the electronics products and services of Virgin? Answer: ……………………………………………………………………
- Who are your direct and indirect competitors? Answer: …………………………………………………………………………….
- Can you mention and constraint factor while introducing and developing such strategy? Answer: …………………………………………………
- At present, are you thinking of any new technical strategy that will add new dimension to your company for attracting customers?Answer: ………………………………………………………………………………………….